In collaboration with the Autonomous Disinformation Research Network – @DisinfoResearch
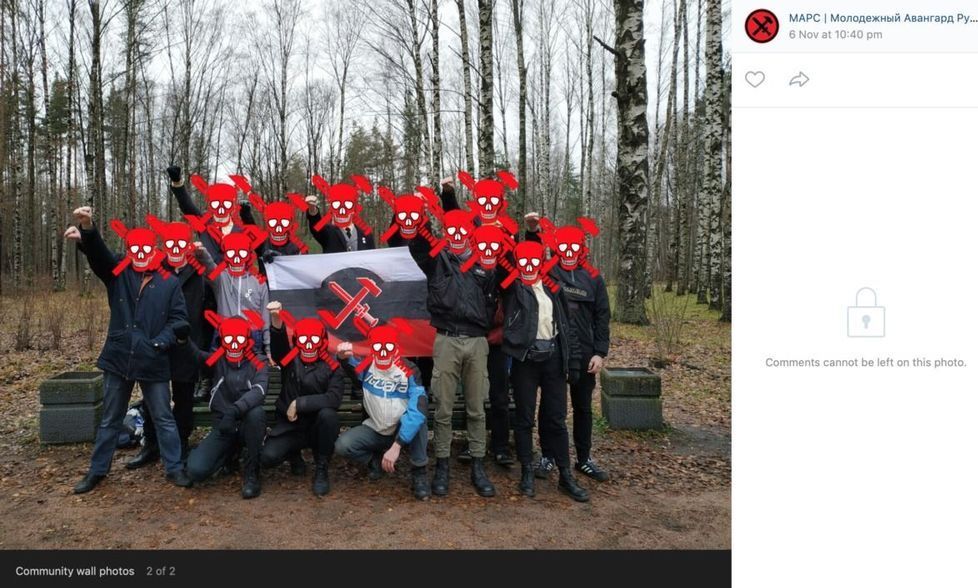
On Wednesday, November 6, 2019, leaked data from the defunct neo-Nazi forum, Iron March, emerged online, exposing the personal information of more than 1,200 members, including the locations of their IP addresses and, in some cases, their real names. Already, activists sifting through the database have uncovered several fascists around the country, including some in uniform. A thoroughly transnational network, Iron March stemmed from a site called International Third Position Forum, was launched by a Russian, produced a terror group in the U.S., and facilitated coordination among terror groupings in the U.K. and elsewhere, all through the power of the internet.
Perhaps most intriguingly, Iron March involved members whose goals of recruiting through the U.S. military underlied their fantasies of ultimately destroying liberal democracy through a fascist paramilitary insurgency. It went on to develop a small but lethal “accelerationist” terrorist group called Atomwaffen Division (Nuclear Weapons Division), responsible for murders, an assassination attempt, and failed bomb plots. It also recently became famous for adding journalists from a Quillette article to a hit-list called “Sunset the Media.” Though what they mostly seem to do is put up stickers in what they laughably call “the stickening.”