Discover the crucial role of antigen presenting cells (APCs) in immunity. Learn about their types, functions, and importance in health and disease.
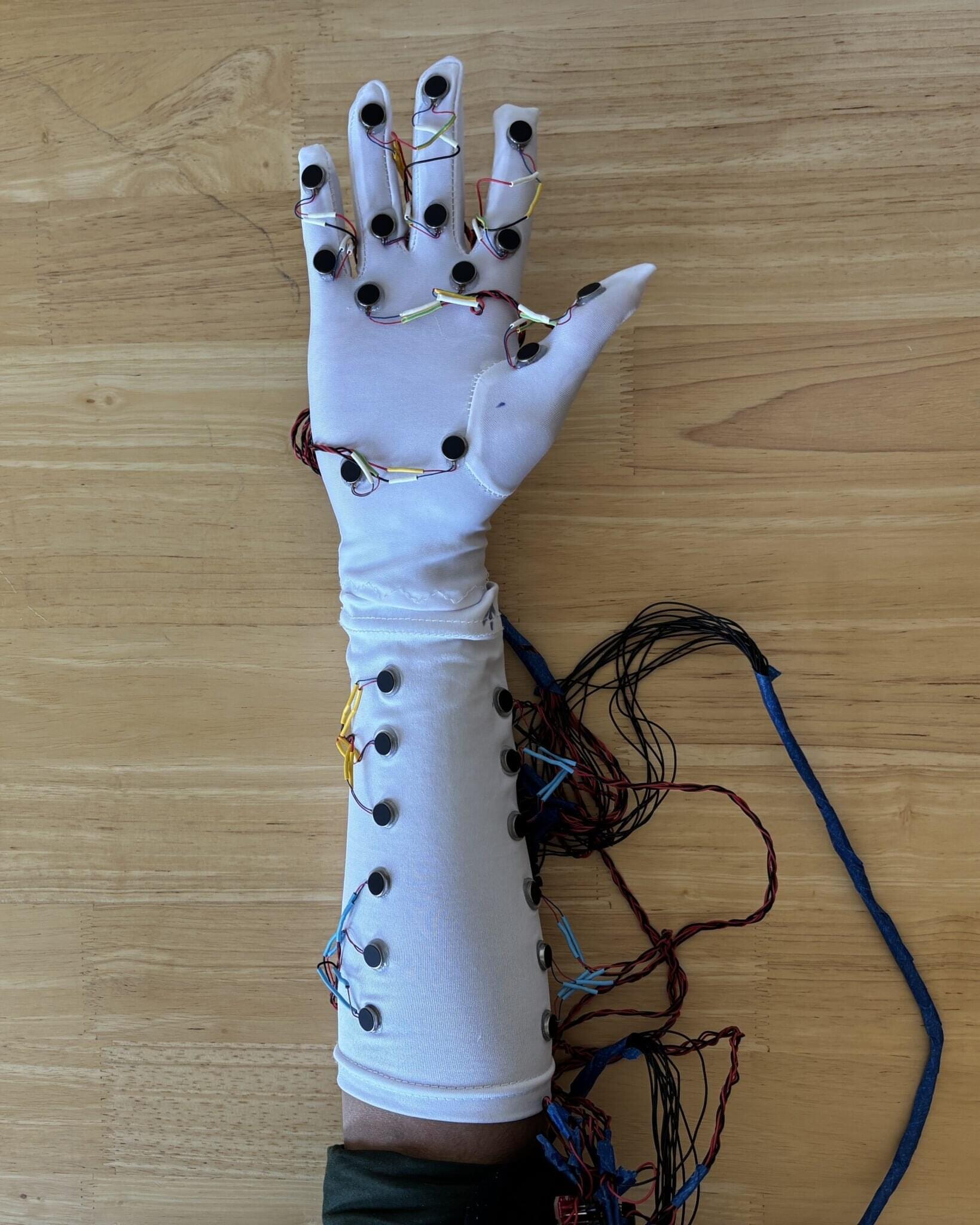


USC scientists have developed a wearable system that enables more natural and emotionally engaging interactions in shared digital spaces, opening new possibilities for remote work, education, health care and beyond.
Touch plays a vital role in how humans communicate and bond. From infancy through adulthood, physical contact helps foster emotional bonds, build trust and regulate stress. Yet in today’s increasingly digital world, where screens mediate many of our relationships, it is often missing.
To bridge the gap, researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering have developed a wearable haptic system that lets users exchange physical gestures in virtual reality and feel them in real time, even when they’re miles apart. Their paper is published on the arXiv preprint server.
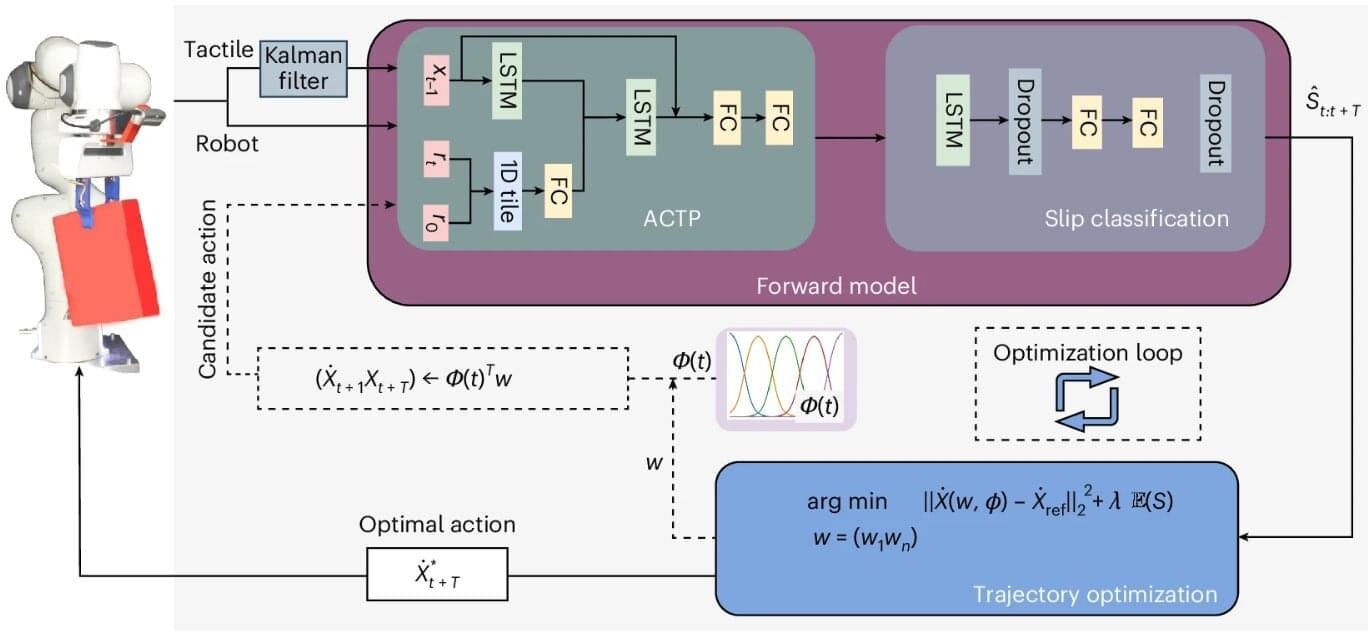
A new slip-prevention method has been shown to improve how robots grip and handle fragile, slippery or asymmetric objects, according to a University of Surrey–led study published in Nature Machine Intelligence. The innovation could pave the way for safer, more reliable automation across industries ranging from manufacturing to health care.
In the study, researchers from Surrey’s School of Computer Science and Electronic Engineering demonstrated how their approach allows robots to predict when an object might slip—and adapt their movements in real-time to prevent it.
Similar to the way humans naturally adjust their motions, this bio-inspired method outperforms traditional grip-force strategies by allowing robots to move more intelligently and maintain a secure hold without simply squeezing harder.
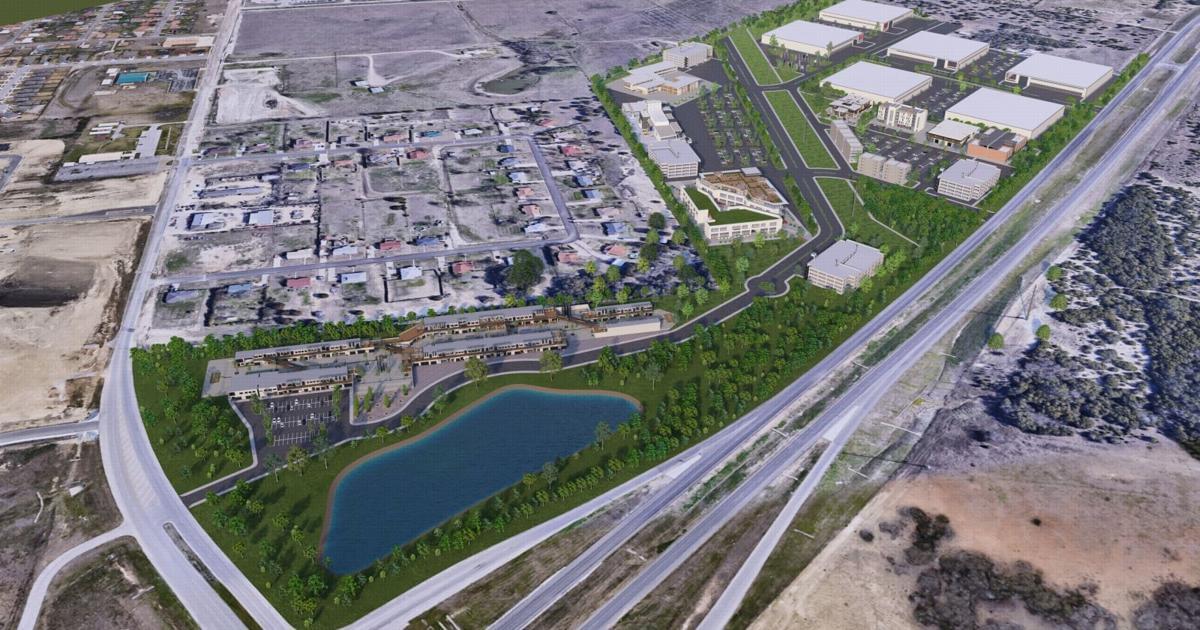

The establishment of a new business park in Killeen is underway.
Wolf Technology Park is set to inhabit 94-acres of real estate located on Texas Highway 195 in south Killeen.
“Wolf Technology Park is a cornerstone of our strategy to attract next-generation employers to Killeen,” Tyler Robert, vice president of the Killeen Economic Development Corporation, said. “With infrastructure investments already in place and sites ready for development, the park is well-positioned to support advanced manufacturing, federal services, health and life sciences, research and development, cybersecurity and semiconductor-related industries.”
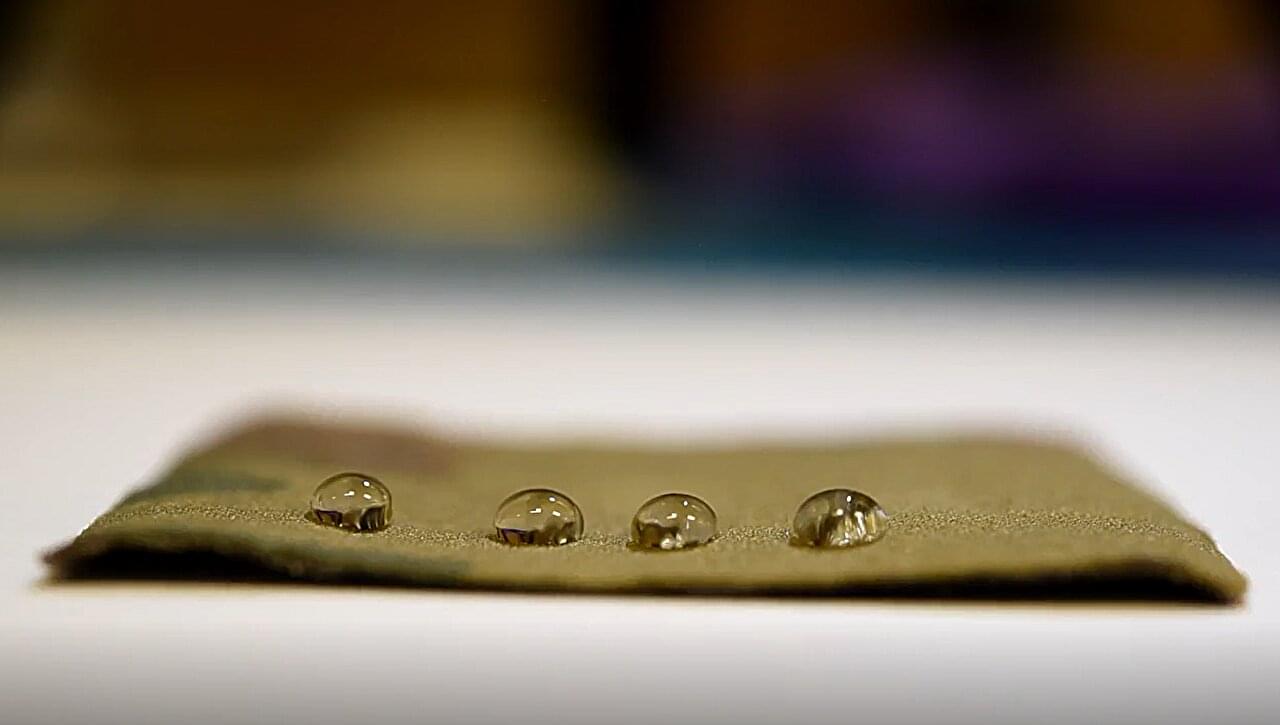

A new material developed by researchers from University of Toronto Engineering could offer a safer alternative to the nonstick chemicals commonly used in cookware and other applications.
The new substance repels both water and grease about as well as standard nonstick coatings—but it contains much lower amounts of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), a family of chemicals that have raised environmental and health concerns.
“The research community has been trying to develop safer alternatives to PFAS for a long time,” says Professor Kevin Golovin, who heads the Durable Repellent Engineered Advanced Materials (DREAM) Laboratory at U of T Engineering.

Copper is an essential trace element for normal development and function throughout the body, including the central nervous system (CNS). Alterations to cellular copper levels result in severe neurological consequences and are linked to a range of CNS disorders, positioning treatments that restore copper balance as promising therapies for these disorders. However, despite the clear relationship between copper balance and CNS health, there are limited tools to measure copper levels in vivo in humans. This constitutes a significant challenge for both diagnosing disorders of copper imbalance and monitoring the efficacy of copper-altering treatments for these disorders. Here we report the synthesis and characterization of Fluorine-labeled Naphthalimide Copper sensor 1 (F-NpCu1), a fluorescent sensor for copper that contains a fluorine atom for future radiolabeling for clinical application. We demonstrate that the probe exhibits good stability and is highly selective for copper above other transition metals present in biological tissues. Copper binding promotes covalent bond formation between the sensor and proximal cellular proteins. F-NpCu1 is nontoxic and can be measured using fluorescence microscopy in living cells and fixed tissue sections from both mouse brain and pancreas. Furthermore, F-NpCu1 exhibits good blood-brain-barrier permeability and can report differences in brain copper levels induced by copper modulating therapies in living mice using intravital fluorescence microscopy. This study represents a promising advance toward the development of the first clinical tool for measuring copper in living humans, including in the CNS, with radiolabeling studies underway to develop 18F-NpCu1 for PET imaging of copper in vivo.
This is a sci-fi documentary looking at the future of genetic engineering and how it applies to space exploration, astronauts, terraforming planets and even Earth.
What is DNA, and how can it be engineered. What is CRISPR, and the future technology used in genetic engineering and biotechnology.
Personal inspiration in creating this video came from: Jurassic Park (the book), and The Expanse TV show (the protomolecule).
Other topics in the video include: how genetic engineering can change food allergies, cryosleep astronauts using hibernation biology borrowed from bears, squirrels and hedgehogs, engineering plants for terraforming other planets, and entries from The Encyclopedia of the Future.
PATREON
The third volume of ‘The Encyclopedia of the Future’ is now available on my Patreon.
Visit my Patreon here: https://www.patreon.com/venturecity.
PFAS have been linked with a range of health issues including decreased fertility, developmental delays in children, and a higher risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular diseases.
Scientists at the University of Cambridge have identified a family of bacterial species, found naturally in the human gut, that absorb various PFAS molecules from their surroundings. When nine of these bacterial species were introduced into the guts of mice to ‘humanise’ the mouse microbiome, the bacteria rapidly accumulated PFAS eaten by the mice — which were then excreted in faeces.
The researchers also found that as the mice were exposed to increasing levels of PFAS, the microbes worked harder, consistently removing the same percentage of the toxic chemicals. Within minutes of exposure, the bacterial species tested soaked up between 25% and 74% of the PFAS.
The results are the first evidence that our gut microbiome could play a helpful role in removing toxic PFAS chemicals from our body — although this has not yet been directly tested in humans.
Scientists have discovered that certain species of microbe found in the human gut can absorb PFAS — the toxic and long-lasting ‘forever chemicals.’ They say boosting these species in our gut microbiome could help protect us from the harmful effects of PFAS.

Brave Software says its privacy-focused browser will block Microsoft’s Windows Recall from capturing screenshots of Brave windows by default to protect users’ privacy.
Windows Recall is an opt-in Windows feature that takes screenshots of active windows every few seconds, analyzes them, and enables Windows 11 users to search for text within the snapshots using natural language. The goal is to make it easy for users to quickly find information about past activities in Windows.
However, the feature has sparked widespread criticism for potentially exposing sensitive data of Windows users, including passwords, emails, health records, and financial information.
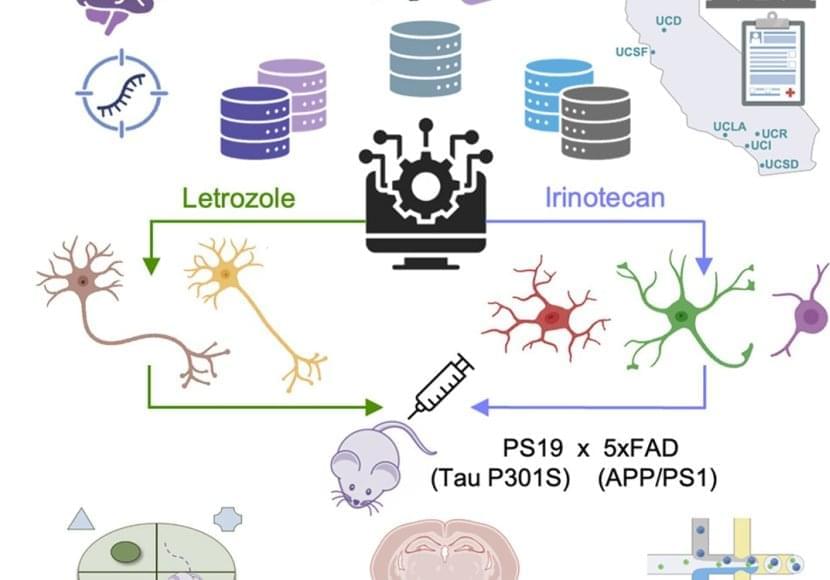
The team took publicly available data from three studies of the Alzheimer’s brain that measured single-cell gene expression in brain cells from deceased donors with or without Alzheimer’s disease. They used this data to produce gene expression signatures for Alzheimer’s disease in neurons and glia.
The researchers compared these signatures with those found in the Connectivity Map, a database of results from testing the effects of thousands of drugs on gene expression in human cells.
Out of 1,300 drugs, 86 reversed the Alzheimer’s disease gene expression signature in one cell type, and 25 reversed the signature in several cell types in the brain. But just 10 had already been approved by the FDA for use in humans.
Poring through records housed in the UC Health Data Warehouse, which includes anonymized health information on 1.4 million people over the age of 65, the group found that several of these drugs seemed to have reduced the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease over time.
“Thanks to all these existing data sources, we went from 1,300 drugs, to 86, to 10, to just 5,” said the lead author of the paper.
The authors chose 2 cancer drugs out of the top 5 drug candidates for laboratory testing. They predicted one drug, letrozole, would remedy Alzheimer’s in neurons; and another, irinotecan, would help glia. Letrozole is usually used to treat breast cancer; irinotecan is usually used to treat colon and lung cancer.
The team used a mouse model of aggressive Alzheimer’s disease with multiple disease-related mutations. As the mice aged, symptoms resembling Alzheimer’s emerged, and they were treated with one or both drugs.