Report warns that swift progress in our ability to manufacture viruses is making us vulnerable to biological attacks.
Ian Sample Science editor.
Report warns that swift progress in our ability to manufacture viruses is making us vulnerable to biological attacks.
Ian Sample Science editor.
Since the Reagan administration, federal agencies have been required to produce cost-benefit analyses of their major regulations. These assessments are designed to ensure that regulators are pursuing actions that make society better off.
In my experience working on the White House economic team in the Clinton and Obama administrations, I found cost-benefit analysis provides a solid foundation for understanding the impacts of regulatory proposals. It also generates thoughtful discussion of ways to design rules to maximize net benefits to the public.
On June 7, Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Scott Pruitt proposed changing the agency’s approach to this process in ways that sound sensible, but in fact are a radical departure from how government agencies have operated for decades.

Almost anywhere in the world, an HIV-infected woman who has an uninfected partner and wants to have a baby would be first in line to receive ARVs. The challenges Katia faced in getting treatment amid Russia’s epidemic highlight the country’s faltering response, which critics have blasted as misguided, lackadaisical, and downright dismissive. Some federal health officials even question the term epidemic. “This is a very large and very serious epidemic, and certainly one of the few epidemics in the world that continues to get worse rather than get better,” says Vinay Saldanha, the Moscow-based regional director for the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. “This is a public health crisis.”
The government has begun to confront its shortcomings, but critics want more aggressive change.

But there’s a recent lesson worth learning from. Globalization and automation caused upheaval in the manufacturing industry from the 1980s through the early 2000s, and millions of factory workers lost their jobs. The disruption to communities is still being felt, and is arguably at the root of a lot of the biggest social and economic problems of this era.
Some big ideas are starting to percolate. But less dramatic ones might work, too.
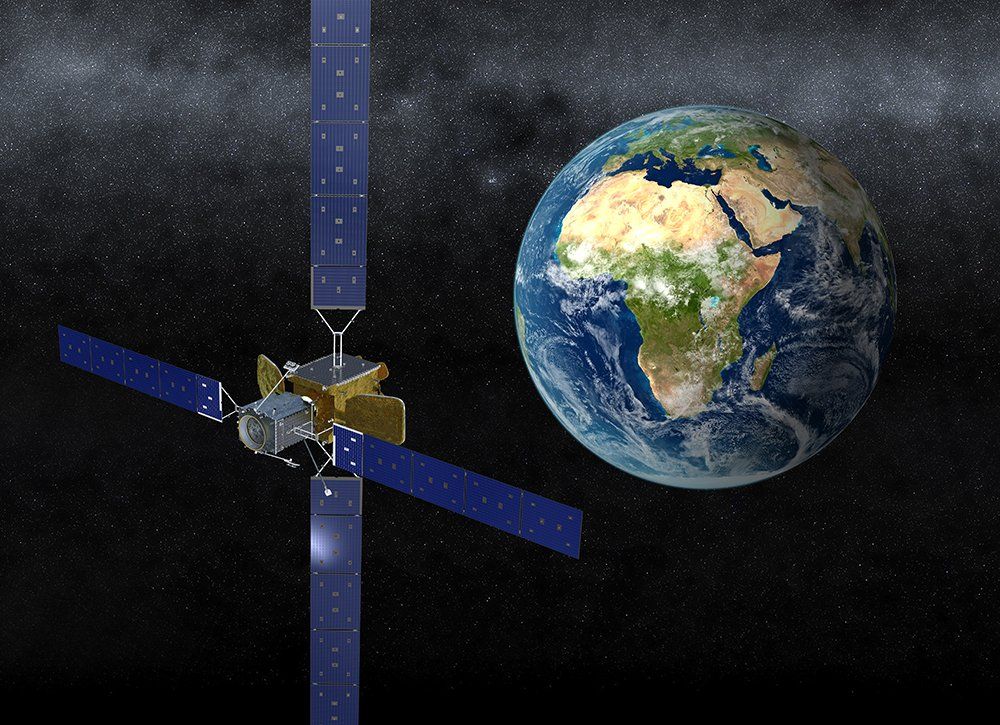

A transition is happening in the satellite business. Fast-moving technology and evolving customer demands are driving operators to rethink major investments in new satellites and consider other options such as squeezing a few more years of service out of their current platforms.
Which makes this an opportune moment for the arrival of in-orbit servicing.
Sometime in early 2019, the first commercial servicing spacecraft is scheduled to launch. The Mission Extension Vehicle built by Orbital ATK on behalf of subsidiary SpaceLogistics, will the first of several such robotic craft that are poised to compete for a share of about $3 billion worth of in-orbit services that satellite operators and government agencies are projected to buy over the coming decade.

“These findings are disturbing. Suicide is one of the top 10 causes of death in the US right now, and it’s one of three causes that is actually increasing recently, so we do consider it a public health problem — and something that is all around us,” Schuchat said. The other two top 10 causes of death that are on the rise are Alzheimer’s disease and drug overdoses, she noted.
Suicide rates increased by 25% across the United States over nearly two decades ending in 2016, according to research published Thursday by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Twenty-five states experienced a rise in suicides by more than 30%, the government report finds.
More than half of those who died by suicide had not been diagnosed with a mental health condition, said Dr. Anne Schuchat, principal deputy director of the CDC.
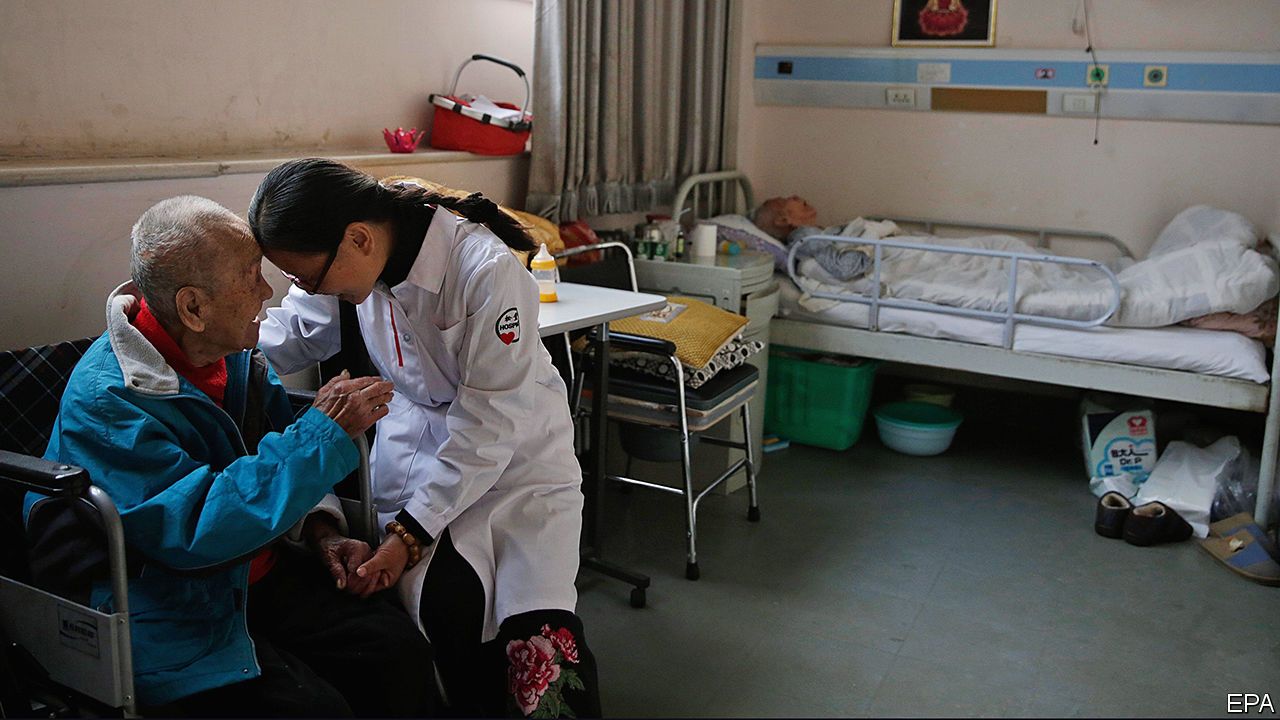

Cultural inhibitions also impede the development of end-of-life care. Talking about death has long been taboo. People often feel that it is their filial duty to ensure that sick parents receive curative treatment, even when doctors advise that there is no chance of recovery and the treatment will be painful. Applications to build hospices are sometimes challenged by local residents who resent the presence of death on their doorsteps. Mr Li says neighbours’ objections have forced Songtang Hospice to move six times.
WHEN Li Songtang was 17, officials overseeing Mao’s chaotic Cultural Revolution sent him from Beijing to Inner Mongolia, a northern province where he became a “barefoot doctor”—a medical worker with rudimentary training. His patients included an academic whom the government had expelled in disgrace from the capital, and who had become terminally ill. The patient grew sicker and increasingly troubled by his political black mark. Unable to console him, Mr Li eventually lied that he had persuaded authorities to wipe the slate clean. The patient grabbed his arm with relief and gratitude, recalls Mr Li. “I can still feel it today.”
Mr Li’s experience of caring for the dying man eventually resulted in the hospice he runs in a three-storey building in Beijing’s outskirts. The facility is home to about 300 people, most of them elderly and with late-stage cancer (a patient there is pictured with a nurse). On a weekend the bright corridors are busy with volunteers who have come to chat with patients. Zhang Zhen’e, a smiley 76-year-old who shares her room with six other women, says she tries to stay cheerful because days spent worrying are “days lost”. A nearby ward for dying babies, painted green and decorated with mobiles, is less easy to visit. Eight children snooze there, asleep in mismatched wooden cots.
Get our daily newsletter
Upgrade your inbox and get our Daily Dispatch and Editor’s Picks.
Quantum computing has made it to the United States Congress. If this field of quantum information is the new space race, the US doesn’t want to fall behind.
After all, China has funded a National Laboratory for Quantum Information Sciences, set to open in 2020, and has launched a satellite meant to test long-distance quantum secure information. Two new bills, one of which is still a draft, are meant to establish the US as a leader in the field.
“Quantum computing is the next technological frontier that will change the world, and we cannot afford to fall behind,” said Senator Kamala Harris (D-California) in a statement passed to Gizmodo. “We must act now to address the challenges we face in the development of this technology—our future depends on it.”

