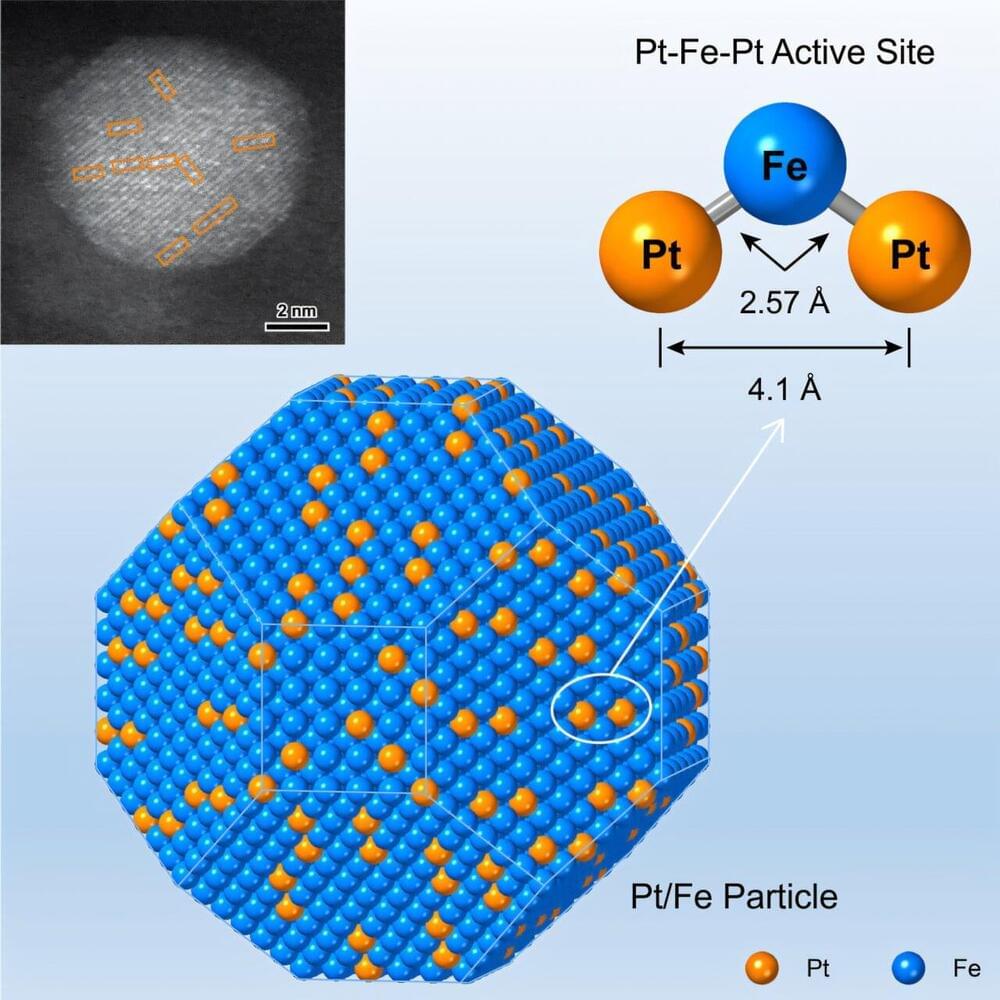
Bimetallic particles, composed of a noble metal and a base metal, exhibit unique catalytic properties in selective heterogeneous hydrogenations due to their distinct geometric and electronic structures. At the molecular level, effective and selective hydrogenation requires site-specific interactions where the active atoms on the catalyst particle selectively engage with the functional group targeted for transformation in the substrate.
Reducing the particle to nanoscale atomic clusters and single-atom alloys enhances surface dispersion and improves the efficient utilization of noble metal atoms. These size reductions also simultaneously change the electronic structure of the active sites, which significantly impacts the intrinsic activity or product distributions.
By precisely tuning the bonding structures of noble metal single atoms with the base metal host, reactants are flexibly accommodated and the electronic properties are fine-tuned to activate specific functional groups. However, the fabrication of such atomically precise active sites remains a challenge.