Dyson helped create modern particle physics, criticized nuclear weapons tests, and imagined how civilizations could take to the stars.


Circa 2008
Okay, so no one has quite perfected laser weapons yet, but that doesn’t mean you can’t at least think about possible defenses. Naval researchers are looking at materials that could deflect high-powered lasers, reports Discovery:
“If you have a ship being hit by a laser, and it was made of this metamaterial, you could reflect the laser beam,” said Simin Feng, one of the study co-authors and a researcher at China Lake.
Unlike normal materials, which derive their properties largely from the chemicals that comprise them, metamaterials are artificially made materials that get their properties from their physical structures.
The material Feng and her co-author Klaus Halterman, also of China Lake, have theorized would be made of three layers of conventional materials, with the metamaterials sandwiched between the three layers. Since the material would be thin it should be easily applied and “wouldn’t weigh things down,” said Halterman.
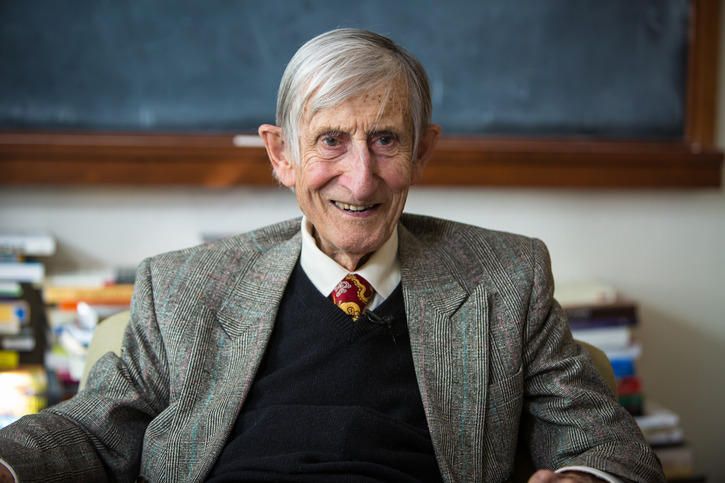

Freeman Dyson, renowned scientist and scholar, has died at 96, according to his daughter Mia.
The British-born scientist and professor emeritus spent much of his career as a physics professor at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, according to his biography on the institute’s website. He was among 29 scientists who supported the Obama administration’s 2015 nuclear deal with Iran. In 1967, he also acted as a military adviser regarding the use of tactical nuclear weapons in the Vietnam War, and in 1984 he wrote a book on the dangers of nuclear warfare.
A futurist and space-enthusiast, Dyson had several scientific concepts named after him, including the “Dyson Tree,” a genetically engineered plant that would be able to survive in a comet and grow in space. One of his ideas, the Dyson Sphere, was featured in an episode of the sci-fi series Star Trek.

Two former top special operations officials say their job was too junior and the Pentagon isn’t taking information warfare seriously enough.
Despite shifting military budgets to better keep up with competitors, there’s one area where countries like China, Russia, and even Iran are proving nimble and frustrating for the Department of Defense: influence operations.
In this new age of information warfare, the military art of influence ops — otherwise sometimes called psychological ops, information ops, or most-recently, military information support ops — lacks the senior level leadership it deserves, say two former Pentagon officials who were in charge of special operations policies. According to them, the position they once held is too junior for the seriousness of the threat and mission, and influence ops is spread so wide, that nobody is sure who is really in charge.


Handicaps: weak private sector, Soviet-style bureaucracy. Helps: Great STEM education — and history.
More than Western governments and even more than China’s, the Russian government is trying to position itself as a facilitator of innovation in artificial intelligence, the technology that Vladimir Putin said will lead whoever masters it to global advantage. Russia seeks “to go our own way,” said Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev, borrowing Lenin’s 1917 words about various anti-capitalist ideologies to describe his government’s 21st-century attempt to shake the world.
Those who doubt that this uniquely state-heavy approach can succeed would do well to remember that today’s internet and mobile telecommunications grew out of Pentagon-funded research, that the Soviet Union led the Space Race for a decade, and that U.S. astronauts currently ascend to orbit atop Russian rockets.


Today’s defense electronics systems rely on radio frequency (RF) mixed-mode electronics – those that integrate RF, analog, and digital circuits onto a single chip – to interface RF signals with digital processors. This technology supports critical communications, radar, and electronic warfare (EW) capabilities, as well as being widely used to support commercial telecommunications. The Department of Defense (DoD) has capability demands that far exceed the requirements of the commercial world in terms of speed, fidelity, capacity, and precision. Current commercial RF mixed-mode systems on a chip (SoCs) are implemented on digital complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) platforms, a technology that has been used for decades to construct integrated circuits, highly integrated transceivers, microprocessors, and beyond. Despite continued advancement and scaling along the trajectory of Moore’s Law for high integration density, these CMOS platforms are unable to support operations at higher frequencies with larger signal bandwidths and higher resolutions, essentially limiting their use in next-generation mixed-mode interfaces needed for emerging defense RF applications.
To advance RF mixed-mode interfaces beyond current limitations, DARPA established the Technologies for Mixed-mode Ultra Scaled Integrated Circuits (T-MUSIC) program. T-MUSIC was first announced in January 2019 as a part of the second phase of DARPA’s Electronics Resurgence Initiative (ERI). One area of research under ERI Phase II focuses on the integration of photonics and RF components directly into advanced circuits and semiconductor manufacturing processes, enabling unique and differentiated domestic manufacturing capabilities. As such, T-MUSIC will explore the integration of mixed-mode electronics into advanced onshore semiconductor manufacturing processes. The goal is to develop highly integrated RF electronics with an unprecedented combination of wide spectral coverage, high resolution, large dynamic range, and high information processing bandwidth.
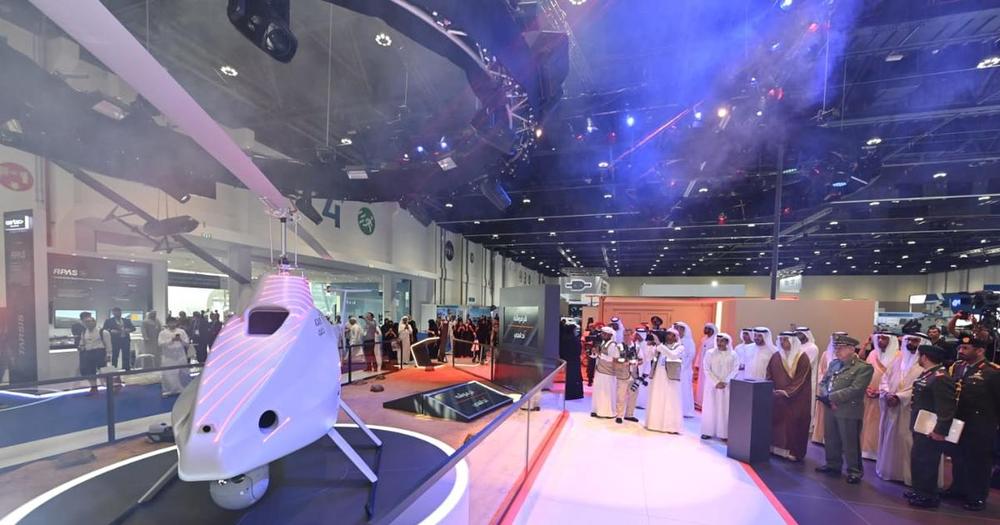

The first UAE-made high-performance drone has taken flight.
ADASI, the regional leader in autonomous systems and services, officially launched the Garmousha vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) drone in a deal with the General Headquarters of the UAE Armed Forces.
The drone is a light military unmanned aircraft designed to carry 100kg over a six-hour period and 150km with a high-definition camera.
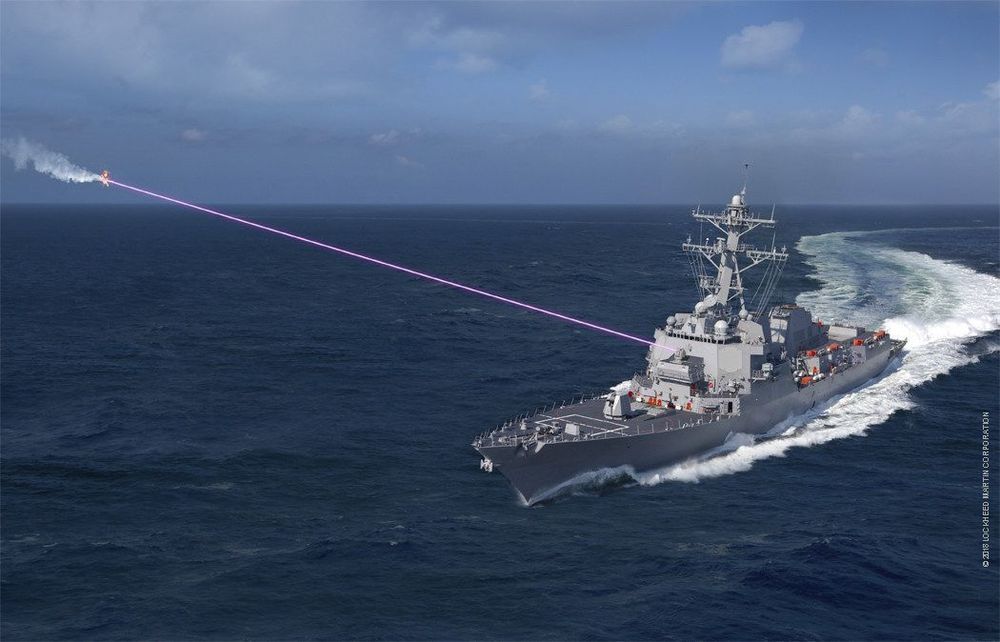

The US Navy has successfully installed its first Optical Dazzling Interdictor, Navy (ODIN) laser weapon aboard one of its warships. During dry-dock operations, the Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyer USS Dewey (DDG 105) received the stand-alone laser system, which is designed to blind the sensors on Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS).
The ODIN laser isn’t the first to be deployed on a US Navy warship. That honor goes to the Office of Naval Research’s (ONR) Laser Weapon System (LaWS), which was deployed on the USS Ponce (LPD-15) in 2014. However, this experience by the team behind LaWS at the Naval Surface Warfare Center (NSWC) Dahlgren Division provided the expertise needed to complete the development of ODIN.
Unlike other laser weapons that are designed to destroy targets with blasts of concentrated laser light, ODIN is what is known as a dazzler laser. That is, it’s one of a class of lasers that are intended to blind or distract rather than destroy. Though the legality of using such lasers against human pilots restricts them to only distracting the person by acting like the glare of oncoming headlamps, such lasers can also disable or destroy delicate optical sensors on drones.