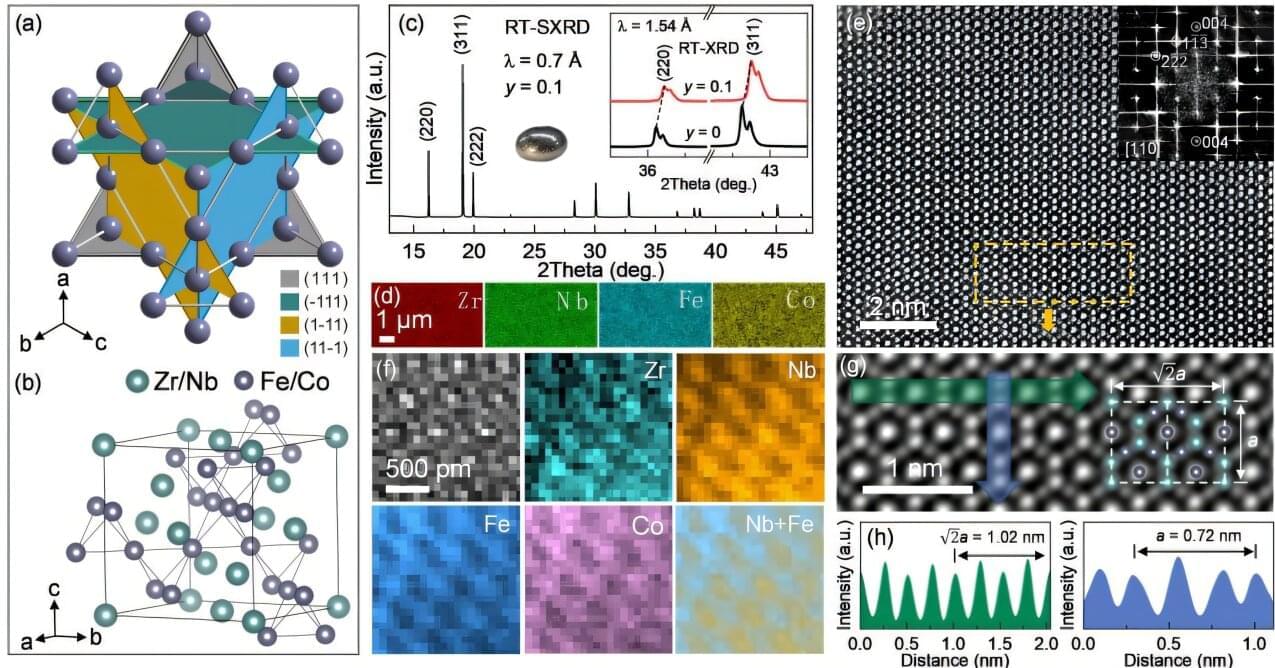
The work garnered impressive results. The enhanced electrolyte had an 84.3% energy retention rate after 700 charge/discharge cycles. Traditional versions typically produce a 37.1% retention rate after 300 cycles, all according to the summary.
The Pohang team is not alone in its impressive battery innovations. Plenty of them are happening in Korea. A pack that can extinguish its own fires is being developed by a team at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, as another example.