“All things are numbers,” avowed Pythagoras. Today, 25 centuries later, algebra and mathematics are everywhere in our lives, whether we see them or not. The Cambrian-like explosion of artificial intelligence (AI) brought numbers even closer to us all, since technological evolution allows for parallel processing of a vast amounts of operations.
Progressively, operations between scalars (numbers) were parallelized into operations between vectors, and subsequently, matrices. Multiplication between matrices now trends as the most time-and energy-demanding operation of contemporary AI computational systems. A technique called “tiled matrix multiplication” (TMM) helps to speed computation by decomposing matrix operations into smaller tiles to be computed by the same system in consecutive time slots. But modern electronic AI engines, employing transistors, are approaching their intrinsic limits and can hardly compute at clock-frequencies higher than ~2 GHz.
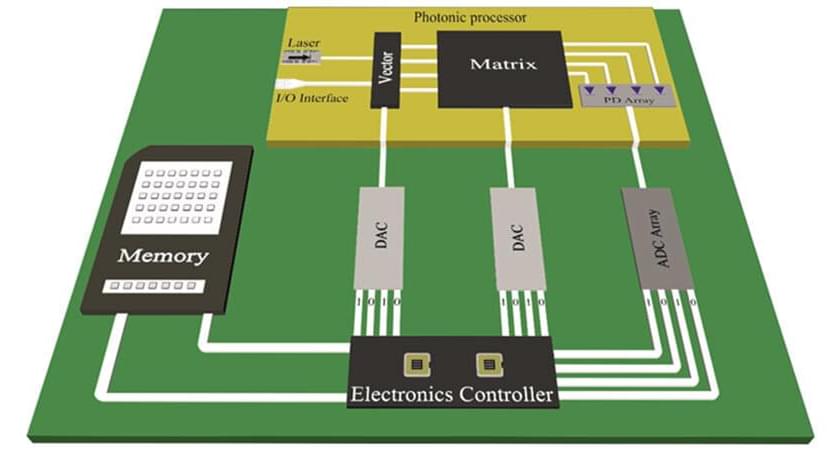
The compelling credentials of light—ultrahigh speeds and significant energy and footprint savings—offer a solution. Recently a team of photonic researchers of the WinPhos Research group, led by Prof. Nikos Pleros from the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, harnessed the power of light to develop a compact silicon photonic computer engine capable of computing TMMs at a record-high 50 GHz clock frequency.