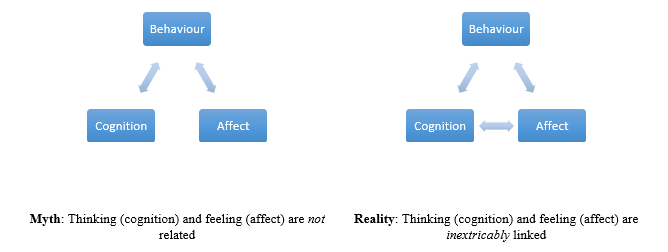
Two information-processing systems determine the human emotional response: the affect ive and cognitive processing systems. The affect ive system operates outside of conscious thought and is reactive, in that a series of psychophysiological events are initiated automatically following the receipt of sensory information. In contrast, the cognitive processing system is conscious and involves analysis of sensory information to influence and even counteract the affect ive system. Affects (i.e. things that induce some change to the affect ive system) are divided into positive and negative groups. Positive affect has the potential to improve creative thinking, while negative affect narrows thinking and has the potential to adversely affect performance on simple tasks. Emotions are the product of changes in the affect ive system brought about by sensory information stimulation. Research suggests positive emotions—such as happiness, comfort, contentedness, and pleasure—help us make decisions, allow us to consider a larger set of options, decide quicker, and develop more creative problem-solving strategies. These findings suggest attractive things really do work better (Norman 2005), even if this is only the case because they make us feel better when we are using them.
Much of the work into how users and customers behave focuses on the emotional responses elicited by a product. However, emotions are the product of complex processing systems, which essentially convert sensory information into the psychophysiological and behavioral changes that we refer to as emotional responses. According to Don Norman, cognition and affect are in charge of these emotional responses. Cognition and affect are information-processing systems, which help us convert information from our environment into accurate representations of the world and make value judgments that determine how we respond and behave.
Norman distinguishes the cognitive and affect ive systems, and defines emotion, thusly: “The cognitive system interprets and makes sense of the world. Affect is the general term for the judgemental system, whether conscious or subconscious. Emotion is the conscious experience of affect, complete with attribution of its cause and identification of its object”. The affect ive and cognitive systems are thought to work independently, but they influence one another, with the former operating unconsciously while the latter operates at the conscious level. For example, imagine you are about to make a speech in front of a room full of people; the affect ive system is immediately called into action, with chemicals released in your body in response to the situation automatically and without your ability to control this physiological response.