We’re closer than ever to a Theory of Everything.


Harvesting human energy into devices.
Engineers find an alternate route toward self-powered devices with foldable material.

Researchers from Brown University have demonstrated an unusual method of putting the brakes on superconductivity, the ability of a material to conduct an electrical current with zero resistance.
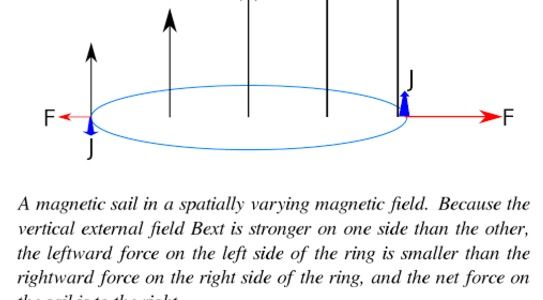
The research shows that weak magnetic fields—far weaker than those that normally interrupt superconductivity—can interact with defects in a material to create a “random gauge field,” a kind of quantum obstacle course that generates resistance for superconducting electrons.
“We’re disrupting superconductivity in a way that people haven’t done before,” said Jim Valles, a professor of physics at Brown who directed the work. “This kind of phase transition involving a random gauge field had been predicted theoretically, but this is the first time it has been demonstrated in an experiment.”
On October 5th 2016, Ranga Dias and Isaac F. Silvera of Lyman Laboratory of Physics, Harvard University released the first experimental evidence that solid metallic hydrogen has been synthesized in the laboratory.
It took 495 GPa pressure to create. The sample is being held in the cryostat in liquid nitrogen.
If as predicted by theory the metallic hydrogen remains metastable when the extreme pressure is removed then the world will eventually be greatly changed.

MOJAVE, California — The world is at the start of a renaissance in supersonic and hypersonic flight that will transform aviation, but the effort will need steady commitment and funding if the United States wants to lead the way, congressional leaders and industry officials said at a forum late last month.
“What’s exciting about aerospace today is that we are in a point here where suddenly, things are happening all across the board in areas that just haven’t been happening for quite a while,” said former U.S. Air Force Maj. Gen. Curtis M. Bedke.
“There was a period where engine technology had just sort of stagnated — a point where all materials technology was going along at about the same pace,” Bedke added. “There just wasn’t much happening. But suddenly, in all sorts of areas that apply to aerospace, things are happening.” [NASA’s Vision of Future Air Travel (Images)].

Metallic hydrogen has been created in a diamond anvil in a Harvard lab.
Diamond anvil cells can use only vanishingly small sample sizes. A typical amount is about 160 cubic micrometers.
If metallic hydrogen is metastable then there are a lot of potential applications.
Metastable would mean that the phases could retain their high-pressure forms for an indefinite period once external forces are removed, much as diamonds formed by high temperatures and pressures deep inside Earth remain diamonds even after they reach the surface, instead of immediately reverting to carbon’s more stable form, graphite. Nellis and others have imagined a host of applications for metastable metallic hydrogen, ranging from.
Engineers from the University of California, San Diego have brought together a couple of nascent technologies that could result in inexpensive and long-lasting electronic devices. The team created a magnetic ink that can print a variety of self-healing components.
The ink is loaded with inexpensive microparticles made of neodymium that are magnetically oriented in such a way that if the material rips, each side of the tear is attracted to the other. This allows components printed with the ink to self-repair tears as wide as 3 mm, which the researchers claim is a new record.
We’ve seen similar properties in boron nitride nanosheets that can repair themselves even after being cut in half, but that material doesn’t conduct electricity. Batteries have been developed that can be self-repaired when they rupture in a similar fashion and other components have been implanted with capsules that rupture when cracks develop in the circuits, releasing a liquid that fills in the crack and dries instantly to restore conductivity.
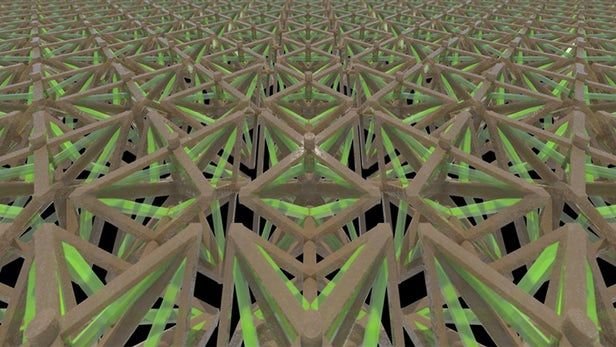
It’s one of the basic facts of science: Heat something and it expands. But a team of US scientists has gone counterintuitive and invented a 3D-printed material that shrinks when heated. Developed as part of DARPA’s program to study materials with controlled microstructure architecture, the lightweight metamaterial exhibits what the researchers call “negative thermal expansion.”
Metamaterials are one of those things that come out of the lab with an air of enchantment about them. Basically, they’re made up of composite materials, like metals, plastics, or ceramics, engineered into repeating, microscopic structures. Depending on how these structures are designed, they can give the metamaterial properties that aren’t found in nature and may not even be derived from the source materials themselves.
The study by a team from the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL) Additive Manufacturing Initiative in partnership with the University of Southern California, MIT, and the University of California, Los Angeles, used a 3D printing process called projection microstereolithograpy to form a polymer and a polymer/copper composite into a highly complex 3D bi-material microlattice structure. To put it more simply, they printed a material made of two substances to form a pattern by printing out the polymer in a layer, cleaning the surface to avoid contamination, then printing the polymer/copper composite, then repeating.

Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory scientists have developed a new “magnetoelectric multiferroic*” material that could lead to a new generation of computing devices with more computing power while consuming a fraction of the energy that today’s electronics require.