Chinese AI startup DeepSeek, known for challenging leading AI vendors with its innovative open-source technologies, today released a new ultra-large model: DeepSeek-V3.


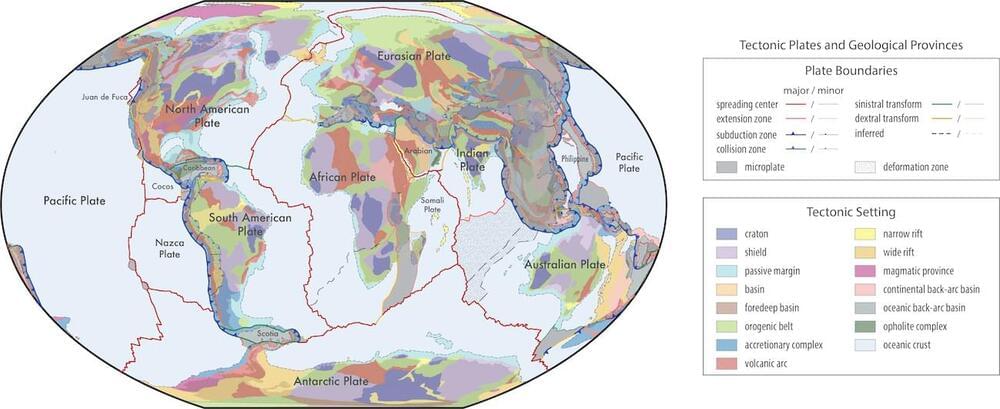
These models are poised to become a standard for classifying geological data across various databases. The models are freely available and open-source, allowing for continual updates and improvements from the geoscience community. This initiative fosters an adaptable and interactive environment, crucial for enhancing our understanding of Earth’s geological history, especially the Mesoproterozoic era and older periods.
A significant innovation is the transition from traditional raster maps to vector format shapefiles. This shift allows for seamless integration of geological data, offering a more nuanced understanding of Earth’s geological fabric. The vector format ensures that each polygon, line, or point can possess multiple unique attributes, enabling a detailed and multidimensional representation of geological features.
In essence, the work paves the way for more precise and comprehensive geological and tectonic models. This is a crucial step towards better predicting and understanding the Earth’s future.

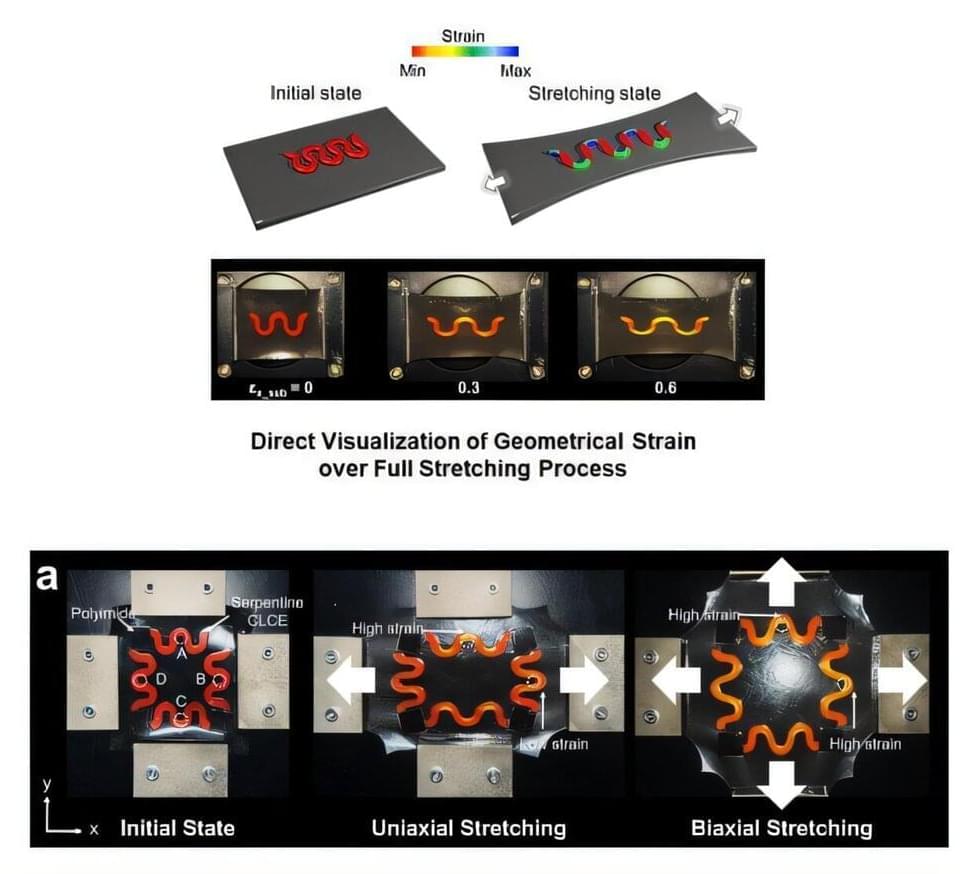
The world of artificial intelligence (AI) has made remarkable strides in recent years, particularly in understanding human language. At the heart of this revolution is the Transformer model, a core innovation that allows large language models (LLMs) to process and understand language with an efficiency that previous models could only dream of. But how do Transformers work? To explain this, let’s take a journey through their inner workings, using stories and analogies to make the complex concepts easier to grasp.

The direct fusion drive could cut travel to Saturn’s moon Titan to just 2 years. Here is some key information for you to watch before deciding to read the whole article. Thanks for visiting us!
Fusion Power for Fast Space Travel
Scientists at Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) are developing a groundbreaking propulsion system called the Direct Fusion Drive (DFD) that could drastically cut down travel time to distant planets. Using this innovative technology, spacecraft could reach Saturn’s moon Titan in just two years, compared to the many years it currently takes. Titan, with its hydrocarbon-rich surface, holds significant scientific interest and may even serve as a future refueling stop for interplanetary missions.
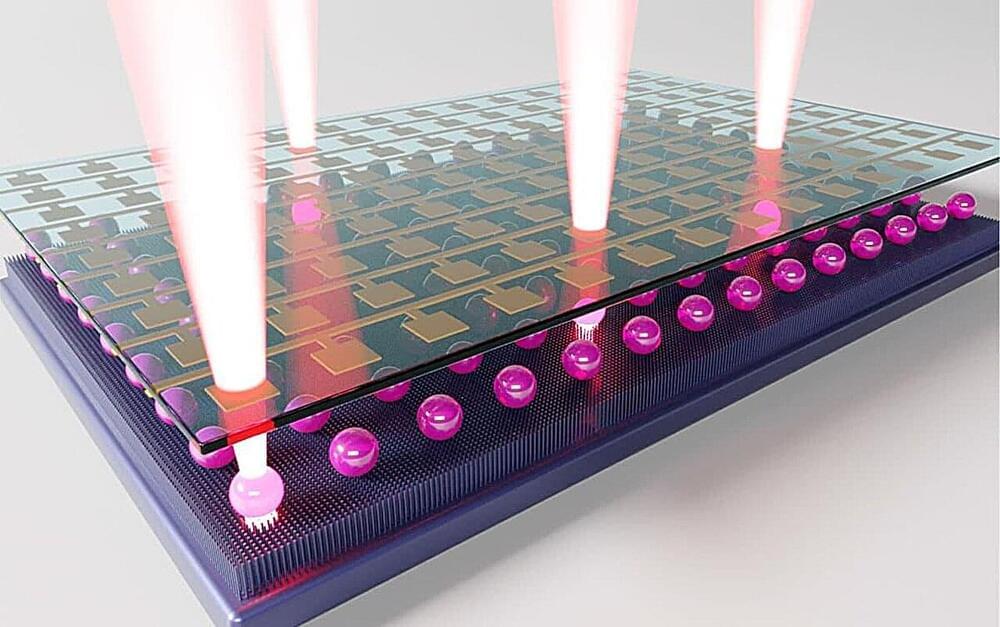
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba have developed an innovative method for rapidly creating laser light sources in large quantities using an inkjet printer that ejects laser-emitting droplets.
By applying an electric field to these droplets, the researchers demonstrated that switching the emission of light on and off is possible. Furthermore, they successfully created a compact laser display by arranging these droplets on a circuit board.
The study is published in Advanced Materials.
The 2024 solar eclipse across North America spurred numerous NASA-supported research projects that observed the eclipse’s impact on the sun’s corona, Earth’s atmosphere, and radio communications.
Significant data were gathered from ground-based telescopes, aircraft, amateur radio transmissions, and student-launched high-altitude balloons.
Sweeping solar eclipse across north america.