Feeling overwhelmed and distracted? New research reveals a potential solution: block mobile internet on your phone. The findings suggest it can boost your mood, sharpen focus, and improve mental well-being.


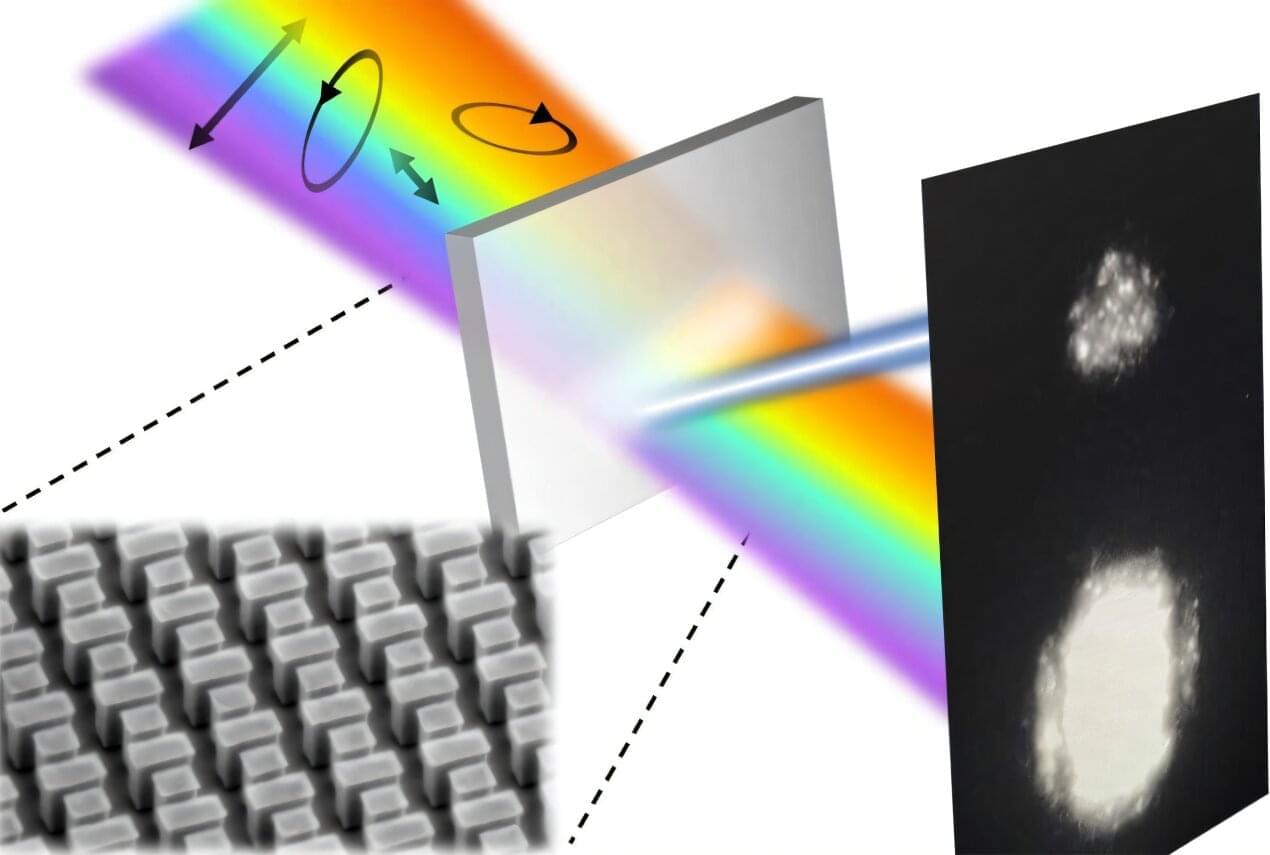
Antennas receive and transmit electromagnetic waves, delivering information to our radios, televisions, cellphones and more. Researchers in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis imagines a future where antennas reshape even more applications.
Their new metasurfaces, ultra-thin materials made of tiny nanoantennas that can both amplify and control light in very precise ways, could replace conventional refractive surfaces from eyeglasses to smartphone lenses and improve dynamic applications such as augmented reality/virtual reality and LiDAR (light detection and ranging).
While metasurfaces can manipulate light very precisely and efficiently, enabling powerful optical devices, they often suffer from a major limitation: Metasurfaces are highly sensitive to the polarization of light, meaning they can only interact with light that is oriented and traveling in a certain direction. While this is useful in polarized sunglasses that block glare and in other communications and imaging technologies, requiring a specific polarization dramatically reduces the flexibility and applicability of metasurfaces.

As tech billionaires around the world continue to experiment with artificial intelligence, a bizarre trend of AI ‘partners’ has emerged whereby people engage in relationships with chatbots — but, far from solving an epidemic of loneliness among singletons, a dark new trend has emerged in which men can indulge in emotionally abusive behaviour.
Threads on Reddit are exposing this disturbing desire which sees people use smartphone apps like Replika to create virtual partners they can verbally berate, abuse, and ‘experiment’ with.
Replika allows people to send and receive messages from a virtual companion or avatar which can be ‘set’ or trained to become a friend or mentor — though more commonly a romantic partner.

In today’s AI news, Galileo launched an Agent Leaderboard on Hugging Face, an open-source AI platform where users can build, train, access, and deploy AI models. The leaderboard is meant to help people learn how AI agents perform in real-world business applications and help teams determine which agent best fits their needs.
In other advancements, Bloomberg reported Friday that xAI is canvassing existing investors, including Sequoia Capital, Andreessen Horowitz, and Valor Equity Partners for the round, which would bring xAI’s total raised to $22.4 billion, according to Crunchbase. Bloomberg also noted that discussions are ongoing and that the terms of the fundraising round may change.
Ve done mobile app development will know how challenging it can be to deliver the right kind of experience on a smartphone. + And, while speaking with former U.K. Prime Minister Tony Blair at the World Governments Summit in Dubai on Wednesday, Oracle cofounder and executive chairman, Larry Ellison said that while government organizations collect massive amounts of data, it is highly fragmented, making it hard to feed it into an AI model.
In videos, the Imagination in Action video series from Davos 2025 is being uploaded and we’re featuring the sessions in today’s newsletter. First we dive into an in-depth panel discussion featuring AI visionaries Max Tegmark, Demis Hassabis, Yoshua Bengio, Dawn Song, and Ya-Qin Zhang. In this engaging conversation, the experts unpack the distinctions between narrow AI, AGI, and super intelligence …
And, an expert panel explores how regulation can drive innovation in AI, featuring perspectives from panelists: Robert Mahari, JD-PhD at Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard Law School, Pablo Arredondo, Vice President of CoCounsel at Thomson Reuters and Founder of Casetext, Part of Thomson Reuters, Julia Apostle, Partner at Orrick, Herrington & Sutcliffe LLP, Gabriele Mazzini, Fellow at MIT Connection Science and Architect of EU AI Act.
Then, join AI pioneer Andrew Ng as he breaks down how artificial intelligence is moving beyond the hype to deliver tangible business results.
In this exclusive conversation with Link Ventures’ John Werner at Davos 2025, Andrew explains how AI innovations are saving costs—from making ships 10% more fuel efficient to boosting profitability in pricing analytics and legal compliance.
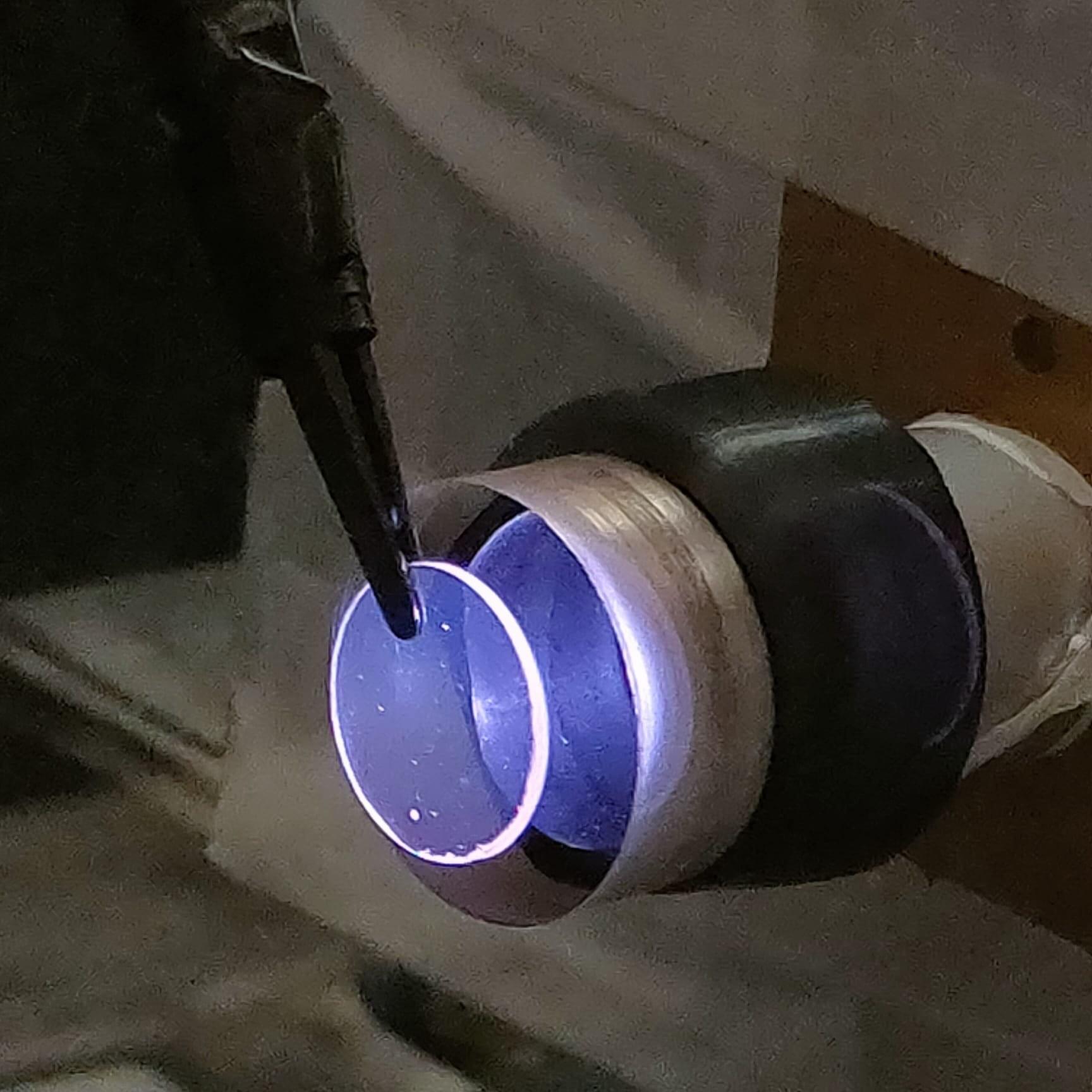
From punch card-operated looms in the 1800s to modern cellphones, if an object has an “on” and an “off” state, it can be used to store information.
In a computer laptop, the binary ones and zeroes are transistors either running at low or high voltage. On a compact disc, the one is a spot where a tiny indented “pit” turns to a flat “land” or vice versa, while a zero is when there’s no change.
Historically, the size of the object making the “ones” and “zeroes” has put a limit on the size of the storage device. But now, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) researchers have explored a technique to make ones and zeroes out of crystal defects, each the size of an individual atom for classical computer memory applications.

Shubham is a passionate tech enthusiast whose world revolves around smartphones and gadgets. His love for gizmos and gaming is plausible. Beyond his t… View More
End of Article.

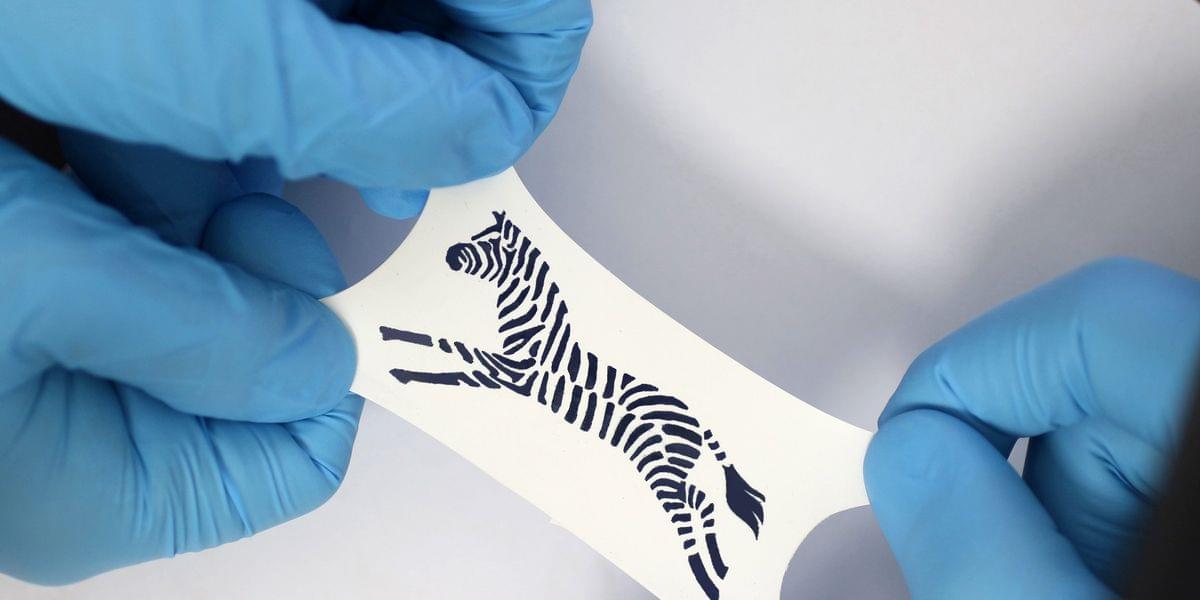
Phones, appliances, and humans all generate heat that usually escapes into the environment as waste energy. Thermoelectric generators, which convert temperature differences into electricity, are a way to capture that wasted heat for power.
Researchers have now made a thermoelectric generator (TEG) that is soft and stretchy and that biodegrades completely when exposed to the environment. Unlike conventional rigid thermoelectric devices, this one, reported in the journal Science Advances, could be easily integrated into fabrics, allowing for body-heat-powered wearable sensors or temperature-detecting disposable face masks.

Your smartphone gallery may contain photos and screenshots of important information you keep there for safety or convenience, such as documents, bank agreements, or seed phrases for recovering cryptocurrency wallets. All of this data can be stolen by a malicious app such as the SparkCat stealer we’ve discovered. This malware is currently configured to steal crypto wallet data, but it could easily be repurposed to steal any other valuable information.
The worst part is that this malware has made its way into official app stores, with almost 250,000 downloads of infected apps from Google Play alone. Although malicious apps have been found in Google Play before, this marks the first time a stealer Trojan has been detected in the App Store. How does this threat work and what can you do to protect yourself?
Spectre-like SLAP and FLOP vulnerabilities in Apple CPUs can be used in real-world attacks.

Your smartphone gallery may contain photos and screenshots of important information you keep there for safety or convenience, such as documents, bank agreements, or seed phrases for recovering cryptocurrency wallets. All of this data can be stolen by a malicious app such as the SparkCat stealer we’ve discovered. This malware is currently configured to steal crypto wallet data, but it could easily be repurposed to steal any other valuable information.
The worst part is that this malware has made its way into official app stores, with almost 250,000 downloads of infected apps from Google Play alone. Although malicious apps have been found in Google Play before, this marks the first time a stealer Trojan has been detected in the App Store. How does this threat work and what can you do to protect yourself?
SparkCat infostealer infected apps in the App Store and Google Play. It scans photos on infected devices and steals crypto wallets.