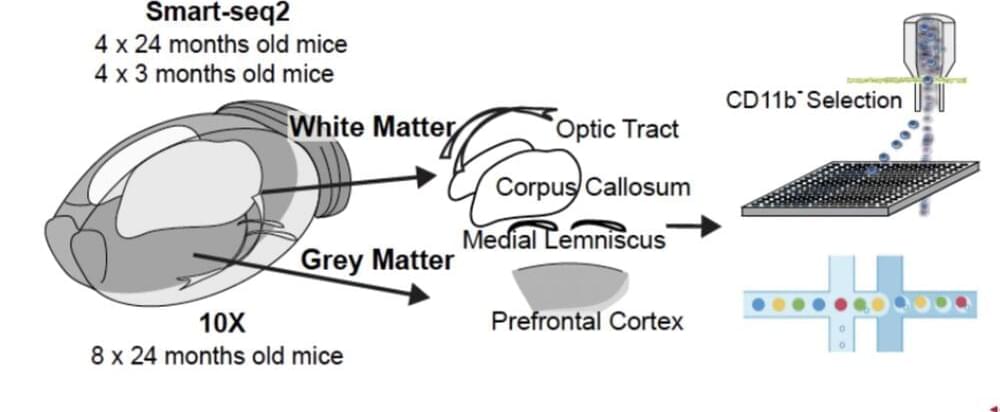
Past neuroscience studies have consistently demonstrated that the aging of the mammalian nervous system is liked with a decline in the volume and functioning of white matter, nerve fibers found in deep brain tissues. Although this is now a well-established finding, the mechanisms underpinning the decline of white matter and associated pathologies are poorly understood.
Researchers at Ludwig Maximilian University (LMU) of Munich, Technical University of Munich, the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases, Munich Cluster of Systems Neurology and University Hospital Würzburg have recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding the neural mechanisms that might result in the deterioration of white matter. Their findings, published in Nature Neuroscience, suggest that adaptive immune responses could promote the loss of cells in aging white matter.
“Among the hallmarks of brain aging is a decline in white matter volume and function which leads to an increase in neurological disorders,” Mikael Simons and Özgün Gökce, two of the researchers who carried out the study, told Medical Xpress. “White matter contains nerve fibers (axons), which are extensions of nerve cells (neurons). Many of these nerve fibers are surrounded by a type of sheath or covering called myelin, which allows our neurons to communicate fast, and gives white matter its color.”