Imagine a sheet of material just one layer of atoms thick—less than a millionth of a millimeter. While this may sound fantastical, such a material exists: it is called graphene and it is made from carbon atoms in a honeycomb arrangement. First synthesized in 2004 and then soon hailed as a substance with wondrous characteristics, scientists are still working on understanding it.
Postdoc Areg Ghazaryan and Professor Maksym Serbyn at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) together with colleagues Dr. Tobias Holder and Professor Erez Berg from the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel have been studying graphene for years and have now published their newest findings on its superconducting properties in a research paper in the journal Physical Review B.
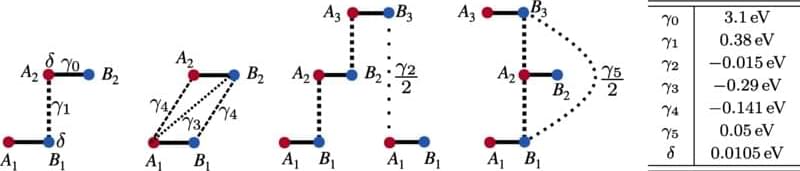
“Multilayered graphene has many promising qualities ranging from widely tunable band structure and special optical properties to new forms of superconductivity—meaning being able to conduct electrical current without resistance,” Ghazaryan explains.