A pioneering Large Language Model for Law https://huggingface.co/papers/2403.
In this paper, we introduce SaulLM-7B, a large language model (LLM) tailored for the legal domain.
Join the discussion on this paper page.
A pioneering Large Language Model for Law https://huggingface.co/papers/2403.
In this paper, we introduce SaulLM-7B, a large language model (LLM) tailored for the legal domain.
Join the discussion on this paper page.

A Michigan state senator introduced a bill that would require health insurance companies in the state to cover cutting-edge cancer treatments, even if they are not categorized as a “cancer drug.”
State Sen. Jeff Irwin (D-Mich.) announced his new bill in a video on X, formerly Twitter, on Tuesday. The legislation would build on an existing law that already says cancer drugs must be covered by health insurance companies.

Nothing of the mind is foreign to David Eagleman, neuroscientist, technologist, entrepreneur and one of the most interesting scientific writers of our time. Born in New Mexico 52 years ago, he now researches cerebral plasticity, synesthesia, perception of time and what he called neurolaw, the intersection of the brain’s knowledge and its legal implications. His 2011 book Incognito: The Secret Lives of the Brain has been translated into 28 languages, and he returned to publishing with Livewired: The Inside Story of the Ever-Changing Brain, which focuses on a fundamental idea for today’s neuroscience: that the brain is constantly changing to be able to adapt to experience and learning. The science he brings to us isn’t merely top-notch, but firsthand, and his brilliant, crystal-clear writing — a perfect reflection of his mind — turns one of the most complex subjects of modern-day research into food for thought for the interested reader. We spoke with him in California by videoconference, the first interview that he’s given to a Spanish publication in a decade.
Could a newborn brain learn to live in a five-dimensional word? “We don’t actually know which things are pre-programmed and how much is experiential in our brains,” he replies. “If you could raise a baby in a five-dimensional world, which, of course, is unethical to do as an experiment, you might find that it’s perfectly able to function in that world. The general story of brain plasticity is that everything is more surprising than we thought, in terms of the brain’s ability to learn whatever world it drops into.”
Eagleman pulls out a sizable bowl of salad from somewhere, scoops a forkful into his mouth and continues his argument: “The five-dimensional world is hypothetical, but what we do see, of course, is that babies dropping into very different cultures around the planet, whether that’s a hyper-religious culture or an atheist culture, whether it’s a culture that lives on agriculture or a culture that is super technically advanced like here in Silicon Valley, the brain has no problem adjusting. My kids, when they were very young, could operate an iPad or cell phone just as easily as somebody growing up in a different place would operate farming equipment. So, we do know that brains are extremely flexible.”

Elon Musk is suing OpenAI and Sam Altman for allegedly abandoning OpenAI’s original mission to develop artificial intelligence to benefit humanity.
“OpenAI, Inc. has been transformed into a closed-source de facto subsidiary of the largest technology company in the world: Microsoft,” Musk’s lawyers wrote in the lawsuit, which was filed late on Thursday in San Francisco.
“Under its new board, it is not just developing but is refining an AGI [Artificial General Intelligence] to maximize profits for Microsoft, rather than for the benefit of humanity,” claims the filing. “On information and belief, GPT-4 is an AGI algorithm.”

While trying to slim down a bit for her wedding day, one woman decided to take gray market semaglutide — and it landed her in the emergency room.
That woman, whom Healthline refers to as Amy Jenson to protect her privacy in its report, learned she was nearing prediabetic levels of the hemoglobin A1C at a visit to her naturopathic doctor. The naturopath suggested Jenson try semaglutide, the active ingredient in the Ozempic and Wegovy injectables, to help reach her goal weight and head off full-blown diabetes.
She purchased some semaglutide with B12 shots, which are often sold together in injectable forms from online and in-person pharmacies that operate in a legal grey area, from a compounding facility. She was initially prescribed a low dose that increased by small increments each month.
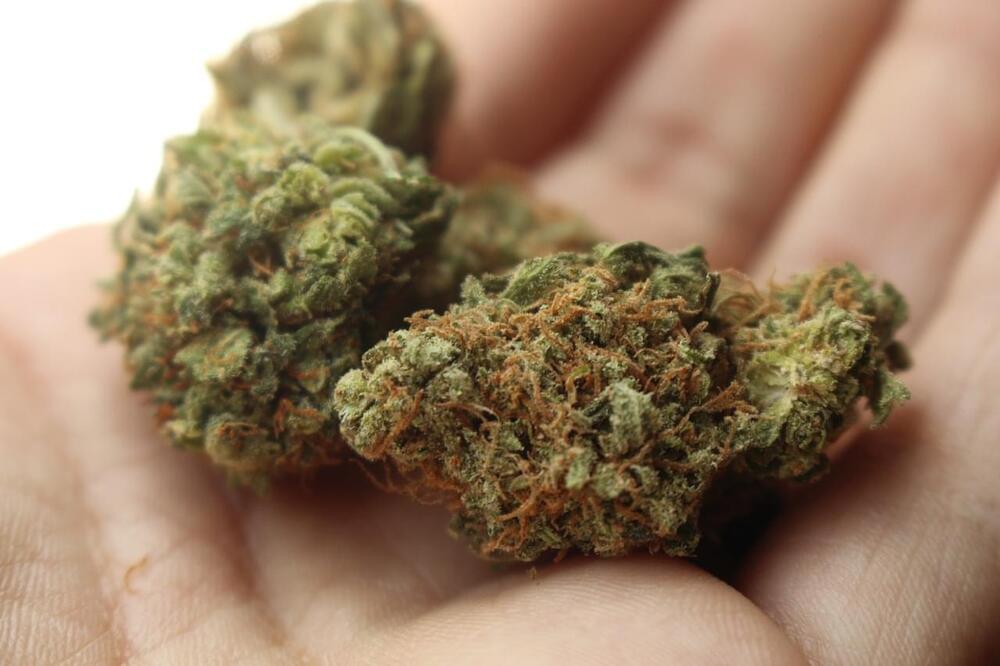

“Cannabis use is increasing in both prevalence and frequency, while conventional tobacco smoking is declining,” said Salomeh Keyhani, MD, MPH. “Cannabis use by itself might, over time, become the more important risk factor.”
Can smoking cannabis bring the same risk of heart attack and stroke as smoking cigarettes? This is what a recent study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association hopes to address as a team of researchers from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) investigated the likelihood that cannabis use would lead to a heart attack and/or stroke. This study comes as recreational cannabis use is slowly becoming legal across the United States and holds the potential to help researchers, medical professionals, legislators, and the public better understand the long-term health risks associated with cannabis use, specifically smoking cannabis.
For the study, the team compared data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance Survey between 2016 and 2020 across 27 American states and 2 territories and 434,104 survey participants between ages 18 and 74 to ascertain a link between their cannabis use and likelihood for heart problems. The team classified cannabis use as the number of times a participant smoked cannabis within a previous 30 days while accounting for self-reported heart issues and tobacco use, as well.
In the end, the team found that 4 percent of participants use cannabis daily while 7.1 percent did not. When combined with the self-reported heart issues of the daily cannabis users, the team found this group exhibited a 25 percent chance of having a heart attack and a 42 percent chance of having a stroke.

Elon Musk claims OpenAI is using GPT-4 to ‘maximize profits’ instead of ‘for the benefit of humanity.’
The lawsuit claims that the GPT-4 model OpenAI released in March 2023 isn’t just capable of reasoning but is also actually “better at reasoning than average humans,” having scored in the 90th percentile on the Uniform Bar Examination for lawyers. The company is rumored to be developing a more advanced model, known as “Q Star,” that has a stronger claim to being true artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Altman was fired (and subsequently rehired five days later) by OpenAI in 2023 over vague claims that his communication with the board was “hindering its ability to exercise its responsibilities.” The lawsuit filed by Musk alleges that in the days following this event, Altman, Brockman, and Microsoft “exploited Microsoft’s significant leverage over OpenAI” to replace board members with handpicked alternatives that were better approved of by Microsoft.
“The new Board members lack substantial AI expertise and, on information and belief, are ill equipped by design to make an independent determination of whether and when OpenAI has attained AGI — and hence when it has developed an algorithm that is outside the scope of Microsoft’s license,” claims the lawsuit. The partnership between OpenAI and Microsoft is currently being examined by regulators in the UK, EU, and US to assess if their shared relationship impacts competition.

Interestingly enough, although Elon Musk’s Neuralink received a great deal of media attention, early in 2023, Synchron published results from its first-in-human study of four patients with severe paralysis who received its first-generation Stentrode neuroprosthesis implant. The implant allowed participants to create digital switches that controlled daily tasks like sending texts and emails, partaking in online banking, and communicating care needs. The study’s findings were published in a paper in JAMA Neurology in January 2023. Then, before September, the first six US patients had the Synchron BCI implanted. The study’s findings are expected by late 2024.
Let’s return to Upgrade. “One part The Six Million Dollar Man, one part Death Wish revenge fantasy” was how critics described the movie. While Death Wish is a 1974 American vigilante action-thriller movie that is partially based on Brian Garfield’s 1972 novel of the same name, the American sci-fi television series The Six Million Dollar Man from the 1970s, based on Martin Caidin’s 1972 novel Cyborg, could be considered a landmark in the context of human-AI symbiosis, although in fantasy’s domain. Oscar Goldman’s opening line in The Six Million Dollar Man was, “Gentlemen, we can rebuild him. We have the technology. We have the capability to make the world’s first bionic man… Better than he was before. Better—stronger—faster.” The term “cyborg” is a portmanteau of the words “cybernetic” and “organism,” which was coined in 1960 by two scientists, Manfred Clynes and Nathan S Kline.
At the moment, “cyborg” doesn’t seem to be a narrative of a distant future, though. Rather, it’s very much a story of today. We are just inches away from becoming cyborgs, perhaps, thanks to the brain chip implants, although Elon Musk perceives that “we are already a cyborg to some degree,” and he may be right. Cyborgs, however, pose a threat, while the dystopian idea of being ruled by Big Brother also haunts. Around the world, chip implants have already sparked heated discussions on a variety of topics, including privacy, the law, technology, medicine, security, politics, and religion. USA Today published a piece headlined “You will get chipped—eventually” as early as August 2017. And an article published in The Atlantic in September 2018 discussed how (not only brain chips but) microchip implants, in general, are evolving from a tech-geek curiosity to a legitimate health utility and that there may not be as many reasons to say “no.” But numerous concerns about privacy and cybersecurity would keep us haunted. It would be extremely difficult for policymakers to formulate laws pertaining to such sensitive yet quickly developing technology.

The lawsuit said Altman, along with OpenAI’s co-founder Greg Brockman, originally approached Musk to make an open source, non-profit company that would develop artificial intelligence technology for the “benefit of humanity”
The Microsoft-backed company’s focus on seeking profits breaks that agreement, lawyers for Musk said in the lawsuit.
OpenAI, Microsoft and Musk did not immediately respond to Reuters requests for comment.

OpenAI is accusing the New York Times of “hacking” its products in the ongoing copyright dispute.
In a legal filing, OpenAI claims that an individual paid by the Times used “deceptive prompts” to create copies of NYT articles. These prompts would violate OpenAI’s terms of service.
The NYT demonstrated that OpenAI’s GPT models could generate copies of NYT articles when it filed a lawsuit against OpenAI for copyright infringement.