An artificial intelligence algorithm can detect subtle differences in the way people with Alzheimer’s use language.


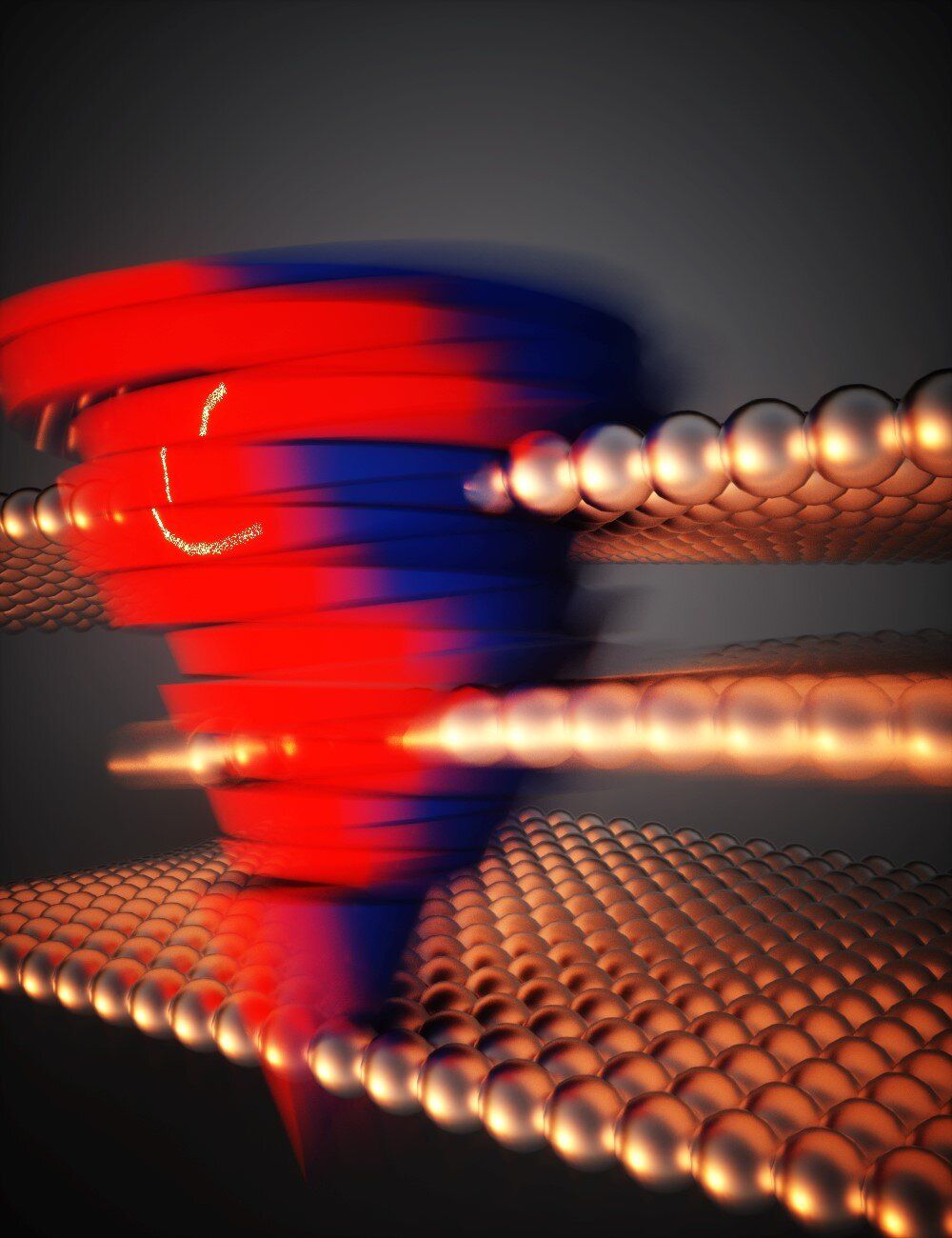
The emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques is changing the world dramatically with novel applications such as internet of things, autonomous vehicles, real-time imaging processing and big data analytics in healthcare. In 2020, the global data volume is estimated to reach 44 Zettabytes, and it will continue to grow beyond the current capacity of computing and storage devices. At the same time, the related electricity consumption will increase 15 times by 2030, swallowing 8% of the global energy demand. Therefore, reducing energy consumption and increasing speed of information storage technology is in urgent need.
Berkeley researchers led by HKU President Professor Xiang Zhang when he was in Berkeley, in collaboration with Professor Aaron Lindenberg’s team at Stanford University, invented a new data storage method: They make odd numbered layers slide relative to even-number layers in tungsten ditelluride, which is only 3nm thick. The arrangement of these atomic layers represents 0 and 1 for data storage. These researchers creatively make use of quantum geometry: Berry curvature, to read information out. Therefore, this material platform works ideally for memory, with independent ‘write’ and ‘read’ operation. The energy consumption using this novel data storage method can be over 100 times less than the traditional method.
This work is a conceptual innovation for non-volatile storage types and can potentially bring technological revolution. For the first time, the researchers prove that two-dimensional semi-metals, going beyond traditional silicon material, can be used for information storage and reading. This work was published in the latest issue of the journal Nature Physics. Compared with the existing non-volatile (NVW) memory, this new material platform is expected to increase storage speed by two orders and decrease energy cost by three orders, and it can greatly facilitate the realization of emerging in-memory computing and neural network computing.
AI has found religion.
Or at least one engineer and quantum researcher has brought a bit of religion to his AI project.
George Davila Durendal fed the entire text of the King James Bible into his algorithms designed to churn out dialogue in the style of the Old Testament.
Durendal claimed his project, AI Jesus, learned and absorbed “every word more thoroughly than all the monks of all the monasteries that have ever been,” offering a little biblical style verse of his own.

Denis Shiryaev uses algorithms to colorize and sharpen old movies, bumping them up to a smooth 60 frames per second. The result is a stunning glimpse at the past.
Abstract: Advances in high speed imaging techniques have opened new possibilities for capturing ultrafast phenomena such as light propagation in air or through media. Capturing light-in-flight in 3-dimensional xyt-space has been reported based on various types of imaging systems, whereas reconstruction of light-in-flight information in the fourth dimension z has been a challenge. We demonstrate the first 4-dimensional light-in-flight imaging based on the observation of a superluminal motion captured by a new time-gated megapixel single-photon avalanche diode camera. A high resolution light-in-flight video is generated with no laser scanning, camera translation, interpolation, nor dark noise subtraction. A machine learning technique is applied to analyze the measured spatio-temporal data set. A theoretical formula is introduced to perform least-square regression, and extra-dimensional information is recovered without prior knowledge. The algorithm relies on the mathematical formulation equivalent to the superluminal motion in astrophysics, which is scaled by a factor of a quadrillionth. The reconstructed light-in-flight trajectory shows a good agreement with the actual geometry of the light path. Our approach could potentially provide novel functionalities to high speed imaging applications such as non-line-of-sight imaging and time-resolved optical tomography.

One of the biggest impediments to adoption of new technologies is trust in AI.
Now, a new tool developed by USC Viterbi Engineering researchers generates automatic indicators if data and predictions generated by AI algorithms are trustworthy. Their research paper, “There Is Hope After All: Quantifying Opinion and Trustworthiness in Neural Networks” by Mingxi Cheng, Shahin Nazarian and Paul Bogdan of the USC Cyber Physical Systems Group, was featured in Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence.
Neural networks are a type of artificial intelligence that are modeled after the brain and generate predictions. But can the predictions these neural networks generate be trusted? One of the key barriers to adoption of self-driving cars is that the vehicles need to act as independent decision-makers on auto-pilot and quickly decipher and recognize objects on the road—whether an object is a speed bump, an inanimate object, a pet or a child—and make decisions on how to act if another vehicle is swerving towards it.
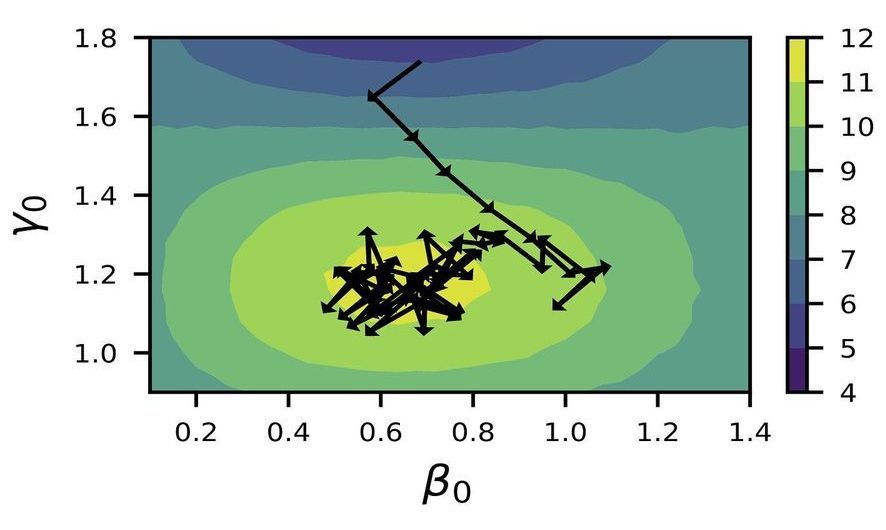
Recent advancements in quantum computing have driven the scientific community’s quest to solve a certain class of complex problems for which quantum computers would be better suited than traditional supercomputers. To improve the efficiency with which quantum computers can solve these problems, scientists are investigating the use of artificial intelligence approaches.
In a new study, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have developed a new algorithm based on reinforcement learning to find the optimal parameters for the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), which allows a quantum computer to solve certain combinatorial problems such as those that arise in materials design, chemistry and wireless communications.
“Combinatorial optimization problems are those for which the solution space gets exponentially larger as you expand the number of decision variables,” said Argonne computer scientist Prasanna Balaprakash. “In one traditional example, you can find the shortest route for a salesman who needs to visit a few cities once by enumerating all possible routes, but given a couple thousand cities, the number of possible routes far exceeds the number of stars in the universe; even the fastest supercomputers cannot find the shortest route in a reasonable time.”
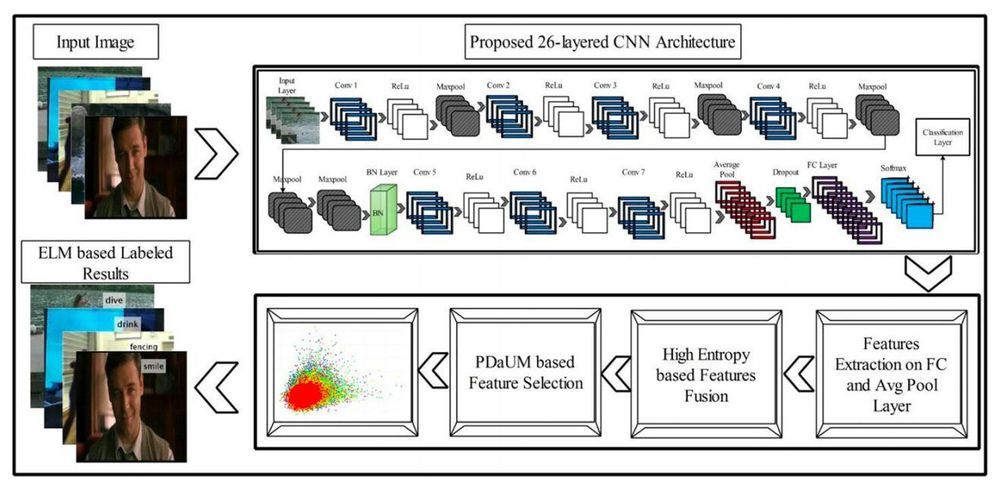
Deep learning algorithms, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have achieved remarkable results on a variety of tasks, including those that involve recognizing specific people or objects in images. A task that computer scientists have often tried to tackle using deep learning is vision-based human action recognition (HAR), which specifically entails recognizing the actions of humans who have been captured in images or videos.
Researchers at HITEC University and Foundation University Islamabad in Pakistan, Sejong University and Chung-Ang University in South Korea, University of Leicester in the UK, and Prince Sultan University in Saudi Arabia have recently developed a new CNN for recognizing human actions in videos. This CNN, presented in a paper published in Springer Link’s Multimedia Tools and Applications journal, was trained to differentiate between several different human actions, including boxing, clapping, waving, jogging, running and walking.
“We designed a new 26-layered convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture for accurate complex action recognition,” the researchers wrote in their paper. “The features are extracted from the global average pooling layer and fully connected (FC) layer and fused by a proposed high entropy-based approach.”

Accurate computational prediction of chemical processes from the quantum mechanical laws that govern them is a tool that can unlock new frontiers in chemistry, improving a wide variety of industries. Unfortunately, the exact solution of quantum chemical equations for all but the smallest systems remains out of reach for modern classical computers, due to the exponential scaling in the number and statistics of quantum variables. However, by using a quantum computer, which by its very nature takes advantage of unique quantum mechanical properties to handle calculations intractable to its classical counterpart, simulations of complex chemical processes can be achieved. While today’s quantum computers are powerful enough for a clear computational advantage at some tasks, it is an open question whether such devices can be used to accelerate our current quantum chemistry simulation techniques.
In “Hartree-Fock on a Superconducting Qubit Quantum Computer”, appearing today in Science, the Google AI Quantum team explores this complex question by performing the largest chemical simulation performed on a quantum computer to date. In our experiment, we used a noise-robust variational quantum eigensolver (VQE) to directly simulate a chemical mechanism via a quantum algorithm. Though the calculation focused on the Hartree-Fock approximation of a real chemical system, it was twice as large as previous chemistry calculations on a quantum computer, and contained ten times as many quantum gate operations. Importantly, we validate that algorithms being developed for currently available quantum computers can achieve the precision required for experimental predictions, revealing pathways towards realistic simulations of quantum chemical systems.