Google’s AI scam defenses now block 20x more malicious pages, cutting airline and visa scams by 80%+ in 2024.


The rules about magnetic order may need to be rewritten. Researchers have discovered that chromium selenide (Cr₂Se₃) — traditionally non-magnetic in bulk form — transforms into a magnetic material when reduced to atomically thin layers. This finding contradicts previous theoretical predictions, and opens new possibilities for spintronics applications. This could lead to faster, smaller, and more efficient electronic components for smartphones, data storage, and other essential technologies.
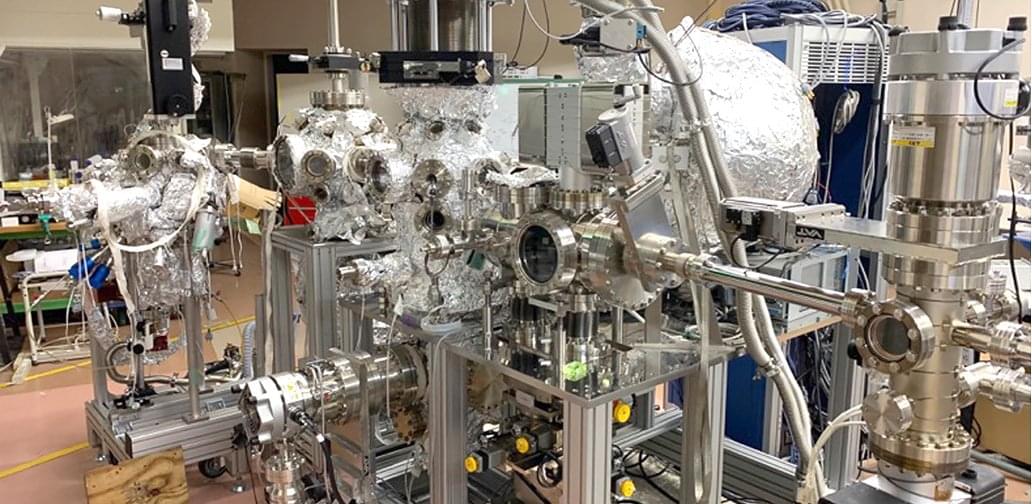
An international research team from Tohoku University, Université de Lorraine (Synchrotron SOLEIL), the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center (NSRRC), High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, and National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology successfully grew two-dimensional Cr₂Se₃ thin films on graphene using molecular beam epitaxy. By systematically reducing the thickness from three layers to one layer and analyzing them with high-brightness synchrotron X-rays, the team made a surprising discovery. This finding challenges conventional theoretical predictions that two-dimensional materials cannot maintain magnetic order.
“When we first observed the ferromagnetic behavior in these ultra-thin films, we were genuinely shocked,” explains Professor Takafumi Sato (WPI-AIMR, Tohoku University), the lead researcher. “Conventional theory told us this shouldn’t happen. What’s even more fascinating is that the thinner we made the films, the stronger the magnetic properties became—completely contrary to what we expected.”
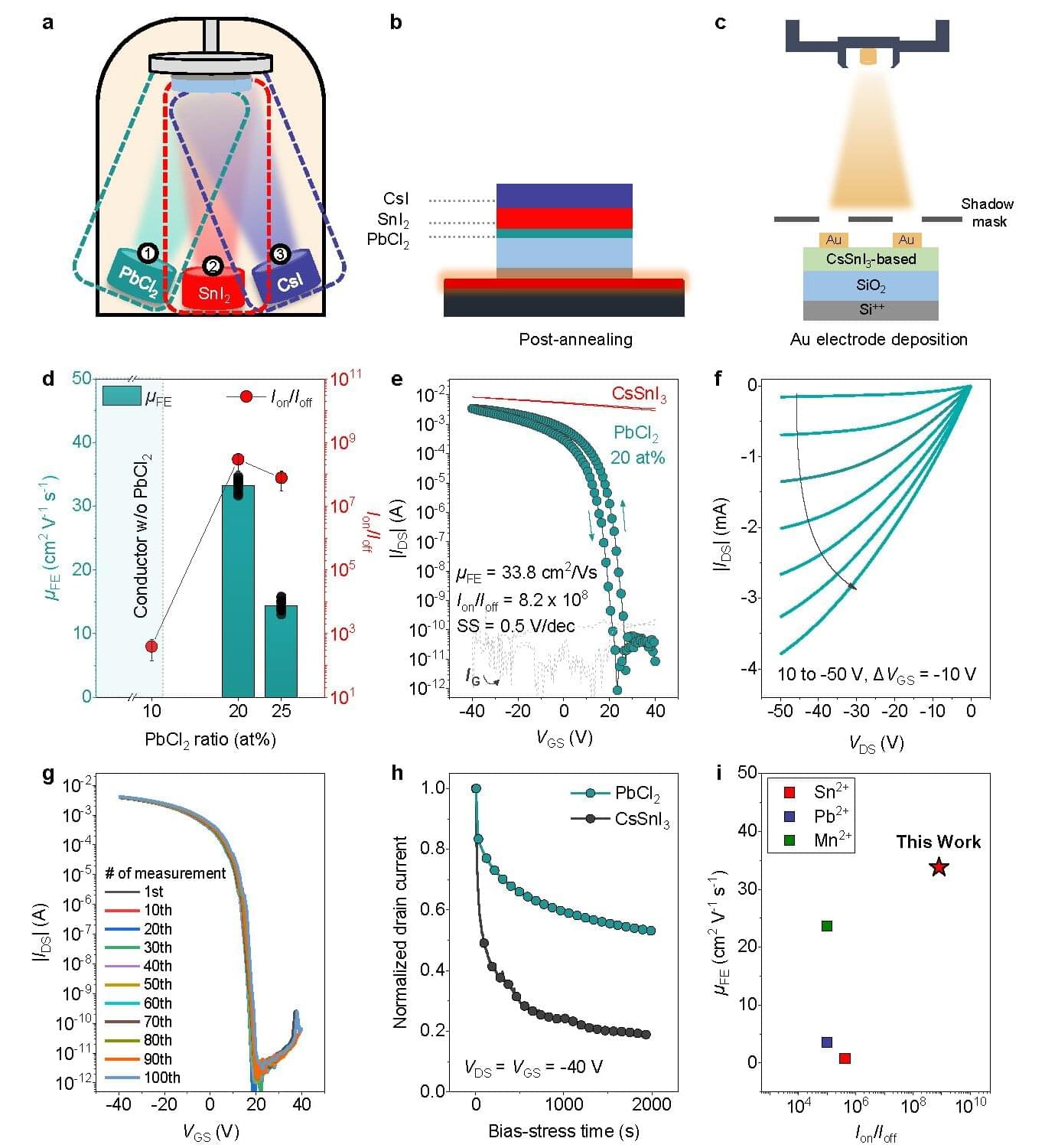
A research team led by Professor Yong-Young Noh and Dr. Youjin Reo from the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) has developed a technology poised to transform next-generation displays and electronic devices.
The project was a collaborative effort with Professors Ao Liu and Huihui Zhu from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), and the findings were published in Nature Electronics.
Every time we stream videos or play games on our smartphones, thousands of transistors operate tirelessly behind the scenes. These microscopic components function like traffic signals, regulating electric currents to display images and ensure smooth app operation.

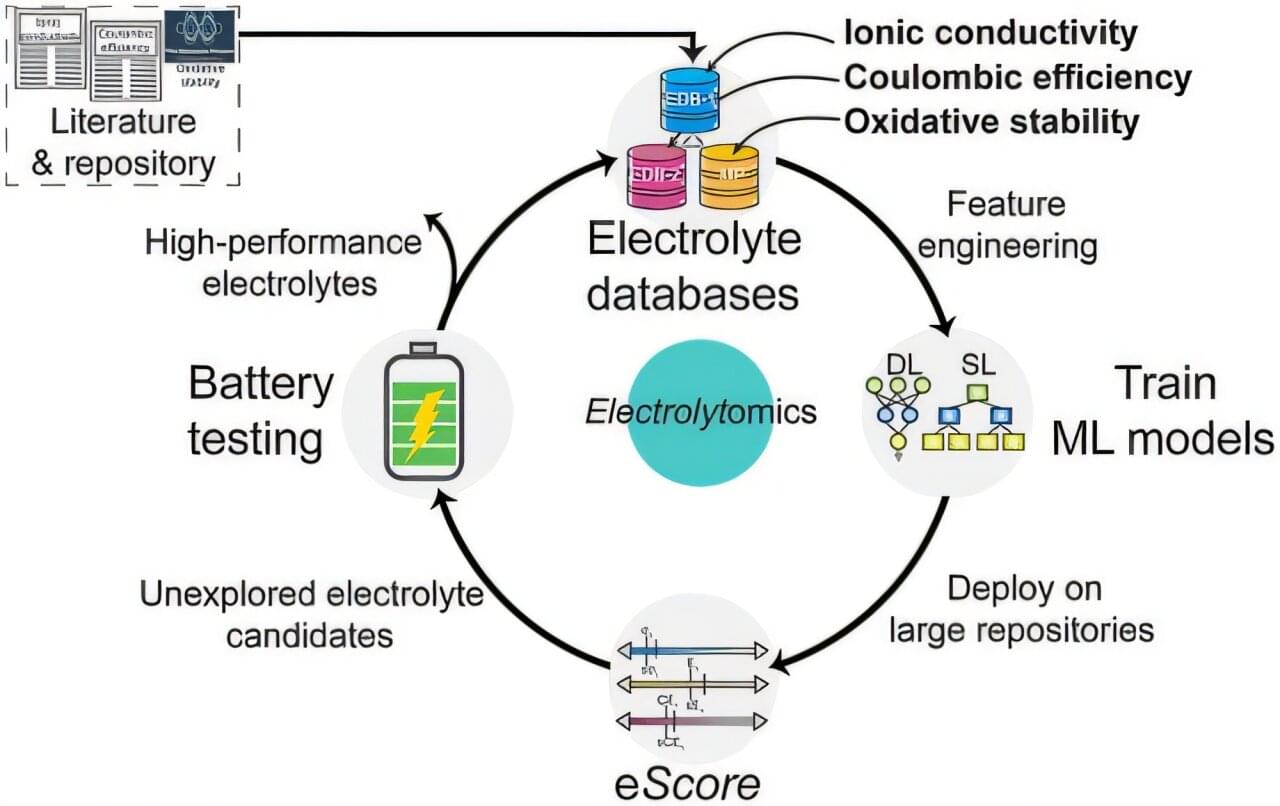
Discovering new, powerful electrolytes is one of the major bottlenecks in designing next-generation batteries for electric vehicles, phones, laptops and grid-scale energy storage.
The most stable electrolytes are not always the most conductive. The most efficient batteries are not always the most stable. And so on.
“The electrodes have to satisfy very different properties at the same time. They always conflict with each other,” said Ritesh Kumar, an Eric and Wendy Schimdt AI in Science Postdoctoral Fellow working in the Amanchukwu Lab at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME).
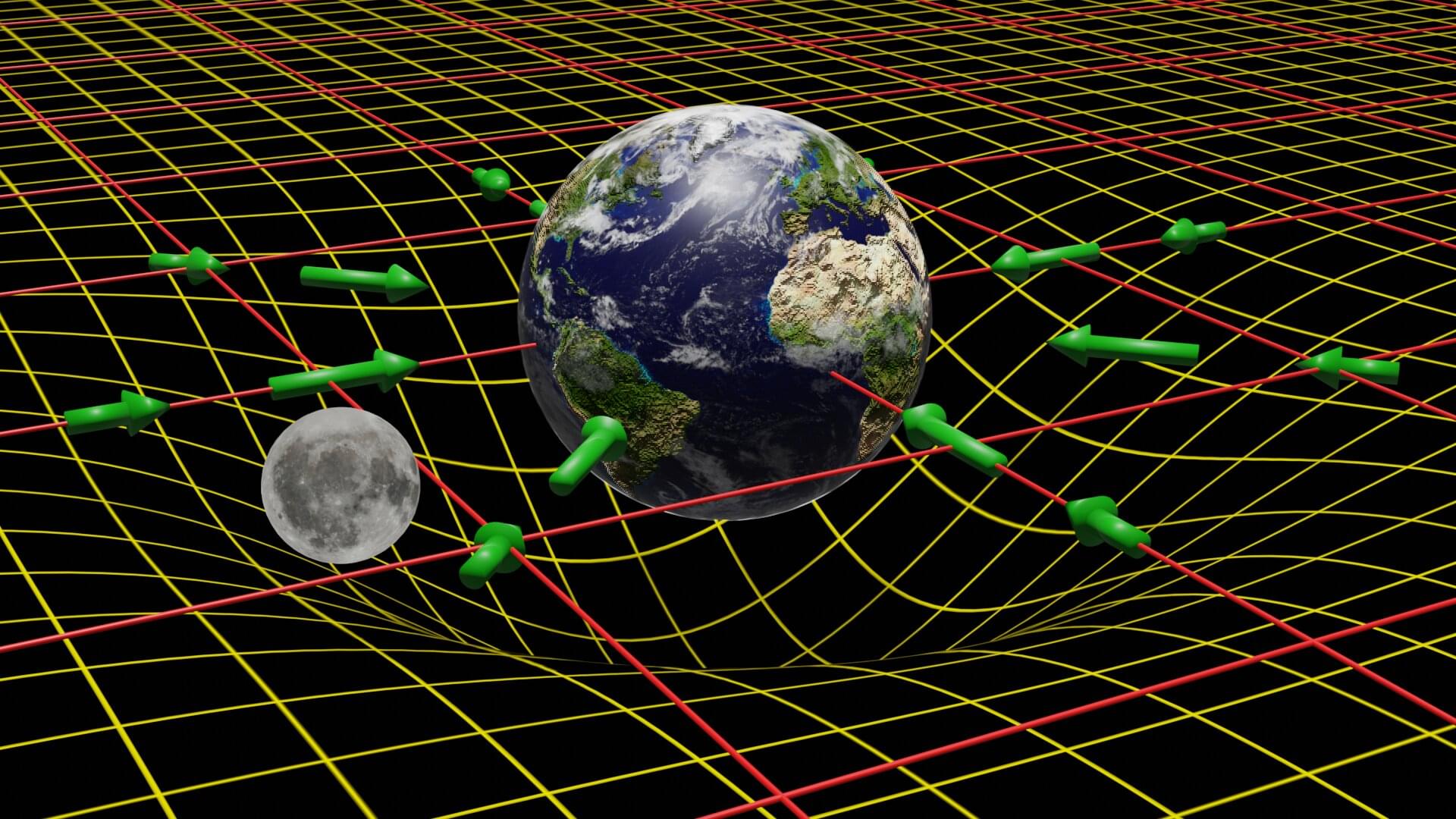
At long last, a unified theory combining gravity with the other fundamental forces—electromagnetism and the strong and weak nuclear forces—is within reach. Bringing gravity into the fold has been the goal of generations of physicists, who have struggled to reconcile the incompatibility of two cornerstones of modern physics: quantum field theory and Einstein’s theory of gravity.
Researchers at Aalto University have developed a new quantum theory of gravity which describes gravity in a way that’s compatible with the standard model of particle physics, opening the door to an improved understanding of how the universe began.
While the world of theoretical physics may seem remote from applicable tech, the findings are remarkable. Modern technology is built on such fundamental advances—for example, the GPS in your smartphone works thanks to Einstein’s theory of gravity.

Google is constantly releasing new Android Auto updates, but new features often feel few and far between. What’s on the roadmap? In this post, we’ll break down new features coming to Android Auto.
Timeline: More news at Google I/O
Officially confirmed by Google itself, Gemini is on its way to Android Auto.
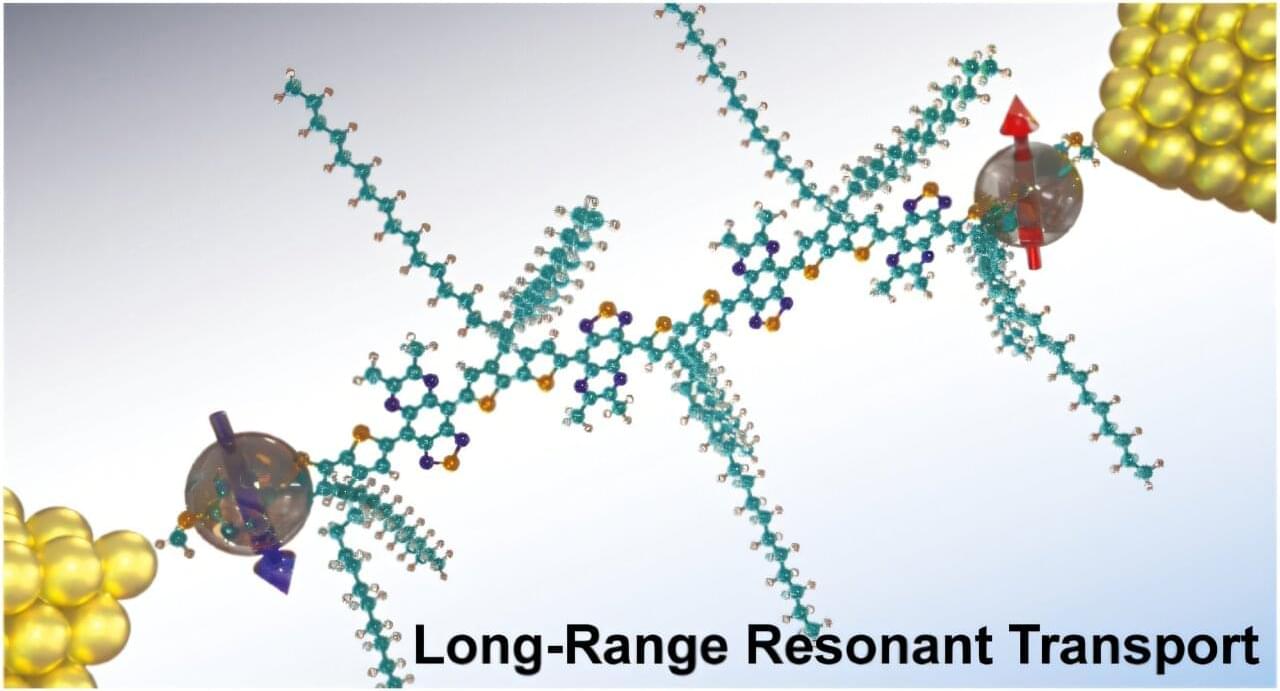
Today, most of us carry a fairly powerful computer in our hand—a smartphone. But computers weren’t always so portable. Since the 1980s, they have become smaller, lighter, and better equipped to store and process vast troves of data. Yet the silicon chips that power computers can only get so small.
“Over the past 50 years, the number of transistors we can put on a chip has doubled every two years,” said Kun Wang, assistant professor of physics at the University of Miami College of Arts and Sciences. “But we are rapidly reaching the physical limits for silicon-based electronics, and it’s more challenging to miniaturize electronic components using the we have been using for half a century.”
It’s a problem that Wang and many in his field of molecular electronics are hoping to solve. Specifically, they are looking for a way to conduct electricity without using silicon or metal, which are used to create computer chips today. Using tiny molecular materials for functional components, like transistors, sensors, and interconnects in electronic chips offers several advantages, especially as traditional silicon-based technologies approach their physical and performance limits.
About 20% to 35% of the population suffers from chronic sleep disorders—and up to half of all people in older age. Moreover, almost every teenager or adult has experienced short-term sleep deprivation at some point. There are many reasons for not getting enough sleep, whether it be partying, a long day at work, caring for relatives, or simply whiling away time on smartphones.
In a recent meta-study, Jülich researchers have now been able to show that the brain regions involved in the short-term and long-term conditions differ significantly. The results of the study were published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry.
“Poor sleep is one of the most important—but changeable—risk factors for mental illnesses in adolescents and older people,” says Jülich researcher and Privatdozent Dr. Masoud Tahmasian, who coordinated the study. In contrast, long-term pathological sleep disorders, such as insomnia, obstructive sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and short-term sleep deprivation, are located in different parts of the brain.
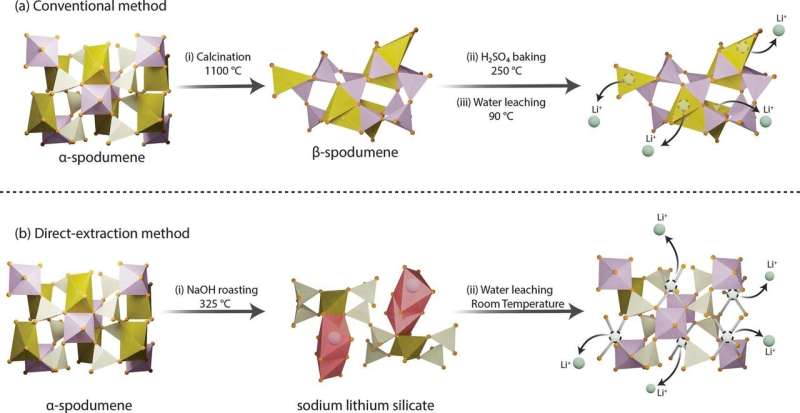
Lightweight lithium metal is a heavy-hitting critical mineral, serving as the key ingredient in the rechargeable batteries that power phones, laptops, electric vehicles and more. As ubiquitous as lithium is in modern technology, extracting the metal is complex and expensive. A new method, developed by researchers at Penn State and recently granted patent rights, enables high-efficiency lithium extraction—in minutes, not hours—using low temperatures and simple water-based leaching.
“Lithium powers the technologies that define our modern lives—from smartphones to electric vehicles—and has applications in grid energy storage, ceramics, glass, lubricants, and even medical and nuclear technologies,” said Mohammad Rezaee, the Centennial Career Development Professor in Mining Engineering at Penn State, who led the team that published their approach in Chemical Engineering Journal.
“But its extraction must also be environmentally responsible. Our research shows that we can extract lithium, and other critical minerals, more efficiently while drastically reducing energy use, greenhouse gas emissions and waste that’s difficult to manage or dispose of.”