A nanomaterials chemist has figured out a good way to mimic leaves and turn water and carbon dioxide into things we need.

A nanomaterials chemist has figured out a good way to mimic leaves and turn water and carbon dioxide into things we need.
Graphene is a super strong, two-dimensional material with atom-thick layers. But now, a team of scientists have developed a new material with a similar structure that they’re calling borophene, and it may have graphene beat.
Borophene, a one atom thick sheet of boron, is being introduced by scientists as the next big thing after graphene, another two-dimensional material that made headlines back in 2004. If you aren’t aware, graphene is basically a supermaterial. A single layer of this is about 100 times stronger than steel and it is extremely flexible.
Now, according to research that was published in the journal Nature, borophene’s properties could potentially exceed those of graphene and other, similar materials in the 2D nanomaterial family.
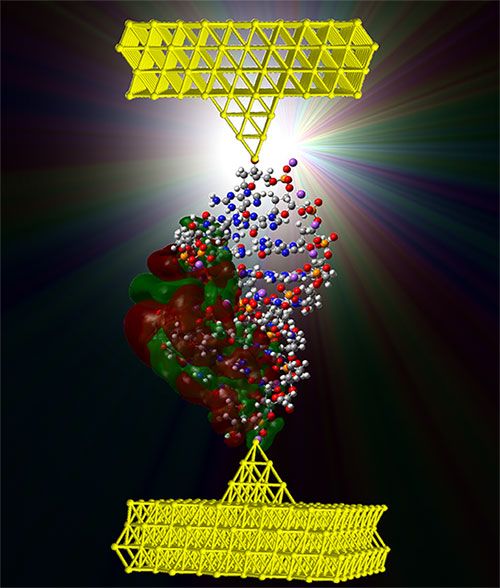
A model of one form of double-stranded DNA attached to two electrodes (credit: UC Davis)
What do you call a DNA molecule that changes between high and low electrical conductance (amount of current flow)?
Answer: a molecular switch (transistor) for nanoscale computing. That’s what a team of researchers from the University of California, Davis and the University of Washington have documented in a paper published in Nature Communications Dec. 9.
“Inhuman: The Next & Final Phase of Man is Here” is not fiction or a mockudrama but a new investigative documentary from Defender Films and Raiders News Productions.
Inhuman travels the globe to unveil for the first time how breakthrough advances in science, technology and philosophy—including cybernetics, bioengineering, nanotechnology, machine intelligence and synthetic biology are poised to create mind-boggling game changes to everything we have known until now about Homo sapiens.
As astonishing technological developments push the frontiers of humanity toward far-reaching morphological transformation (which promises in the very near future to redefine what it means to be human), an intellectual and fast-growing cultural movement known as transhumanism intends the use of these powerful new fields of science and technology as tools that will radically redesign our minds, our memories, our physiology, our offspring, and even perhaps—as Professor Joel Garreau, Lincoln Professor of Law, claims—our immortal souls.
Big Hero 6’s programmable nanobots are on the horizon.
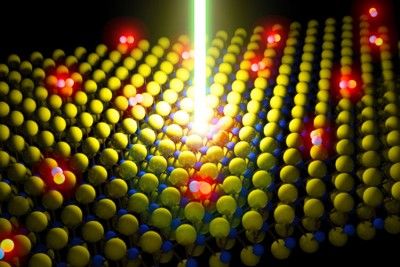
An emerging class of atomically thin materials known as monolayer semiconductors has generated a great deal of buzz in the world of materials science. Monolayers hold promise in the development of transparent LED displays, ultra-high efficiency solar cells, photo detectors and nanoscale transistors. Their downside? The films are notoriously riddled with defects, killing their performance.

Humai, a technology company based in Los Angeles, says that it is working on a project known as “Atom & Eve” that would let human consciousness be transferred to an artificial body after their death.
Artificial intelligence, the most important and major discovery of science will be one of the most helpful things in the whole project. The Humai have already started working on human rebirth using artificial intelligence.
The three technologies collectively used by the tech giant company are “Nanotechnology, bionics & artificial intelligence”. The company is expecting the whole system to be ready in 3 decades and, of course, this type of work requires this much time.
As advancements in technology continue at an ever-increasing pace, will there ever come a day when we’ll be able to use science to cheat death? Australian startup company Humai seems to think so; it claims to be working on a way to transfer a person’s consciousness into an artificial body after they’ve died.
“We want to bring you back to life after you die,” says Humai CEO Josh Bocanegra on the company’s website. “We’re using artificial intelligence and nanotechnology to store data of conversational styles, behavioral patterns, thought processes and information about how your body functions from the inside-out. This data will be coded into multiple sensor technologies, which will be built into an artificial body with the brain of a deceased human. Using cloning technology, we will restore the brain as it matures.”
In an interview with Australian Popular Science, Bocanegra said: “We’ll first collect extensive data on our members for years prior to their death via various apps we’re developing.” After death, the company will cryogenically freeze members’ brains until the technology is fully developed, at which point the brains will be implanted into an artificial body.
A company has announced its intention to resurrect the dead by storing their memories and using artificial intelligence to return them to life. In the future, of course.
Yeaaaaaah. What?
The company is called Humai, and at the moment, it is pretty sparse on details – and we’re still not sure it’s not a marketing ploy or a hoax. At any rate, the company says they want to store the “conversational styles, behavioral patterns, thought processes and information about how your body functions from the inside-out” on a silicon chip using AI and nanotechnology, according to their website.
Ray Kurzweil: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ray_Kurzweil#Health_and_aging
Raymond “Ray” Kurzweil is an American author, computer scientist, inventor and futurist. Aside from futurology, he is involved in fields such as optical character recognition (OCR), text-to-speech synthesis, speech recognition technology, and electronic keyboard instruments. He has written books on health, artificial intelligence (AI), transhumanism, the technological singularity, and futurism. Kurzweil is a public advocate for the futurist and transhumanist movements, and gives public talks to share his optimistic outlook on life extension technologies and the future of nanotechnology, robotics, and biotechnology.
Kurzweil admits that he cared little for his health until age 35, when he was found to suffer from a glucose intolerance, an early form of type II diabetes (a major risk factor for heart disease). Kurzweil then found a doctor (Terry Grossman, M.D.) who shares his non-conventional beliefs to develop an extreme regimen involving hundreds of pills, chemical intravenous treatments, red wine, and various other methods to attempt to live longer. Kurzweil was ingesting “250 supplements, eight to 10 glasses of alkaline water and 10 cups of green tea” every day and drinking several glasses of red wine a week in an effort to “reprogram” his biochemistry. Lately, he has cut down the number of supplement pills to 150.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/agingreversed