Circa 2008
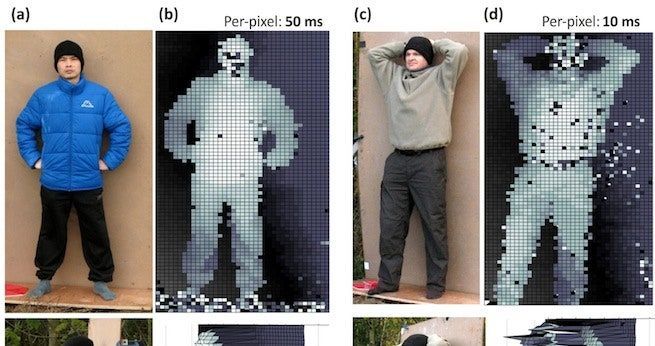
Using superconducting nanowires and lasers, a new camera system can produce high-resolution 3D images of objects from up to a kilometer away.
Circa 2007
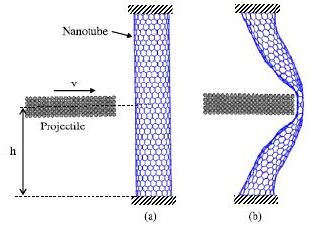
Robocops could soon leave the realm of science fiction thanks to a new bullet-proof material proposed by engineers in Australia. According to computer simulations done by the team, bullets would be no match for vests made of the material, and would simply bounce off owing to the high elasticity of the nanotubes. The researchers claim that the material, which has not been made yet, would be a great improvement on existing anti-ballistic clothing that stop bullets from penetrating by spreading the bullet’s force — something that can still cause serious injury (Nanotechnology 18 475701).
Circa 2006 o.,o.
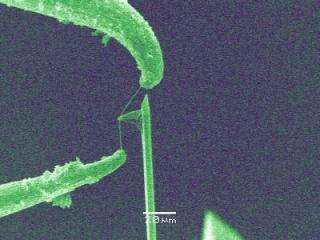
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the University of Colorado at Boulder have designed a carbon nanotube knife that, in theory, would work like a tight-wire cheese slicer.
In a paper presented this month at the 2006 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, the research team announced a prototype nanoknife that could, in the future, become a tabletop tool of biology, allowing scientists to cut and study cells more precisely than they can today.
For years, biologists have wrestled with conventional diamond or glass knives, which cut frozen cell samples at a large angle, forcing the samples to bend and sometimes later crack. Because carbon nanotubes are extremely strong and slender in diameter, they make ideal materials for thinly cutting precise slivers of cells. In particular, scientists might use the nanoknife to make 3D images of cells and tissues for electron tomography, which requires samples less than 300 nanometers thick.

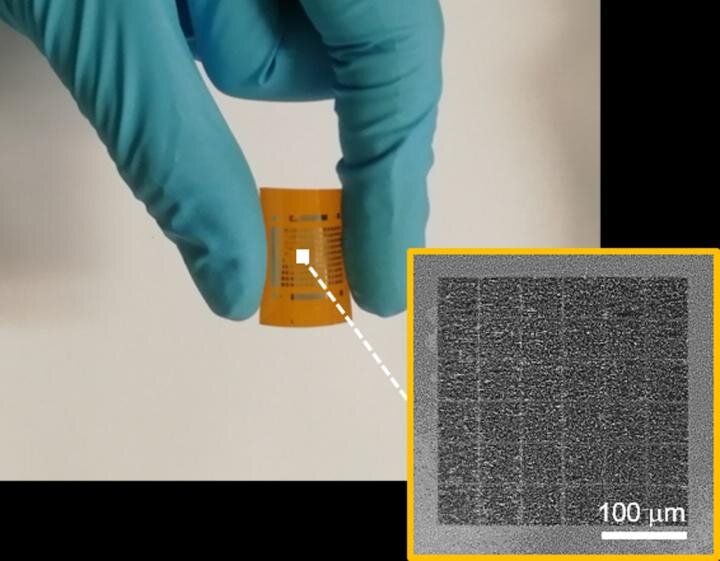
A joint study led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has built an ultralow-power consumption artificial visual system to mimic the human brain, which successfully performed data-intensive cognitive tasks. Their experiment results could provide a promising device system for the next generation of artificial intelligence (AI) applications.
The research team is led by Professor Johnny Chung-yin Ho, Associate Head and Professor of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE) at CityU. Their findings have been published in the scientific journal Science Advances, titled “Artificial visual system enabled by quasi-two-dimensional electron gases in oxide superlattice nanowires.”
As the advances in semiconductor technologies used in digital computing are showing signs of stagnation, neuromorphic (brain-like) computing systems have been regarded as one alternative. Scientists have been trying to develop the next generation of advanced AI computers, which could be as lightweight, energy-efficient and adaptable as the human brain.
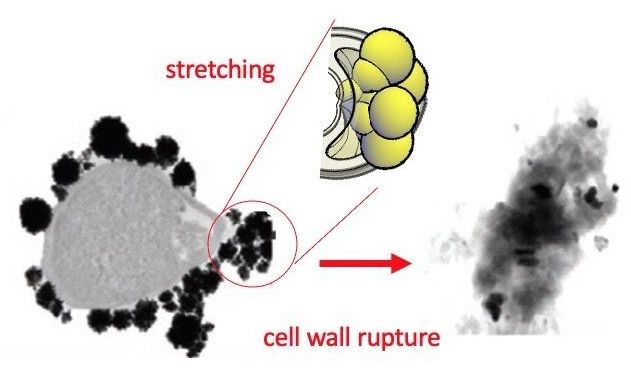
Finding alternatives to antibiotics is one of the biggest challenges facing the research community. Bacteria are increasingly resistant to these drugs, and this resistance leads to the deaths of more than 25,000 around the world. Now, a multidisciplinary team of researchers from the Universitat Rovira i Virgili, the University of Grenoble (France), the University of Saarland (Germany) and RMIT University (Australia) have discovered that the mechanical deformation of bacteria is a toxic mechanism that can kill bacteria with gold nanoparticles. The results of this research have been published in the journal Advanced Materials and are a breakthrough in researchers’ understanding the antibacterial effects of nanoparticles and their efforts to find new materials with bactericide properties.
Since the times of Ancient Egypt, gold has been used in a range of medical applications and, more recently, as for diagnosing and treating diseases such as cancer. This is due to the fact that gold is a chemically inert material, that is, it does not react or change when it comes into contact with an organism. Amongst the scientific community, nanoparticles are known for their ability to make tumors visible and for their applications in nanomedicine.
This new research shows that these chemically inert nanoparticles can kill bacteria thanks to a physical mechanism that deforms the cell wall. To demonstrate this, the researchers have synthesized in the laboratory gold nanoparticles in the shape of an almost perfect sphere and others in the shape of stars, all measuring 100 nanometres (8 times thinner than a hair). The group analyzed how these particle interact with living bacteria. “We find that the bacteria become deformed and deflate like a ball that is having the air let out before dying in the presence of these nanoparticles,” explained Vladimir Baulin, researcher at the Department of Chemical Engineering of the URV. The researchers state the bacteria seem to have died after a massive leak, “as if the cell wall had spontaneously exploded.”
Dr yu shrike zhang phd is assistant professor at harvard medical school and associate bioengineer at brigham and women’s hospital.
Dr. Zhang’s research interests include symbiotic tissue engineering, 3D bio-printing, organ-on-a-chip technology, biomaterials, regenerative engineering, bioanalysis, nanomedicine, and biology.
His scientific contributions have been recognized by over 40 regional, national and international awards. He has been invited to deliver more than 110 lectures worldwide, and has served as reviewer for more than 500 manuscripts for as many as 50 journals.
Dr. Zhang is serving as Editor-in-Chief for Microphysiological Systems, and is Associate Editor for Bio-Design and Manufacturing, Nano Select, Aggregate, and Essays in Biochemistry.
He is also on the Editorial Board of Biofabrication, Bioprinting, Advanced Healthcare Materials, Discover Materials, BMC Biomedical Engineering, Materials Today Bio, and Chinese Chemical Letters, the Editorial Advisory Board of Heliyon and Biomicrofluidics, the International Advisory Board of Advanced NanoBiomed Research and Advanced Materials Technologies, and the Advisory Panel of Nanotechnology.
Dr. Zhang has his PhD in Biomedical Engineering from Georgia Institute of Technology / Emory, his M.S. in Bioengineering and Biomedical Engineering from Washington University in St. Louis, and his B.Eng. in Biomedical Engineering Southeast University in China.

A new label-free optical imaging technique based on unscattered light can detect nanoparticles as small as 25 nm in diameter. The technology overcomes several limitations of other advanced methods for imaging tiny particles, and its developers at the University of Houston and the University of Texas M D Anderson Cancer Center in the US say it might be used to study viruses and other structures at the molecular level.
Imaging nanoscale objects via optical techniques is difficult for two reasons. First, the objects’ small size means that they scatter little light, making it hard to distinguish them from the background. Second, individual nano-objects within a close-packed group tend to be separated by distances that are smaller than the diffraction limit for visible light (around a few hundred nanometres) making it impossible to resolve them with conventional methods.
In groundbreaking new research, an international team of researchers led by the University of Minnesota Twin Cities has developed a unique process for producing a quantum state that is part light and part matter.
The discovery provides fundamental new insights for more efficiently developing the next generation of quantum-based optical and electronic devices. The research could also have an impact on increasing efficiency of nanoscale chemical reactions.
The research is published in Nature Photonics.
Serena Corr looks at the science behind batteries, discusses why we are hunting for new ones and investigates what tools we use to pave this pathway to discovery.
Watch the Q&A: https://youtu.be/lZjqiR0czLo.
The hunt is on for the next generation of batteries that will power our electric vehicles and help our transition to a renewables-led future. Serena shows how researchers at the Faraday Institution are developing new chemistries and manufacturing processes to deliver safer, cheaper, and longer-lasting batteries and provide higher power or energy densities for electric vehicles.
Serena Corr is a Chair in Functional Materials and Professor in Chemical and Biological Engineering at the University of Sheffield. She works on next-generation battery materials and advanced characterisation techniques for nanomaterials.
This event was generously supported by The Faraday Institution.
–
A very special thank you to our Patreon supporters who help make these videos happen, especially:
János Fekete, Mehdi Razavi, Mark Barden, Taylor Hornby, Rasiel Suarez, Stephan Giersche, William Billy Robillard, Scott Edwardsen, Jeffrey Schweitzer, Gou Ranon, Christina Baum, Frances Dunne, jonas.app, Tim Karr, Adam Leos, Andrew Weir, Michelle J. Zamarron, Andrew Downing, Fairleigh McGill, Alan Latteri, David Crowner, Matt Townsend, Anonymous, Andrew McGhee, Roger Shaw, Robert Reinecke, Paul Brown, Lasse T. Stendan, David Schick, Joe Godenzi, Dave Ostler, Osian Gwyn Williams, David Lindo, Roger Baker, Greg Nagel, and Rebecca Pan.
–
The Ri is on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/TheRoyalInstitution.