ALS is a cruel disease. It robs the body of its ability to control itself—the ability to move, the ability to communicate. While there are currently no effective treatments to reverse its debilitating symptoms, Allen Institute researchers have opened a window of hope.
For the first time ever, scientists have developed a precise genetic toolkit that can target the exact nerve cells destroyed by the disease and potentially deliver therapies where they are needed most—a discovery that could dramatically speed up the quest for a cure. The findings were recently published in the journal Cell Reports.
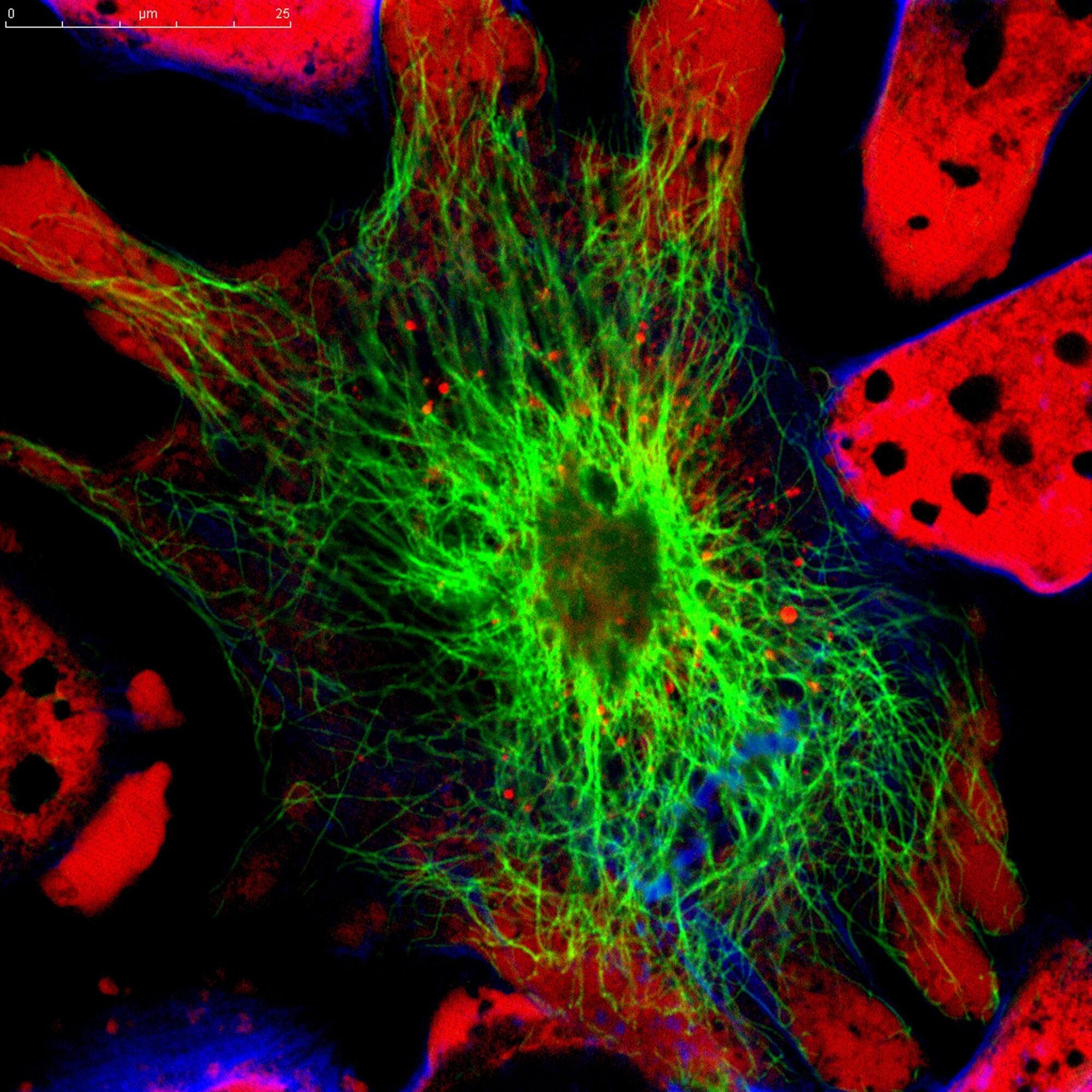
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive and devastating disease that gradually kills off motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord that control voluntary muscle movement. As these neurons die, people with ALS lose the ability to move, speak, and eventually breathe. Despite decades of research, there’s still no effective treatment or cure. Unlike many other brain cells, motor neurons in the spinal cord have been extremely hard to reach with genetic tools. This has slowed down research and made it hard to test new treatments in the cells that matter most.