Article (2017) about oxygen depletion. “There has been a clear decline in the volume of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere over the past 20 years. Although the magnitude of this decrease appears small compared to the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere, it is difficult to predict how this process may evolve, due to the brevity of the collected records. A recently proposed model predicts a non-linear decay, which would result in an increasingly rapid fall-off in atmospheric oxygen concentration, with potentially devastating consequences for human health. We discuss the impact that global deoxygenation, over hundreds of generations, might have on human physiology. Exploring the changes between different native high-altitude populations provides a paradigm of how humans might tolerate worsening hypoxia over time. Using this model of atmospheric change, we predict that humans may continue to survive in an unprotected atmosphere for ~3600 years. Accordingly, without dramatic changes to the way in which we interact with our planet, humans may lose their dominance on Earth during the next few millennia.”
There has been a clear decline in the volume of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere over the past 20 years. Although the magnitude of this decrease appears small compared to the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere, it is difficult to predict how this process may evolve, due to the brevity of the collected records. A recently proposed model predicts a non-linear decay, which would result in an increasingly rapid fall-off in atmospheric oxygen concentration, with potentially devastating consequences for human health. We discuss the impact that global deoxygenation, over hundreds of generations, might have on human physiology. Exploring the changes between different native high-altitude populations provides a paradigm of how humans might tolerate worsening hypoxia over time. Using this model of atmospheric change, we predict that humans may continue to survive in an unprotected atmosphere for ~3600 years. Accordingly, without dramatic changes to the way in which we interact with our planet, humans may lose their dominance on Earth during the next few millennia.
Keywords: Oxygen, Hypoxia, Acclimatization, Physiological adaptation.
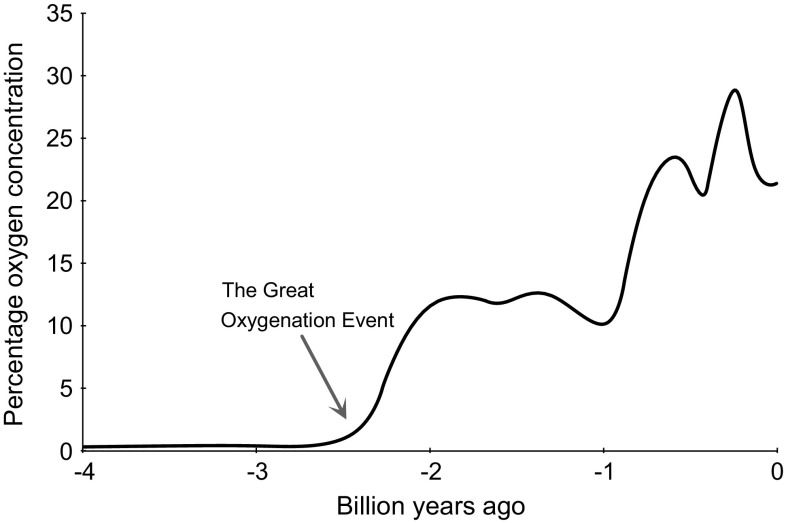
Human dominion over planet Earth is driving profound changes that may culminate in extinction. Loss of natural vegetation and the burning of fossil fuels are altering our atmosphere at an alarming rate [1]. Two interconnected themes have received the most attention: the accelerated rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration and the escalation of global temperatures. These changes are accompanied by natural phenomena with potentially catastrophic consequences, such as increasingly unpredictable climate subsystems and rising sea levels from polar ice cap recession [2–4]. If such environmental hazards were not a sufficient threat to the survival of Earth’s 7 billion plus human inhabitants, there is yet another concerning change already underway, global deoxygenation.