An international research group has applied methods of theoretical physics to investigate the electromagnetic response of the Great Pyramid to radio waves. Scientists predicted that under resonance conditions, the pyramid can concentrate electromagnetic energy in its internal chambers and under the base. The research group plans to use these theoretical results to design nanoparticles capable of reproducing similar effects in the optical range. Such nanoparticles may be used, for example, to develop sensors and highly efficient solar cells. The study was published in the Journal of Applied Physics.
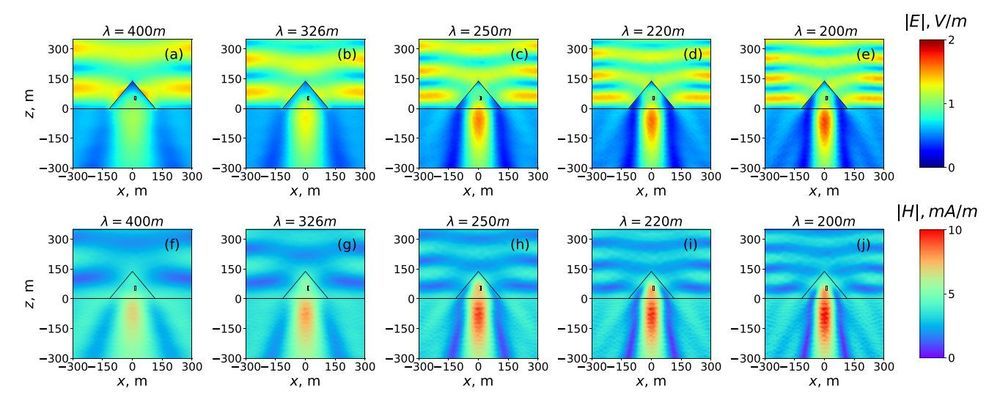
While Egyptian pyramids are surrounded by many myths and legends, researchers have little scientifically reliable information about their physical properties. Physicists recently took an interest in how the Great Pyramid would interact with electromagnetic waves of a resonant length. Calculations showed that in the resonant state, the pyramid can concentrate electromagnetic energy in the its internal chambers as well as under its base, where the third unfinished chamber is located.
These conclusions were derived on the basis of numerical modeling and analytical methods of physics. The researchers first estimated that resonances in the pyramid can be induced by radio waves with a length ranging from 200 to 600 meters. Then they made a model of the electromagnetic response of the pyramid and calculated the extinction cross section. This value helps to estimate which part of the incident wave energy can be scattered or absorbed by the pyramid under resonant conditions. Finally, for the same conditions, the scientists obtained the electromagnetic field distribution inside the pyramid.