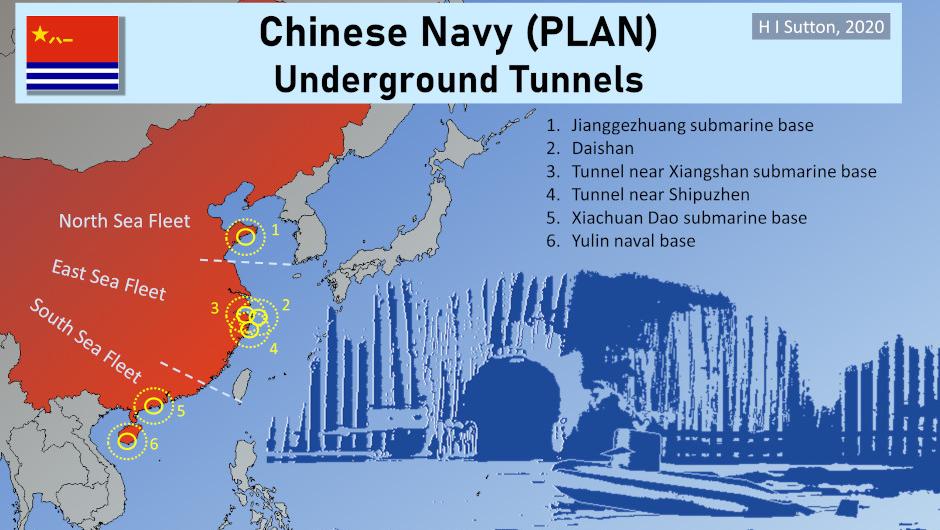
Flyt Aerospace is offering its Red Hummingbird pilot-optional, fully-electric hoverbike for the US Air Force’s (USAF’s) Agility Prime electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) procurement effort.
The eight-motor, multi-rotor Red Hummingbird is designed for speeds of 0–97 km/h in 5.1 seconds, payload capacity of up to 113 kg, a cost of USD2.40 worth of electricity per flight, and the ability to operate for 20–30 minutes per charge. The aircraft is also designed to create only 65 db of noise at 50 ft altitude. Flyt is offering the Red Hummingbird for the Agility Prime 1–2 person capacity area of interest (AOI) 2, according to company founder and CEO Ansel Misfeldt.
Misfeldt told Jane’s on 1 May that the Red Hummingbird has a fully-built prototype currently in flight testing, but that the aircraft has yet to fly with a human. Flyt has so far been flying the aircraft with weights in the pilot seat to ensure system checkout before flying with a pilot.