Hmmm; a walk on the bizarre side.
Home / knowledge / world truth / quantum physics proves that death is an illusion.
Hmmm; a walk on the bizarre side.
Home / knowledge / world truth / quantum physics proves that death is an illusion.
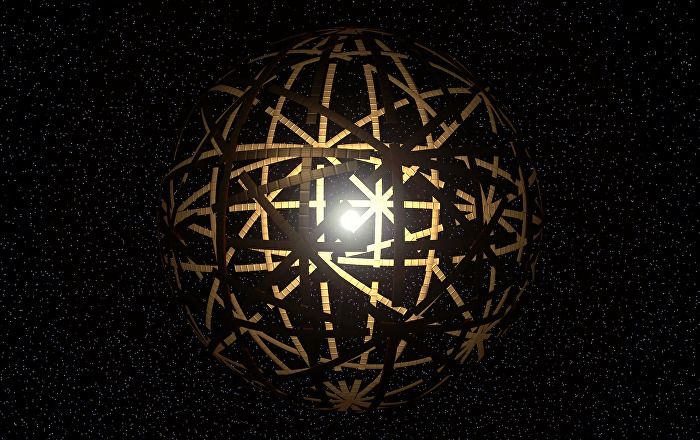

European and American scientists discover a star that may possibly be orbited by alien megastructures.

Realtors are taking home sales beyond glossy pictures and into virtual reality.
Realtors are taking home sales beyond glossy pictures and into virtual reality: http://cnnmon.ie/2bSdIjt
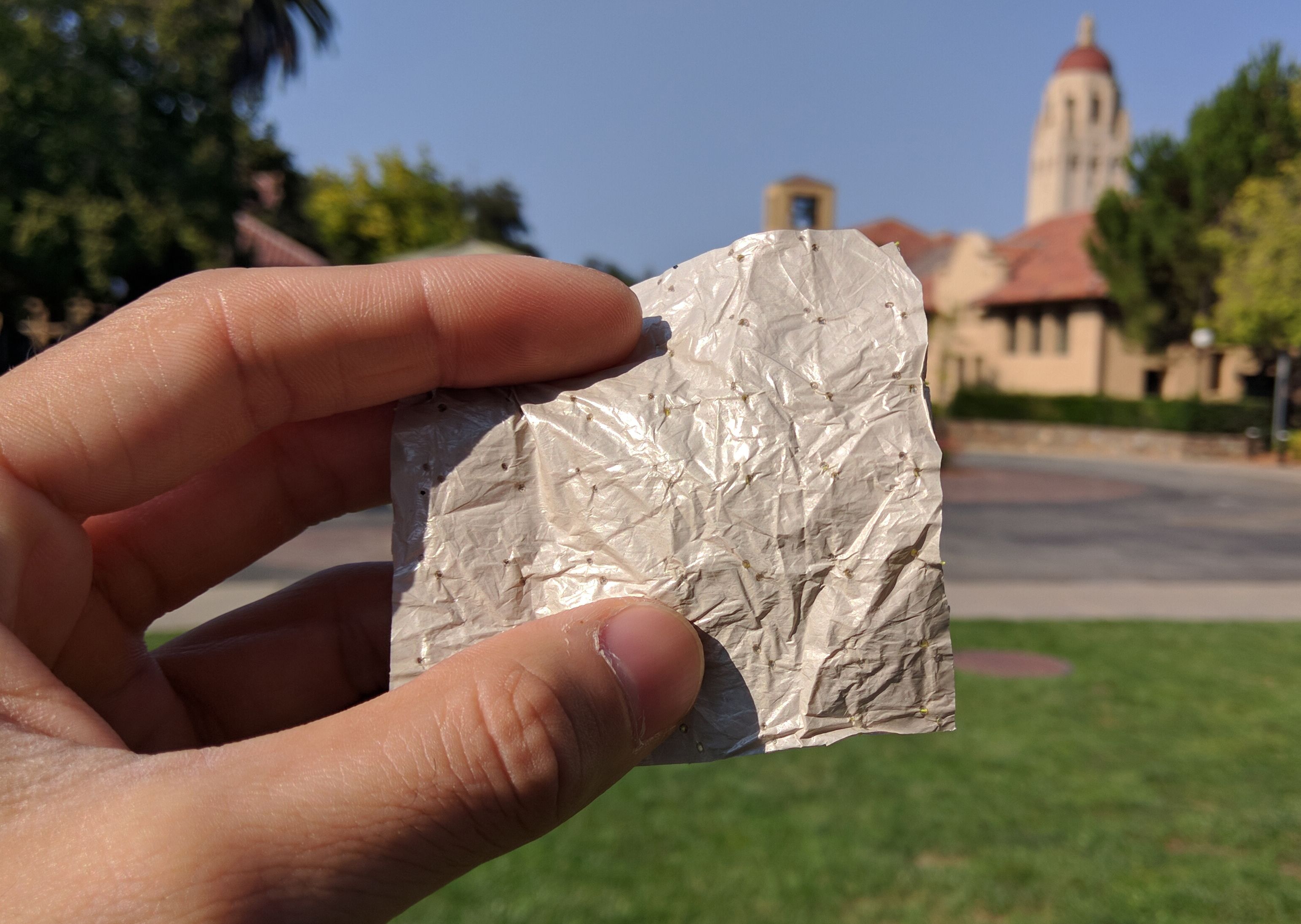

Cannot wait for this material so that I can finally enjoy my run in the park near my US home in August.
WASHINGTON — Engineers have created clothing for a warming world — a fabric that allows your body heat to escape far better than other materials do.
It hasn’t been worn or tested by humans, so outside experts caution this is far from a sure thing, but a team at Stanford University engineered a fabric using nano technology that not only allows moisture to leave the body better, but helps infrared radiation escape better. As a result, they say in Thursday’s journal Science, the body should feel around 4.8 degrees (2.7 degrees Celsius) cooler than cotton and 3.8 degrees (2.1 degrees Celsius) chillier than commercially available synthetics.
This is designed for a warmer world — not just because climate change is making temperatures hotter, but because it takes a lot of energy to heat and cool people’s offices and homes, said study lead author Yi Cui, a professor of materials and engineering.
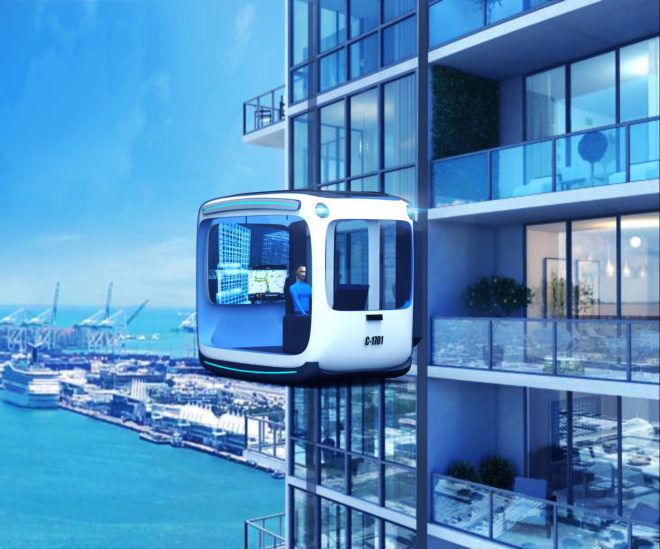

The imminent arrival of the self-driving car will change how people move around city streets, but they could do so much more.
The Tridika is a conceptual driverless electric vehicle I created to change how we use cars in our ever-growing cities, where space is expensive and limited. Inspired by Thyssenkrupp’s Willy Wonka-esque Multi elevator, the Tridika works like a self-driving car you can literally park next to your apartment and use as an additional room.
Did anyone from Lifeboat attend today’s HAARP’s open house in Alaska today?
HAARP, aka the High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program, lives out a quiet existence in the middle of the Alaskan wilderness. But for one reason or another, this ionospheric research facility has become the favorite scratching post for conspiracy theorists – attracting accusations of being a weather-altering superweapon, the force behind chemtrails, and even a mind-control device.
The new management of HAARP – The University of Alaska Fairbanks – aren’t too happy with these claims. So this Saturday, they’re opening its doors and inviting the public to come visit the facility for free. The open house will include facility tours, a mobile planetarium, a permafrost exhibit, science talks, and a barbecue.
“We hope that people will be able to see the actual science of it,” a spokesperson from the University of Alaska, who run HAARP, told Alaska Dispatch News. “We hope to show people that it is not capable of mind control and not capable of weather control and all the other things it’s been accused of.”

Beginning with a twitch in his fingers about six months ago, a Canadian man has successfully re-animated his paralyzed hand after undergoing a nerve transfer surgery.
Tim Raglin regularly dove, headfirst, into the water at his family’s lake house. The 45-year old Canadian man had done so thousands of times without incident. In 2007, though Raglin hit his head on a rock in the shallow water, shattering a vertebra in his cervical spine.
His family pulled him to safety, saving him from drowning. However, for nine years, both his hands and feet were left paralyzed.
Good; glad they are hearing us. Because it is a huge issue for sure especially with some of the things that I seen some of the researchers proposing to use CRISPR, 3D Printers, etc. to create some bizarre creatures. Example, in March to scientists in the UK wanted to use CRISPR to create a dragon; personally I didn’t expect it to be successful. However, the scientists didn’t consider the fallout to the public if they had actually succeeded.
For a few hundred dollars, anyone can start doing genetic editing in the comfort of their own home.

The first stage launches the rocket off of the pad and continues firing for about four minutes. Once the first stage is out of fuel, it separates, and if it’s a SpaceX Falcon 9, flies back home to be reused. If it’s anything else, including the Atlas V, the first stage crash lands in the ocean and sinks. Meanwhile, the second stage fires up its own engine (or engines) to boost the payload the rest of the way into orbit. On the Atlas V, the second stage is called Centaur. Once Centaur gets its payload where it needs to go, it separates, and then suicides down into Earth’s atmosphere.
Getting a payload into space is so expensive because you have to build up this huge and complicated rocket, with engines and guidance systems and fuel tanks and stuff, and then you basically use it for like 15 minutes and throw it all away. This is why SpaceX is trying so hard to recover the first stage of the Falcon 9. But what about the second stage? You’ve got a whole bunch of hardware that made it to orbit, and when getting stuff to orbit costs something like $2,500 per kilogram, you then tell it to go it burn itself up in the atmosphere, because otherwise it’s just useless space junk.