Textbooks say that mitochondria exist to supply cells with energy, but experiments in fruit flies suggest they are also involved in sleep

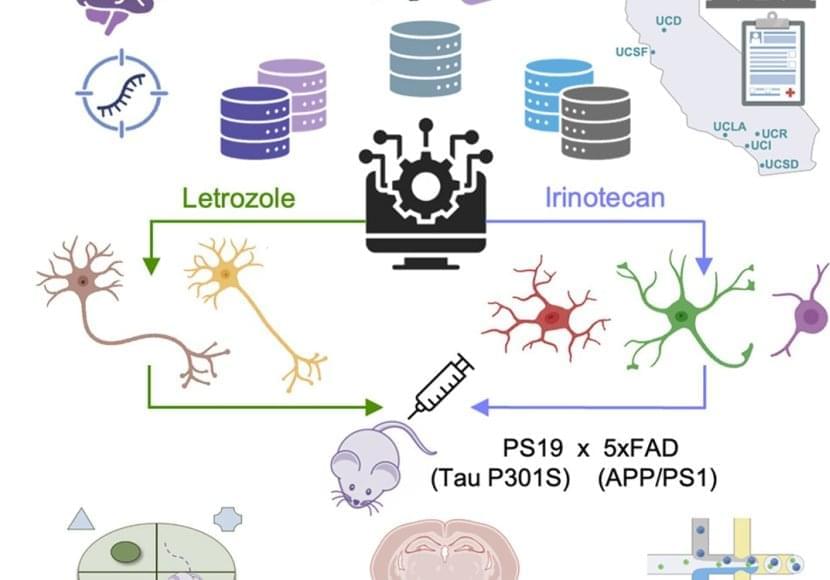
The team took publicly available data from three studies of the Alzheimer’s brain that measured single-cell gene expression in brain cells from deceased donors with or without Alzheimer’s disease. They used this data to produce gene expression signatures for Alzheimer’s disease in neurons and glia.
The researchers compared these signatures with those found in the Connectivity Map, a database of results from testing the effects of thousands of drugs on gene expression in human cells.
Out of 1,300 drugs, 86 reversed the Alzheimer’s disease gene expression signature in one cell type, and 25 reversed the signature in several cell types in the brain. But just 10 had already been approved by the FDA for use in humans.
Poring through records housed in the UC Health Data Warehouse, which includes anonymized health information on 1.4 million people over the age of 65, the group found that several of these drugs seemed to have reduced the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease over time.
“Thanks to all these existing data sources, we went from 1,300 drugs, to 86, to 10, to just 5,” said the lead author of the paper.
The authors chose 2 cancer drugs out of the top 5 drug candidates for laboratory testing. They predicted one drug, letrozole, would remedy Alzheimer’s in neurons; and another, irinotecan, would help glia. Letrozole is usually used to treat breast cancer; irinotecan is usually used to treat colon and lung cancer.
The team used a mouse model of aggressive Alzheimer’s disease with multiple disease-related mutations. As the mice aged, symptoms resembling Alzheimer’s emerged, and they were treated with one or both drugs.
Enhancing Functional Independence For Older Adults — Dr. On-Yee “Amy” Lo, Ph.D. — Marcus Institute for Aging Research / Harvard Medical School.
Dr. On-Yee (Amy) Lo, Ph.D. is Assistant Scientist II at the Marcus Institute for Aging Research (https://www.marcusinstituteforaging.org/who-we-are/profiles… and Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (https://connects.catalyst.harvard.edu…).
Dr. Lo is a physical therapist and research scientist who aims to prevent functional decline and enhance functional independence for older adults with mobility impairments by conducting experimental and translational research. She has expertise and experience in physical therapy, biomechanics, neuroimaging, and neuromodulation.
Dr. Lo has dedicated her career to enhancing functional independence and quality of life in older adults. Her specific research objectives are:
To investigate connections between the brain and body that enable safe navigation throughout daily environments.
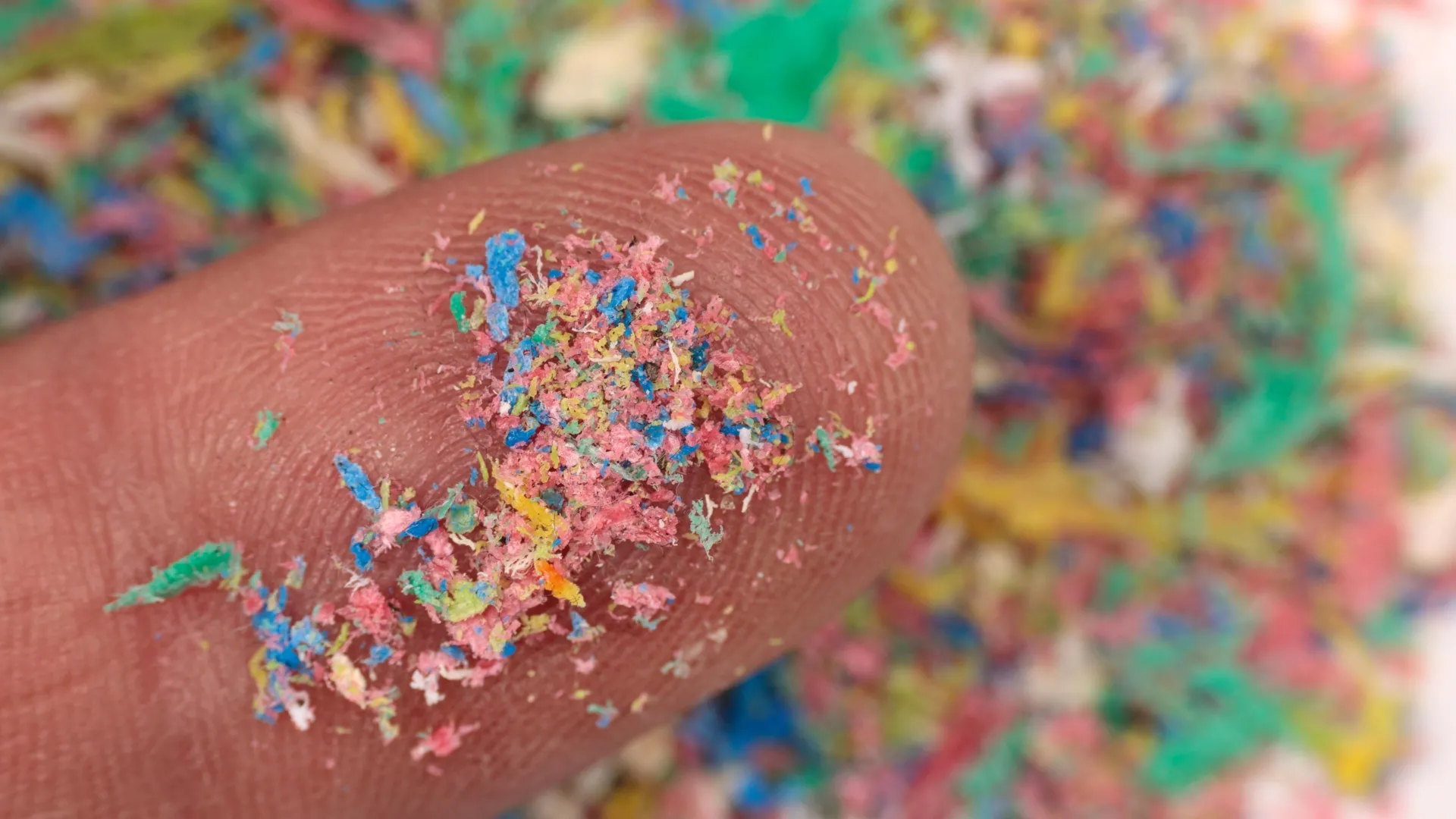

Millions of tons of plastic in the ocean aren't floating in plain sight—they're invisible. Scientists have now confirmed that the most abundant form of plastic in the Atlantic is in the form of nanoplastics, smaller than a micrometer. These particles are everywhere: in rain, rivers, and even the air. They may already be infiltrating entire ecosystems, including the human brain, and researchers say prevention—not cleanup—is our only hope.
The benefits of exercise and its positive influence on physical and mental health are well documented, but a new Yale and VA Connecticut study sheds light on the role genetics plays for physical activity, accounting for some of the differences between individuals and showing differences in biology for physical activity at leisure versus physical activity at work and at home.
Using data from the Million Veteran Program (MVP), a genetic biobank run by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the researchers analyzed genetic influences on leisure, work, and home-time physical activity. They wanted to understand how genetics impacts these three types of physical activity and compare their health benefits.
The study included nearly 190,000 individuals of European ancestry, 27,044 of African ancestry, and 10,263 of Latin-American ancestry. To study the genetics of physical activity during leisure time, the researchers also added data from the UK Biobank, which included about 350,000 individuals.
Broken connections between brain cells play a critical role in multiple neurodegenerative conditions, including Parkinson’s disease. Scientists have now come up with a novel way of repairing our neural wiring.
A team led by University of Pisa biologist Sara De Vincentiis used mini-brains grown in a lab to test a technique they’re calling “nano-pulling”, using tiny magnetic particles controlled by magnetic fields to guide axons (connective nerve fibers) into place.
With further development, the researchers believe this approach could help restore the nigrostriatal pathway, a vital connection in motor control that is compromised in Parkinson’s patients.

Psychology research suggests that the human body, particularly the muscles on our face, plays a key part in the processing of others’ emotions. For instance, past findings suggest that when we see another person smiling or frowning, we often unconsciously mimic their facial expression, and this helps us interpret their emotions.
Theories suggest that the mimicry of facial expressions sends signals from our facial muscles to the brain, broadly referred to as “facial feedback,” which in turn contributes to the interpretation of other people’s emotions. So far, however, the contribution of this feedback to emotion recognition and how its contribution unfolds over time remain poorly understood.
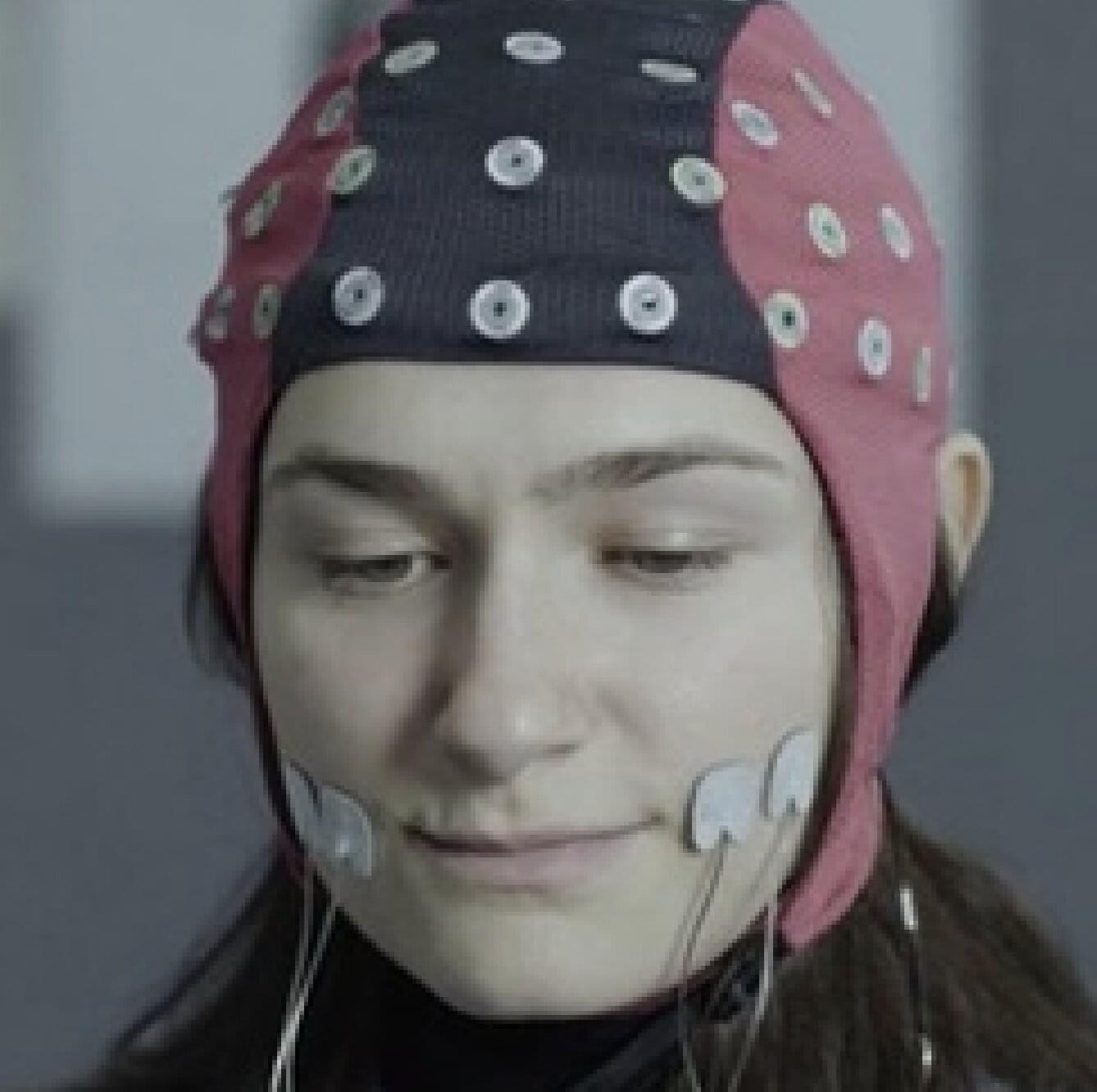
Researchers at the University of Essex recently carried out a study to investigate the effects of facial feedback on the perception of emotions at different stages of visual processing, using a technique known as facial neuromuscular electrical stimulation (fNMES). Their findings, published in Communications Psychology, suggest that signals generated by the movements of muscles on people’s faces influence how they interpret the emotions of others, particularly during the earlier stages of visual processing.