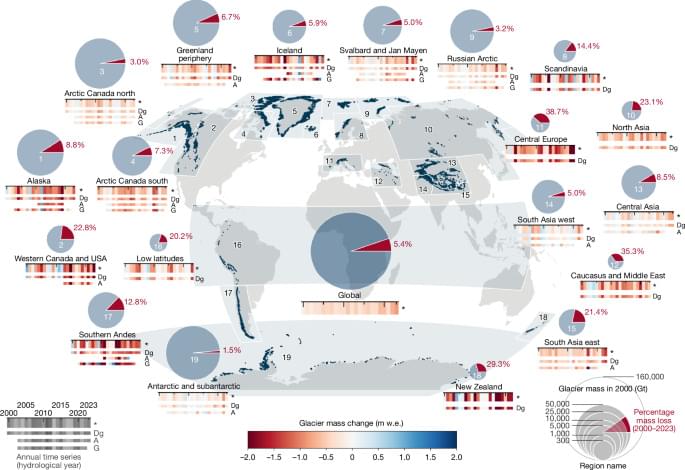
Glaciers separate from the continental ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica covered a global area of approximately 706,000 km2 around the year 200019, with an estimated total volume of 158,170 ± 41,030 km3, equivalent to a potential sea-level rise of 324 ± 84 mm (ref. 20). Glaciers are integral components of Earth’s climate and hydrologic system1. Hence, glacier monitoring is essential for understanding and assessing ongoing changes21,22, providing a basis for impact2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 and modelling11,12,13 studies, and helping to track progress on limiting climate change23. The four main observation methods to derive glacier mass changes include glaciological measurements, digital elevation model (DEM) differencing, altimetry and gravimetry. Additional concepts include hybrid approaches that combine different observation methods. In situ glaciological measurements have been carried out at about 500 unevenly distributed glaciers24, representing less than 1% of Earth’s glaciers19. Glaciological time series provide seasonal-to-annual variability of glacier mass changes25. Although these are generally well correlated regionally, long-term trends of individual glaciers might not always be representative of a given region. Spaceborne observations complement in situ measurements, allowing for glacier monitoring at global scale over recent decades. Several optical and radar sensors allow the derivation of DEMs, which reflect the glacier surface topography. Repeat mapping and calculation of DEM differences provide multi-annual trends in elevation and volume changes26 for all glaciers in the world27. Similarly, laser and radar altimetry determine elevation changes along linear tracks, which can be extrapolated to calculate regional estimates of glacier elevation and volume change28. Unlike DEM differencing, altimetry provides spatially sparse observations but has a high (that is, monthly to annual) temporal resolution26. DEM differencing and altimetry require converting glacier volume to mass changes using density assumptions29. Satellite gravimetry estimates regional glacier mass changes at monthly resolution by measuring changes in Earth’s gravitational field after correcting for solid Earth and hydrological effects30,31. Although satellite gravimetry provides high temporal resolution and direct estimates of mass, it has a spatial resolution of a few hundred kilometres, which is several orders of magnitude lower than DEM differencing or altimetry26.
The heterogeneity of these observation methods in terms of spatial, temporal and observational characteristics, the diversity of approaches within a given method, and the lack of homogenization challenged past assessments of glacier mass changes. In the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6)16, for example, glacier mass changes for the period from 2000 to 2019 relied on DEM differencing from a limited number of global27 and regional studies16. Results from a combination of glaciological and DEM differencing25 as well as from gravimetry30 were used for comparison only. The report calculated regional estimates over a specific baseline period (2000–2019) and as mean mass-change rates based on selected studies per region, which only partly considered the strengths and limitations of the different observation methods.
The spread of reported results—many outside uncertainty margins—and recent updates from different observation methods afford an opportunity to assess regional and global glacier mass loss with a community-led effort. Within the Glacier Mass Balance Intercomparison Exercise (GlaMBIE; https://glambie.org), we collected, homogenized and combined regional results from the observation methods described above to yield a global assessment towards the upcoming IPCC reports of the seventh assessment cycle. At the same time, GlaMBIE provides insights into regional trends and interannual variabilities, quantifies the differences among observation methods, tracks observations within the range of projections, and delivers a refined observational baseline for future impact and modelling studies.