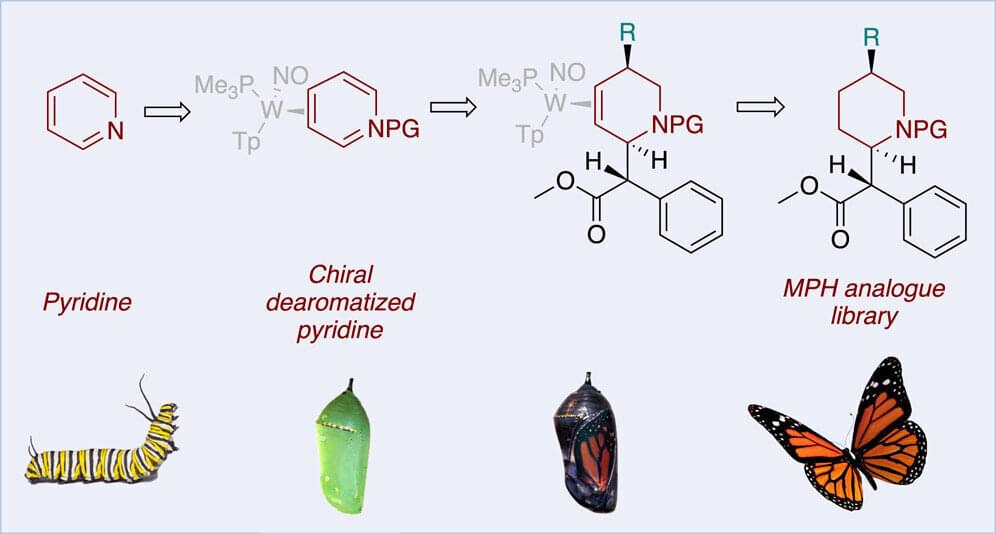
Cocaine use continues to be a public health problem, yet despite concerted efforts, no drugs have been approved to resolve cocaine addiction. Research suggests that the attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder drug methylphenidate (MPH; Ritalin) could serve as a cocaine-replacement therapy, but clinical results have been mixed. Although several labs have produced MPH derivatives for testing, parts of the molecule remained chemically inaccessible. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have cleared that hurdle.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 5 million Americans reported actively using cocaine in 2020, and almost 25,000 Americans died of a cocaine-related overdose in 2021. Although small-molecule drugs have proven effective in treating other drug addictions—for example, methadone as a therapy for heroin abuse—no such medication exists for cocaine abuse.
MPH has been considered a potential treatment because it behaves similarly to the illicit drug, increasing dopamine levels in the brain by blocking dopamine reuptake. Additionally, clinical studies have shown that MPH has a lower risk of abuse than cocaine.