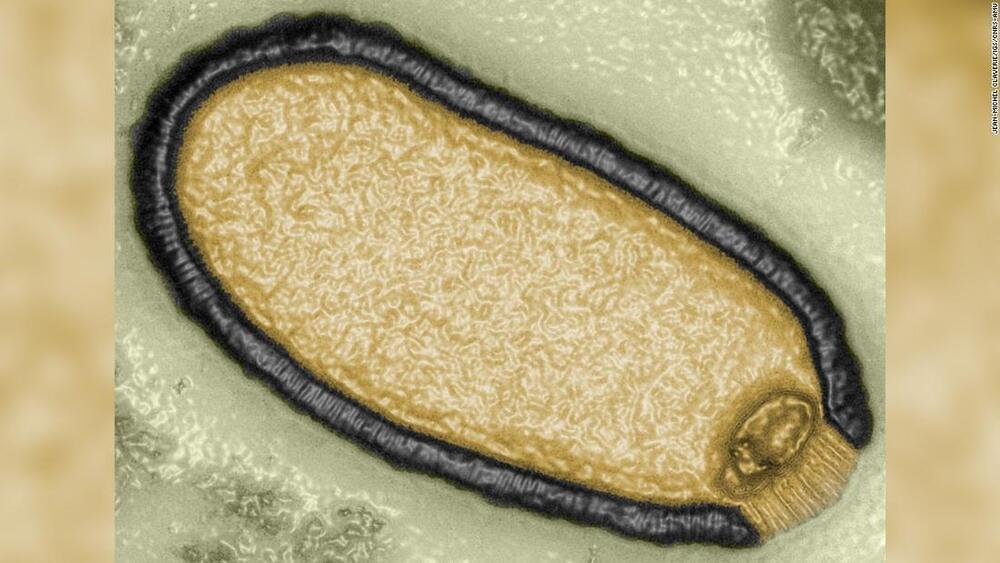
While a pandemic unleashed by a disease from the distant past sounds like the plot of a sci-fi movie, scientists warn that the risks, though low, are underappreciated. Chemical and radioactive waste that dates back to the Cold War, which has the potential to harm wildlife and disrupt ecosystems, may also be released during thaws.
Permafrost covers a fifth of the Northern Hemisphere, having underpinned the Arctic tundra and boreal forests of Alaska, Canada and Russia for millennia. It serves as a kind of time capsule, preserving — in addition to ancient viruses — the mummified remains of a number of extinct animals that scientist have been able to unearth and study in recent years, including two cave lion cubs and a woolly rhino.
Warmer temperatures in the Arctic are thawing the region’s permafrost — a frozen layer of soil beneath the ground — and potentially stirring viruses that, after lying dormant for tens of thousands of years, could endanger animal and human health.
“There’s a lot going on with the permafrost that is of concern, and (it) really shows why it’s super important that we keep as much of the permafrost frozen as possible,” said Kimberley Miner, a climate scientist at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, California.