Research can seem bland to us laypersons. But, Marko Vukolić shares many of my research interests and he exceeds my academic credentials (with just enough overlap for me to understand his work). So, in my opinion, his writing is anything but bland…
Vukolić started his career as a post-doc intern at IBM in Zurich Switzerland. After a teaching stint as assistant professor at Eurecom and visiting professor at ETH Zurich, he rejoined the IBM research staff in both cloud computing infrastructure and the Blockchain Group.*
As a researcher and academic, Vukolić is a rising star in consensus-based mechanisms and low latency replicated state machines. At Institut Mines-Télécom in Paris, he wrote papers and participated in research projects on fault tolerance, scalability, cloud computing and distributed trust mechanisms.
Now, at IBM Zurich, Vukolić has published a superior analysis addressing the first and biggest elephant in the Bitcoin ballroom, Each elephant addresses an urgent need:
- Scalability & throughput
- Incentivize (as mining reward withers)
- Grow & diversify governance & geographic influence
- Anonymize transactions to protect privacy
- Recognize & preserve ownership
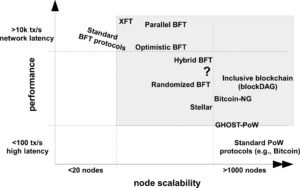 Regarding the first elephant, scalability, Bitcoin urgently needs to grow its Blockchain dynamics into something that is living and manageable. To that end, Vukolić refers to a transaction bookkeeping mechanism that works as a “fabric”. That is, it does not require every miner to access the history-of-the-world and append each transaction onto the same chain in serial fashion. Rather than growing an ever bigger blockchain—with ever bigger computers—we need a more 3D approach that uses relational databases in a multi-threaded, transactional environment, while still preserving the distributed, p2p trust mechanisms of the original blockchain.
Regarding the first elephant, scalability, Bitcoin urgently needs to grow its Blockchain dynamics into something that is living and manageable. To that end, Vukolić refers to a transaction bookkeeping mechanism that works as a “fabric”. That is, it does not require every miner to access the history-of-the-world and append each transaction onto the same chain in serial fashion. Rather than growing an ever bigger blockchain—with ever bigger computers—we need a more 3D approach that uses relational databases in a multi-threaded, transactional environment, while still preserving the distributed, p2p trust mechanisms of the original blockchain.
While clearly technical, it is a good read, even for lay enthusiasts. It directly relates to one of the elephants in the room.
I have pasted Marko’s Abstract below. The full paper is 10½ pages (14 with references).
Bitcoin cryptocurrency demonstrated the utility of global consensus across thousands of nodes, changing the world of digital transactions forever. In the early days of Bitcoin, the performance of its probabilistic proof-of-work (PoW) based consensus fabric, also known as blockchain, was not a major issue. Bitcoin became a success story, despite its consensus latencies on the order of an hour and the theoretical peak throughput of only up to 7 transactions per second.
The situation today is radically different and the poor performance scalability of early PoW blockchains no longer makes sense. Specifically, the trend of modern cryptocurrency platforms, such as Ethereum, is to support execution of arbitrary distributed applications on blockchain fabric, needing much better performance. This approach, however, makes cryptocurrency platforms step away from their original purpose and enter the domain of database-replication protocols, notably, the classical state-machine replication, and in particular its Byzantine fault-tolerant (BFT) variants.
In this paper, we contrast PoW-based blockchains to those based on BFT state machine replication, focusing on their scalability limits. We also discuss recent proposals to overcoming these scalability limits and outline key outstanding open problems in the quest for the “ultimate” blockchain fabric(s). Keywords: Bitcoin, blockchain, Byzantine fault tolerance, consensus, proof-of-work, scalability, state machine replication
* Like Marko, Blockchains, Cloud computing, and Privacy are, also my primary reserach interests, (GMTA!). But, I cede the rigorous, academic credentials to Marko.
† BFT = Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus protocols
Related—and recently in the news:
Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA and The Bitcoin Event. A columnist & board member at Lifeboat Foundation
he edits AWildDuck. He will deliver the keynote address at Digital Currency Summit in Johannesburg.


 problem, punishment schemes and heartbeat transactions. Could Alkan’s distributed consensus mechanism be too complex for the public to understand or use?…
problem, punishment schemes and heartbeat transactions. Could Alkan’s distributed consensus mechanism be too complex for the public to understand or use?…



 Regarding the first elephant, scalability, Bitcoin urgently needs to grow its Blockchain dynamics into something that is living and manageable. To that end, Vukolić refers to a transaction bookkeeping mechanism that works as a “fabric”. That is, it does not require every miner to access the history-of-the-world and append each transaction onto the same chain in serial fashion. Rather than growing an ever bigger blockchain—with ever bigger computers—we need a more 3D approach that uses relational databases in a multi-threaded, transactional environment, while still preserving the distributed, p2p trust mechanisms of the original blockchain.
Regarding the first elephant, scalability, Bitcoin urgently needs to grow its Blockchain dynamics into something that is living and manageable. To that end, Vukolić refers to a transaction bookkeeping mechanism that works as a “fabric”. That is, it does not require every miner to access the history-of-the-world and append each transaction onto the same chain in serial fashion. Rather than growing an ever bigger blockchain—with ever bigger computers—we need a more 3D approach that uses relational databases in a multi-threaded, transactional environment, while still preserving the distributed, p2p trust mechanisms of the original blockchain.