Among the drugs being investigated is remdesivir, an experimental antiviral made by the US drug company Gilead Sciences. It has been characterized as one of the most promising by health authorities, including WHO officials —though that optimism is inspired only by anecdotal information. US data on remdesivir’s performance in controlled clinical trials is expected next month, and data from late-stage trials conducted in China will be released by the end of April.
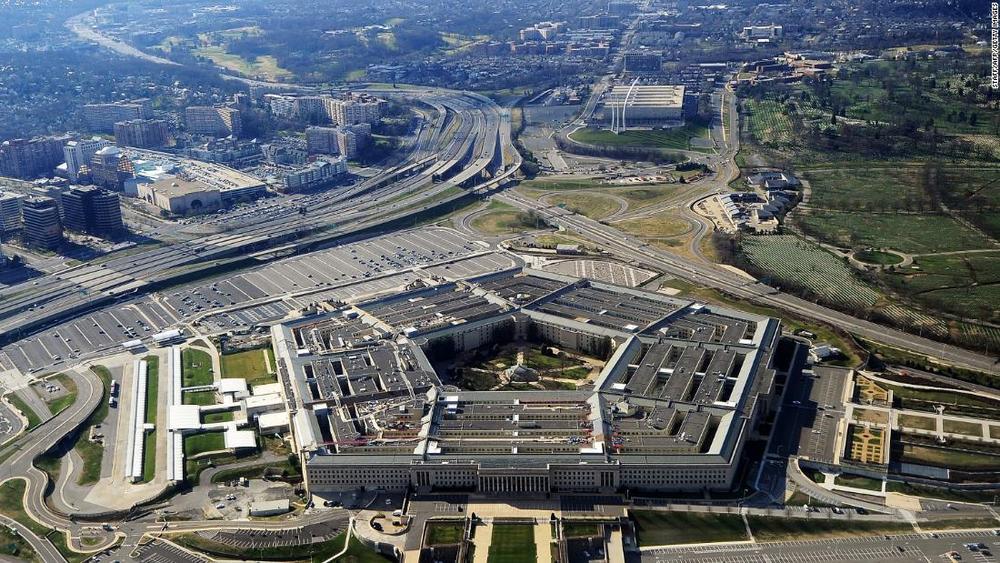
The US military, however, has already secured access to remdesivir for its service members.
On March 10, the Pentagon announced a deal with Gilead Sciences in which the pharmaceutical company would supply the military with the intravenous drug at no cost. “Together with our government and industry partners, we are progressing at almost revolutionary rates to deliver effective treatment and prevention products that will protect the citizens of the world and preserve the readiness and lethality of our service members,” Army Brig. Gen. Michael Talley, commanding general of the US Army Medical Research and Development Command (USAMRDC) and Fort Detrick, Maryland, said in a media statement at the time.