Meta’s push to put computing into a headset will end in tears.


After spending two years on the ocean’s floor, Microsoft’s underwater data center had a much lower server failure rate than land-based data centers.
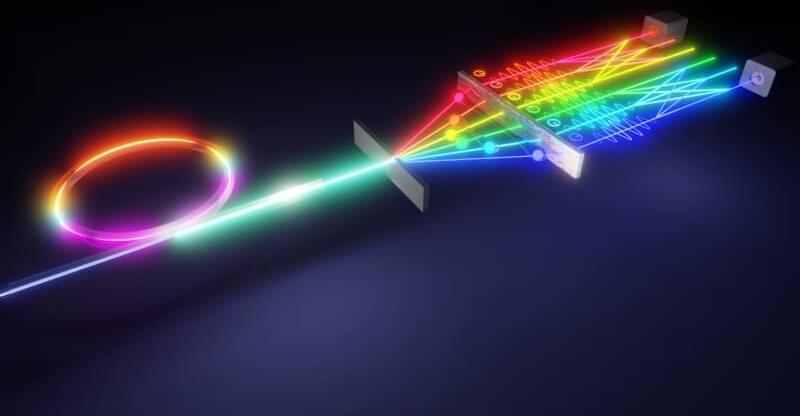
Using existing experimental and computational resources, a multi-institutional team has developed an effective method for measuring high-dimensional qudits encoded in quantum frequency combs, which are a type of photon source, on a single optical chip.
Although the word “qudit” might look like a typo, this lesser-known cousin of the qubit, or quantum bit, can carry more information and is more resistant to noise—both of which are key qualities needed to improve the performance of quantum networks, quantum key distribution systems and, eventually, the quantum internet.
Classical computer bits categorize data as ones or zeroes, whereas qubits can hold values of one, zero or both—simultaneously—owing to superposition, which is a phenomenon that allows multiple quantum states to exist at the same time. The “d” in qudit stands for the number of different levels or values that can be encoded on a photon. Traditional qubits have two levels, but adding more levels transforms them into qudits.
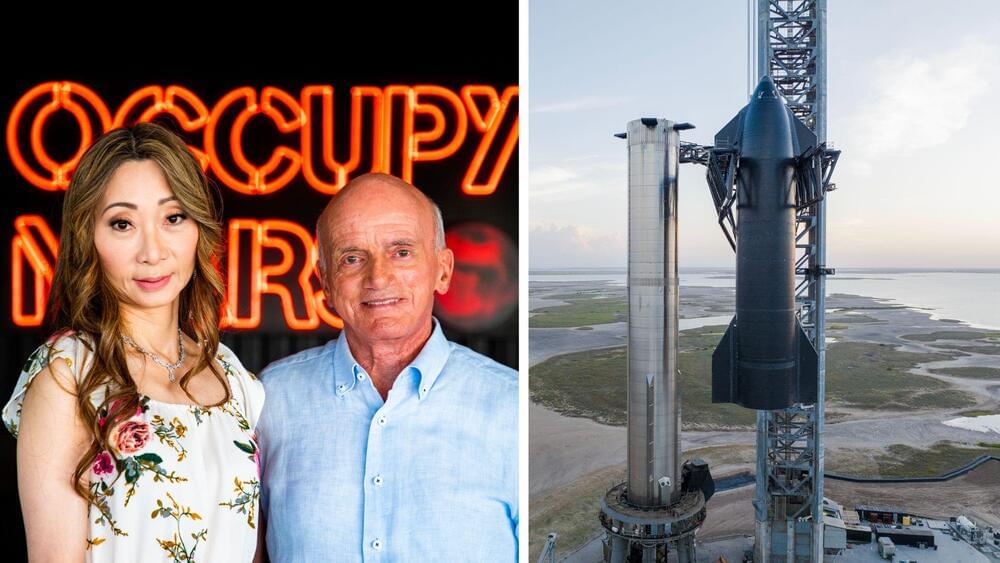

Starship could launch to orbit for the first time next month.
Entrepreneur Dennis Tito was the first-ever space tourist when he paid to fly aboard a Russian Soyuz rocket to the International Space Station (ISS) back in 2001.
Those missions will be a precursor to Starship’s eventual crewed missions to Mars, which will be partly funded by SpaceX’s space tourism launches and its Starlink internet service.
1, 2
Now, SpaceX has announced Dennis Tito and his wife Akiko is “the first two crewmembers on Starship’s second commercial spaceflight around the Moon.”

Though available only to select customers, this reaffirms faith in the blockchain method of payments.
Technology major Google has teamed up with cryptocurrency exchange platform Coinbase as it looks to allow cryptocurrency payments for its cloud services. According to a press release, the two entities will leverage their strengths towards building the next iteration of the internet, dubbed Web3.
400tmax/iStock.
Web3 is the vision for the world wide web, where the ownership of platforms is also decentralized. This is expected to happen through the use of blockchain technology, the one that also powers cryptocurrencies and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Tech leaders such as Elon Musk and Jack Dorsey have been claiming that the advent of this version of the internet is inevitable, and Google’s recent move may be a sign of Big Tech companies warming up to the idea.

“All bets are off if the nukes start flying,” Musk recently tweeted.
Elon Musk reportedly rejected a request from within Ukraine to extend SpaceX’s Starlink satellite internet coverage to Crimea, according to a newsletter from political analyst Ian Bremmer.
However, Musk has taken to Twitter after those reports were published and has cast doubt on their veracity by claiming that “nobody should trust Bremmer”.
Source: 1, 2
According to the newsletter, first reported by Vice, Musk also directly spoke to Russian President Vladimir Putin about the potential for nuclear escalation in relation to Crimea.

Nadla/iStock.
“ESnet6 represents a transformational change in the way networks are built for research, with improved capacity, resiliency, and flexibility,” ESnet executive director Inder Monga said in a press release. “Together, these new capabilities make it faster, easier, and more efficient for scientists around the world to conduct and collaborate on ground-breaking research.”

So at this year’s Connect, which kicks off at 10 AM PT tomorrow with a keynote from Zuckerberg, the stakes feel even higher. And we still have a lot of questions about what it really means to be a “metaverse company.”
It’s perhaps the most obvious issue, but in the nearly a year since Zuckerberg first attempted to articulate what a metaverse is, it’s still not very clear. Last year, Zuckerberg described it as “an embodied internet where you’re in the experience, not just looking at it.” The company’s website currently says the metaverse is “the next evolution in social connection and the successor to the mobile internet.”
But what those words mean to most people is fuzzy at best. “Outside of early adopters and tech-savvy people, there’s still confusion as to what is the metaverse and what we’re going to be doing with it,” says Carolina Milanesi, a consumer analyst with Creative Strategies.


The woman transferred 4.4 million yen after the scammer promised to marry her after returning to Earth.
A 65-year-old Japanese woman was scammed online by a scammer claiming to be a Russian astronaut onboard the International Space Station (ISS), Vice.
With the rise in internet usage, the number of online scams has also increased considerably. At Interesting Engineering, we report the latest crypto-scams so that people do not fall for them in their attempts to connect with the new-age technology.