The military wants to apply quantum computing to secure communications and inertial navigation in GPS denied environments.

Their task was to ensure that the radioactive materials did not fall into the wrong hands on the way back to Idaho, where the government maintains a stockpile of nuclear explosive materials for the military and others.
To ensure they got the right items, the specialists from Idaho brought radiation detectors and small samples of dangerous materials to calibrate them: specifically, a plastic-covered disk of plutonium, a material that can be used to fuel nuclear weapons, and another of cesium, a highly radioactive isotope that could potentially be used in a so-called “dirty” radioactive bomb.
But when they stopped at a Marriott hotel just off Highway 410, in a high-crime neighborhood filled with temp agencies and ranch homes, they left those sensors on the back seat of their rented Ford Expedition. When they awoke the next morning, the window had been smashed and the special valises holding these sensors and nuclear materials had vanished.

Monsignor Georges Lemaître was a Belgian Roman Catholic priest, physicist and astronomer. He is usually credited with the first definitive formulation of the idea of an expanding universe and what was to become known as the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe, which Lemaître himself called his “hypothesis of the primeval atom” or the “Cosmic Egg”.
Georges Henri Joseph Édouard Lemaître was born on 17 July 1894 at Charleroi, Belgium. After a classical education at a Jesuit secondary school, the Collège du Sacré-Coeur in Charleroi, he began studying civil engineering at the Catholic University of Leuven (Louvain) at the age of 17. In 1914, he interrupted his studies to serve as an artillery officer in the Belgian army for the duration of World War I, at the end of which he received the Military Cross with palms.
Move over, Iron Man.
What makes this possible are the unique properties of carbon nanotubes: a large surface area that is strong, conductive and heat-resistant.
UC’s College of Engineering and Applied Science has a five-year agreement with the Air Force Research Laboratory to conduct research that can enhance military technology applications.
Tactical Robotics’ Cormorant drone design allows it to navigate tight areas where a helicopter’s blades would get caught on the environment. The remote-controlled military drone can transport two injured people from a battle zone. The Israeli-based company believes the drone could one day also be used to inspect bridges, deliver medical supplies and spray crops.
Elon Musk Wants You to Watch ‘Do You Trust This Computer?’ in Memory of Stephen Hawking, and It’s Free.
Because “nothing will affect the future of humanity more than digital super-intelligence,” Elon Musk thinks you should watch Chris Paine’s artificial-intelligence movie “Do You Trust This Computer?” And, wouldn’t you know it, the film is streaming for free until later tonight.
Here’s the synopsis: “Science fiction has long anticipated the rise of machine intelligence. Today, a new generation of self-learning computers has begun to reshape every aspect of our lives. Incomprehensible amounts of data are being created, interpreted, and fed back to us in a tsunami of apps, personal assistants, smart devices, and targeted advertisements. Virtually every industry on earth is experiencing this transformation, from job automation to medical diagnostics, even military operations. ‘Do You Trust This Computer?’ explores the promises and perils of our new era. Will A.I. usher in an age of unprecedented potential, or prove to be our final invention?”
Nothing will affect the future of humanity more than digital super-intelligence. Watch Chris Paine’s new AI movie for free until Sunday night at http://doyoutrustthiscomputer.org/watch
[email protected]
Telegram Group: https://telegram.me/mcgregorrecruitme…
Telegram Channel: https://telegram.me/vacanciesinuae
LinkedIn Group: https://www.linkedin.com/groups/12102…
Some of the new weapons, which are set to enter service in Russia between 2018 and 2027, surpass the existing and even future weapons systems used by other nations, including the NATO member states, Borisov said as he listed what he called six Russian cutting-edge weapons.
The Russian Armed Forces are expected to get new state-of-the-art weapons systems, which have no equals anywhere in the world, a Russian government’s top official said. The new equipment is set to enter service within a decade.
The Russian military is undergoing a large-scale rearmament, which will allow it to make use of some of the world’s most advanced weapon systems, Yury Borisov, the Russian deputy prime minister, who oversees Russia’s military-industrial complex and military-technical policy, said during his speech at the Military Academy of the General Staff.

https://paper.li/e-1437691924#/
They have been called the main news channel internationally and have a wider range than CNN and Al Jazeera. They have also taken the right to broadcast the best documentary on the development of mind control as a major political program. The Spanish TV-producer Daniel Estulin made the 25 minute presentation and interviewed Magnus Olsson who presented examples of victims that can be subjected to life-destructive research without their consent. The introduction gives a picture from the 1960s CIA project MKULTRA with tens of thousands of victims and a research based on state crime, medical abuse and kept beyond public attention.
University hospitals in the United States and Europe were central places where patients were implanted, utilized and misused for a life time of brain research and experiments. That situation has a similar pattern internationally and was built in behind the military and intelligence agencys classified operations. In Sweden the military research institution FOI became the innovator, knowledge bank and educated professors and physicians in collaboration with hospitals where the project was given highest priority.
The documentary’s original language is Spanish but has got English subtitles to be shown world-wide. Daniel Estulin has by far made the strongest warning about the hidden techno-political development. Mr. Estulin is also one with the strength of the challenge and his presentation gives an expression that fits the crucial mission he proclaims. While interviewing people on the street of Madrid, both school children and adults show examples of the unknown technology and its use:”…I have never heard about it … It sounds too fantastic… Can it really be like that…” Something normal of a techno-political development hidden from media and the public.
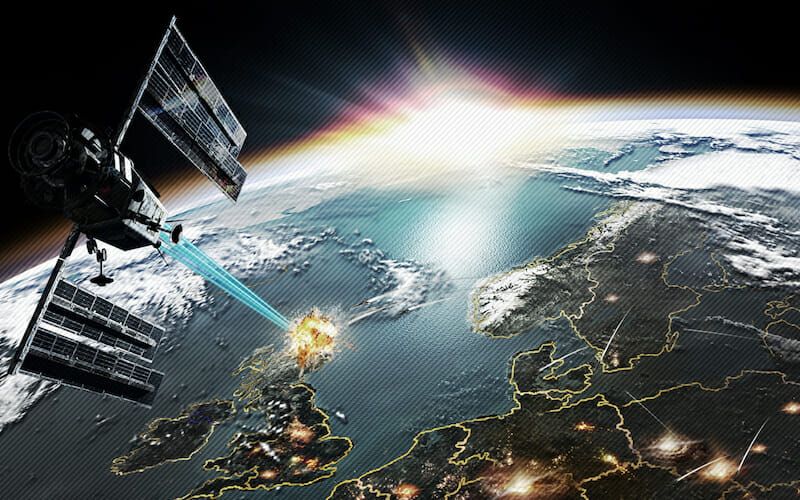

There is increasing chatter among the world’s major military powers about how space is fast becoming the next battleground. China, Russia, and the United States are all taking steps that will ultimately result in the weaponisation of space. Any satellite that can change orbit can be considered a space weapon, but since many of the possible space-based scenarios have yet to occur, cybersecurity experts, military commanders, and policymakers do not fully understand the range of potential consequences that could result.
During the Cold War, the Soviet Union was interested in paralysing America’s strategic forces, strategic command, and control and communications, so that its military command could not communicate with its forces. They would do so by first causing electromagnetic pulse (EMP) to sever communication and operational capabilities, and then launch a mass attack across the North Pole to blow up US Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs).
In 1967, the US, UK and Soviet Union signed the Outer Space Treaty, which was either ratified by or acceded to 105 countries (including China). It set in place laws regarding the use of outer space and banned any nation from stationing nuclear warheads, chemical or biological weapons in space. However, the Treaty does not prohibit the placement of conventional weapons in orbit, so such weapons as kinetic bombardment (i.e. attacking Earth with a projectile) are not strictly prohibited.

The US already has the Air Force Space Command and the Space Mission Force.
President Donald Trump on Monday said he wanted to create a sixth military division called the Space Force. But Mark Kelly, a retired NASA astronaut and Navy veteran, tweeted that it was “a dumb idea” because the US Air Force already has a Space Command and a space force.