In a new study using AI and machine learning, EPFL researchers have found that it’s not only what we eat, but how consistently we eat it that plays a crucial role in gut health.
The gut microbiota is the community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microbes, that lives in our digestive systems—some of these microbes are helpful and others can be harmful.
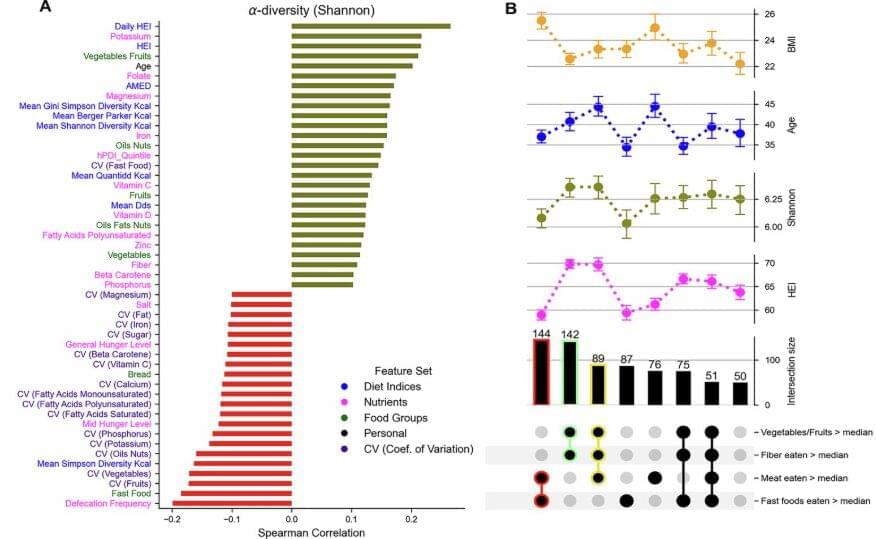
Many previous studies have shown that what we eat has an impact on our gut microbiota. Healthy diets rich in fruit, vegetables, fiber and nuts are strongly associated with increased microbial diversity and better stomach health.