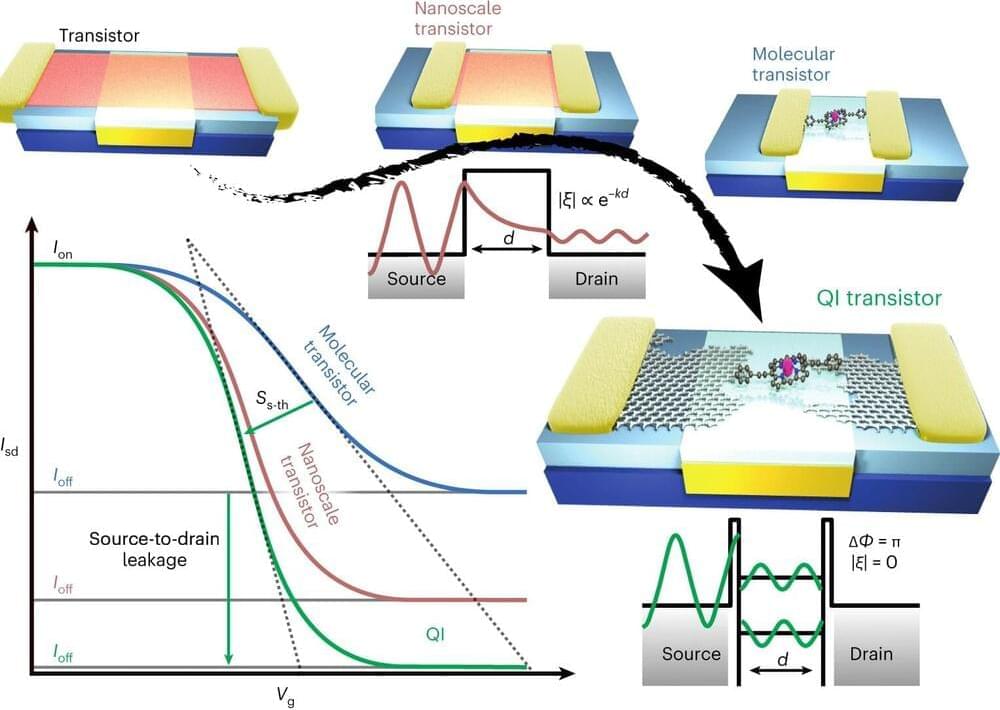
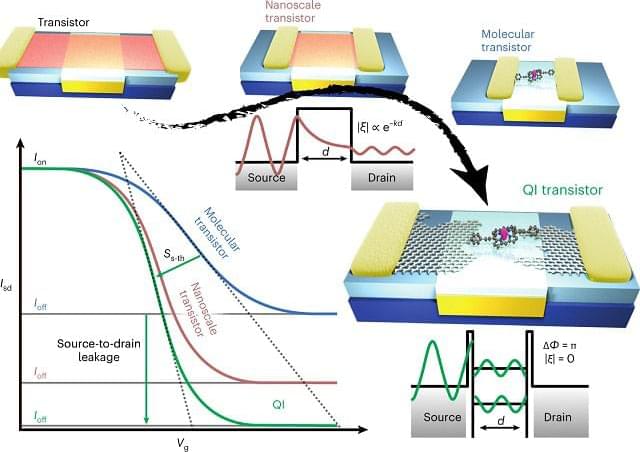
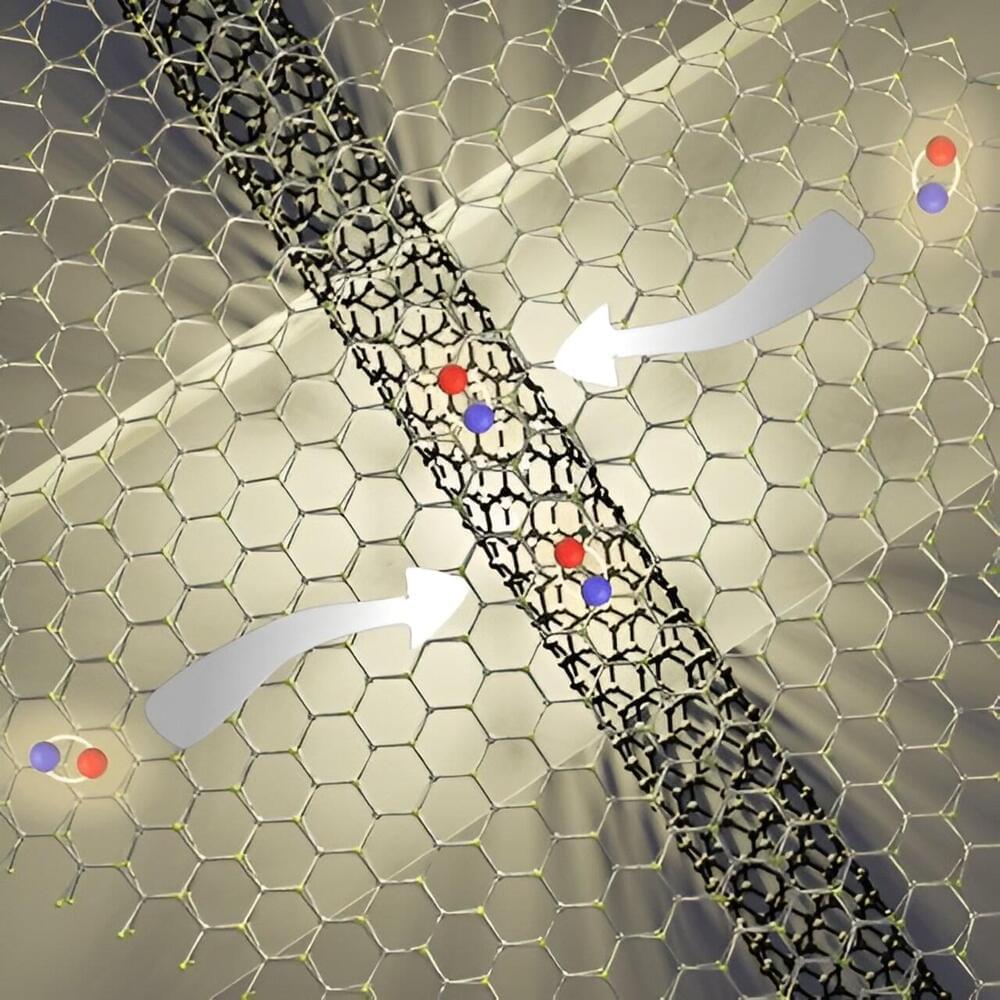
An international team of researchers from Queen Mary University of London, the University of Oxford, Lancaster University, and the University of Waterloo have developed a new single-molecule transistor that uses quantum interference to control the flow of electrons. The transistor, which is described in a paper published in the Nature Nanotechnology (“Quantum interference enhances the performance of single-molecule transistors”), opens new possibilities for using quantum effects in electronic devices.
Transistor are the basic building blocks of modern electronics. They are used to amplify and switch electrical signals, and they are essential for everything from smartphones to spaceships. However, the traditional method of making transistors, which involves etching silicon into tiny channels, is reaching its limits.
As transistors get smaller, they become increasingly inefficient and susceptible to errors, as electrons can leak through the device even when it is supposed to be switched off, by a process known as quantum tunnelling. Researchers are exploring new types of switching mechanisms that can be used with different materials to remove this effect.