Nanotechnology is without a doubt one of the most exciting future technologies, but what is it exactly? And how will it benefit mankind? Well sit back and get comfy because in todays video, we will be answering all of those questions and more!IPhone wireless charging cases — https://amzn.to/3bz0oRg.
IPhone Backup — https://amzn.to/3w8Usbj.
Wireless Earbuds — https://amzn.to/2ZTjwau.
IPhone Bargains — https://amzn.to/3jXvCGb**** Gears and Equipment we use****
1. Fully Automatic Espresso Machine — https://amzn.to/3bdHcbr.
2. Perfect Desk Chair — https://amzn.to/2ZlMNd2
3. Wireless Mechanical Keyboard — https://amzn.to/3pA71Lw.
4. Wireless DTS Headphone — https://amzn.to/3juz2Qv.
5. Vocal Microphone — https://amzn.to/2XEDsN4
6. UltraWide Monitor — https://amzn.to/3jyteWg**** Free Handy Tools YOU must try ****Tubebuddy In-depth channel/video analysis– https://bit.ly/3y0SOc6
Amazon Prime — https://amzn.to/3mb0BzG
Epidemic Music — https://bit.ly/3FDplbT
Fiverr — Freelance Marketplace — https://bit.ly/3FFARnL
Here at Future Now we aim to bring you the most informative, fascinating and engaging Technology videos on YouTube.🔔 Subscribe To Our Channel: https://bit.ly/3nRoVH8
Copyright Disclaimer:
Under section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for “fair use” for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, education and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use. *DISCLOSURE*
We are affiliated, but not sponsored by any product featured in this video.
Some links in the description are affiliate links to products, which means if you click on them and buy the product, we will receive a small commission.
Not being sponsored allows us to keep our own opinions and provide product reviews without bias. From the millions of products, we appreciate your support.#NanoTech #Nanotechnology #NanoTechHacking
Category: nanotechnology – Page 117
The Nano Robots Inside You
Inside of you, at all times, there are trillions of natural nano robots walking around, taking out the trash, and packaging strands of DNA. Below the calm, ordered exterior of a living organism lies a complex collection of molecular machines working together to create something greater than themselves. Physicist and author of “Life’s Ratchet” Peter Hoffmann shows us the tiny city beneath the surface.
Watch the full program here: https://youtu.be/FzFY5ms3AUc.
Original program date: May 30, 2013
The World Science Festival gathers great minds in science and the arts to produce live and digital content that allows a broad general audience to engage with scientific discoveries. Our mission is to cultivate a general public informed by science, inspired by its wonder, convinced of its value, and prepared to engage with its implications for the future.
Visit our Website: http://www.worldsciencefestival.com/
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldsciencefestival.
Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/WorldSciFest

New Research Sheds Light on the Formation of One of Nature’s Most Fundamental Molecules
Life runs on ribosomes. Every cell across the globe requires ribosomes to convert genetic data into the vital proteins required for the organism’s operation, and, subsequently, for the production of more ribosomes. However, scientists still lack a clear understanding of how these essential nanomachines are assembled.
Now, new high-resolution images of the large ribosomal subunit are shedding light on how arguably nature’s most fundamental molecule coalesces in human cells. The findings, published in Science, bring us one step closer to a complete picture of ribosome assembly.
“We now have a pretty good idea of how the large ribosomal subunit is assembled in humans,” says Rockefeller’s Sebastian Klinge. “We still have quite a few gaps in our understanding, but we certainly now have a much better idea than we had before.”
Nano-Biological Computing — Quantum Computer Alternative!
Subscribe here: https://goo.gl/9FS8uF
Check out the previous episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5lpOskKF9I
Become a Patreon!: https://www.patreon.com/ColdFusion_TV
Here it is, the bio computer. A new type of parallel computing method that could rival the infamous quantum computer at a much lower price while being more practical to boot.
Hi, welcome to ColdFusion (formally known as ColdfusTion).
Experience the cutting edge of the world around us in a fun relaxed atmosphere.
Sources:
http://www.mind.ilstu.edu/curriculum/nature_of_computers/computer_types.php.
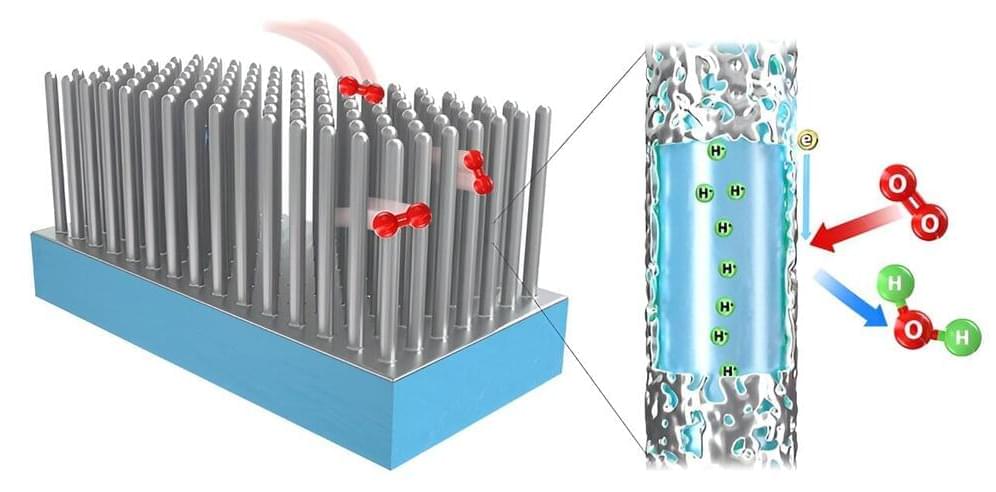
New fuel cell architecture uses nanowires to deliver durability
A promising, more durable fuel cell design could help transform heavy-duty trucking and other clean fuel cell applications. Consisting of nanowires that are less susceptible to corrosion than other designs, the innovative electrode—the heart of a polymer electrolyte-membrane fuel cell—could usher in a new era for fuel cells, which use hydrogen as emission-free power for vehicles.
“In real-world terms, this means that we can have a more durable fuel cell that will provide high fuel economy over a longer lifetime,” said Jacob Spendelow, a scientist with the Los Alamos National Laboratory team that described its results in the journal Advanced Materials. “This work demonstrates that we can get rid of conventional carbon-based catalyst supports, eliminating the degradation problems associated with carbon corrosion, while still achieving high fuel cell performance.”
The improved durability makes this fuel cell a promising candidate for use in heavy-duty trucking applications, which require fuel cell lifetimes of more than 25,000 hours.
New technique opens door for encoding data on single photons
Researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory have successfully developed a new way to produce a specific type of photon that could prove critical for quantum data exchange, notably encryption. The specific kind of photons, called “circularly polarized light,” have thus far proved challenging to create and control, but this new technique makes the process easier and, importantly, cheaper. This was achieved, the team explains, by stacking two different, atomically thin materials to “twist” (polarize) photons in a predictable fashion.
Encoded, “twisted,” photons
“Our research shows that it is possible for a monolayer semiconductor to emit circularly polarized light without the help of an external magnetic field,” explained Han Htoon, a scientist at Los Alamos National Laboratory. “This effect has only been achieved before with high magnetic fields created by bulky superconducting magnets, by coupling quantum emitters to very complex nanoscale photonics structures, or by injecting spin-polarized carriers into quantum emitters. Our proximity-effect approach has the advantage of low-cost fabrication and reliability,” he added.

Gilded mysteries unveiled: Ancient art meets nanotechnology in nanoscale goldbeating
Goldbeating, an age-old craft pioneered by ancient Egyptian artisans more than five millennia ago, involves the meticulous thinning of bulk gold into gossamer-like leaves. Throughout history, this intricate process has adorned various masterpieces, such as the tombs of Thebes and Saqqara, and has cemented its place in art and adornments across cultures. Today, nanoscale gold is used not only for decorating fancy desserts, but is indispensable for modern applications ranging from microelectronics to nanomedicine.

“Truly Mind-Boggling” Breakthrough: Graphene Surprise Could Help Generate Hydrogen Cheaply and Sustainably
Researchers have discovered that graphene.
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon in the form of a single layer of atoms in a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice in which one atom forms each vertex. It is the basic structural element of other allotropes of carbon, including graphite, charcoal, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. In proportion to its thickness, it is about 100 times stronger than the strongest steel.

Long Considered Impossible in Physics: Nonlinear Circuit Harvests Clean Power Using Graphene
The discovery overturns more than a century of physics orthodoxy by identifying a new form of energy that can be extracted from ambient heat using graphene.
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon in the form of a single layer of atoms in a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice in which one atom forms each vertex. It is the basic structural element of other allotropes of carbon, including graphite, charcoal, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. In proportion to its thickness, it is about 100 times stronger than the strongest steel.