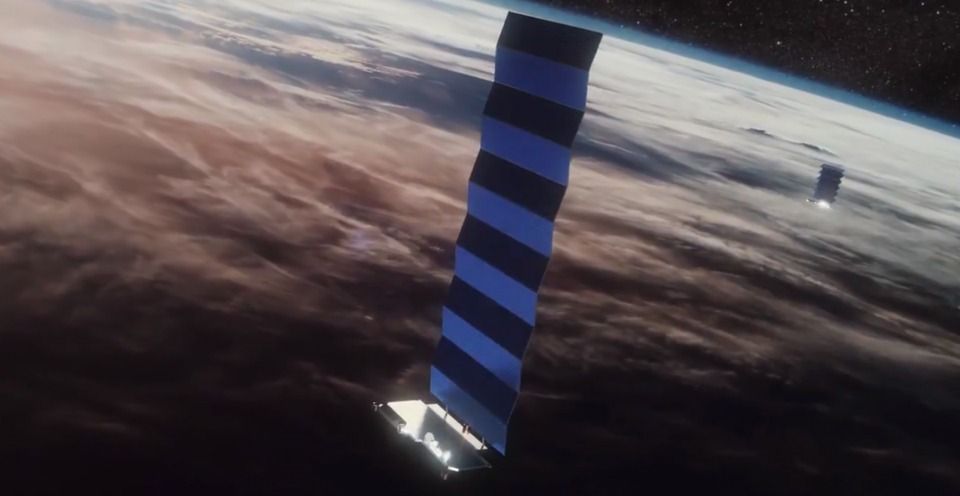
SpaceX has said it is taking measures to tackle some of the concerns raised by astronomers about its Starlink constellation, as it gears up to launch more than a thousand satellites in the next 12 months.
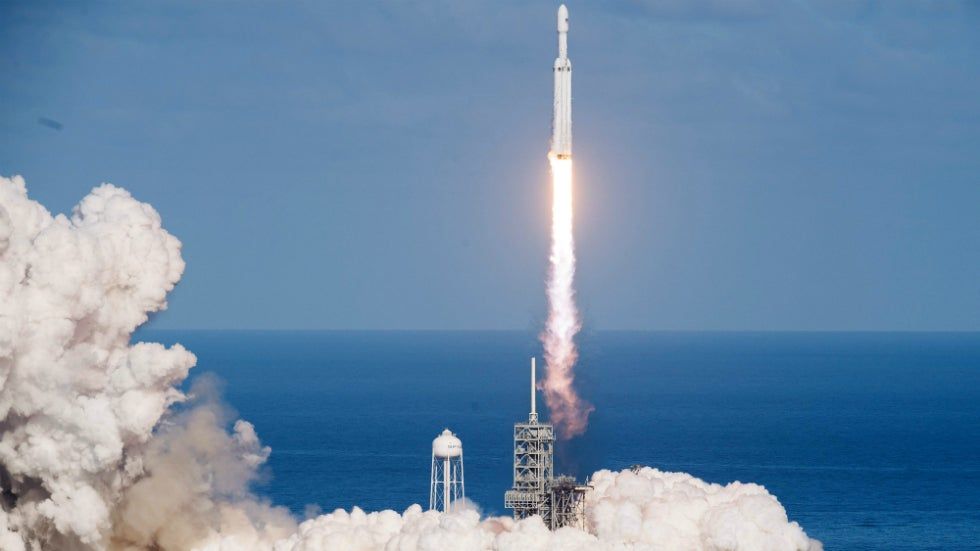
The company’s Starlink mega constellation, which will add up to 42,000 satellites to orbit (only 2,000 active satellites in total orbit Earth today) to beam high-speed internet around the globe, has been taking shape in 2019. The company launched its first 60 satellites in May, followed by a second launch in November.
A third launch is planned in late December, and a fourth in January – with 24 in total planned by the end of 2020. The company hopes to launch 60 Starlink satellites roughly once every two weeks, adding more than 1,500 satellites to orbit by the end of next year alone.