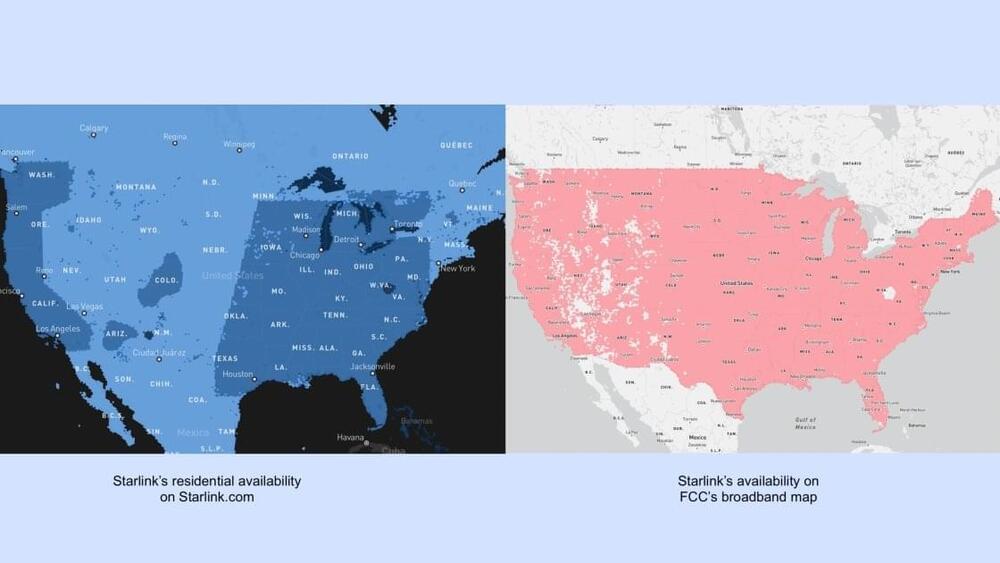
With the rapid development of chatbots and other AI systems, questions about whether they will ever gain true understanding, become conscious, or even develop a feeling agency have become more pressing. When it comes to making sense of these qualities in humans, our ability for counterfactual thinking is key. The existence of alternative worlds where things happen differently, however, is not just an exercise in imagination – it’s a key prediction of quantum mechanics. Perhaps our brains are able to ponder how things could have been because in essence they are quantum computers, accessing information from alternative worlds, argues Tim Palmer.
Ask a chatbot “How many prime numbers are there?” and it will surely tell you that there are an infinite number. Ask the chatbot “How do we know?” and it will reply that there are many ways to show this, the original going back to the mathematician Euclid of ancient Greece. Ask the chatbot to describe Euclid’s proof and it will answer correctly [ii]. [ii.
Of course, the chatbot has got all this information from the internet. Additional software in the computer can check that each of the steps in Euclid’s proof is valid and hence can confirm that the proof is a good one. But the computer doesn’t understand the proof. Understanding is a kind of Aha! moment, when you see why the proof works, and why it wouldn’t work if a minor element in it was different (for example the proof in the footnotes doesn’t work if any number but 1 is added when creating the number Q). Chatbots don’t have Aha! moments, but we do. Why?