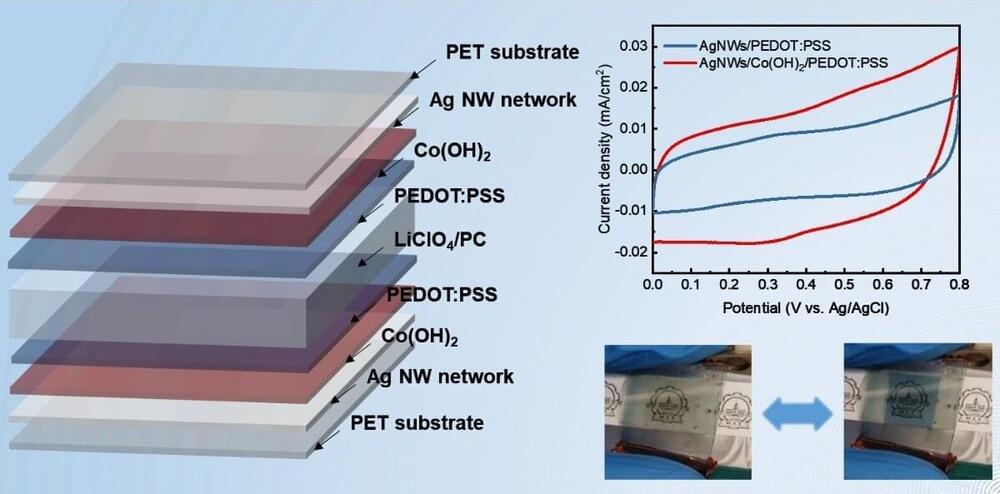
Researchers from the Harbin Institute of Technology and Southern University of Science and Technology have fabricated bifunctional flexible electrochromic energy-storage devices based on silver nanowire flexible transparent electrodes.
Publishing in the International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, the team used silver nanowire flexible transparent electrodes as the current collector for a bifunctional flexible electrochromic supercapacitor.
This bifunctional flexible device can exhibit its energy status through color changes, and can serve as an energy supplier for various wearable electronics, such as physiological sensors. The findings could have a widespread impact on the future development of smart windows for energy-efficient buildings.