Category: genetics – Page 456
Embrace human genome editing
Imagine then, the emancipatory potential of genome editing for these millions.
Realizing this potential, however, will require that genome editing meet with societal approval. The typical response right now when you talk to someone about genetic engineering or reproductive technology is a reference to ‘designer babies,’ eugenics, Nazism, and other evils. These arguments have a very powerful emotional hold over many people, but in my opinion, they simply don’t stand up to scrutiny.
Numerous traits, both physical and mental, are too complex to ever be able to engineer, and a Gattaca-like future of ‘designer babies’ is probably just as improbable as time-travel. No serious scientist or ethicist is advocating for government mandated ‘genetic correction’ of the sort Nazism or eugenics implies. As for physical appearance, everyone has their own ideas about the ‘physical ideal.’ Not every visitor to a cosmetic surgeon comes out looking Northern European.
Scientists explore how females shut off their second X chromosome
Researchers at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg and Institut Curie in Paris have shown that the protein SPEN plays a crucial role in the process of X-chromosome inactivation, whereby female mammalian embryos silence gene expression on one of their two X chromosomes.
In their landmark research published in Nature on 5 February, the scientists reveal how SPEN targets and silences active genes on the X chromosome, providing important new insights into the molecular basis of X-inactivation.
In mammals, males and females differ genetically in their sex chromosomes—XX in females and XY in males. This leads to a potential imbalance, as more than a thousand genes on the X chromosome would be expressed in a double dose in females compared to males. To avoid this imbalance, which has been shown to lead to early embryonic lethality, female embryos shut down the expression of genes on one of their two X chromosomes.
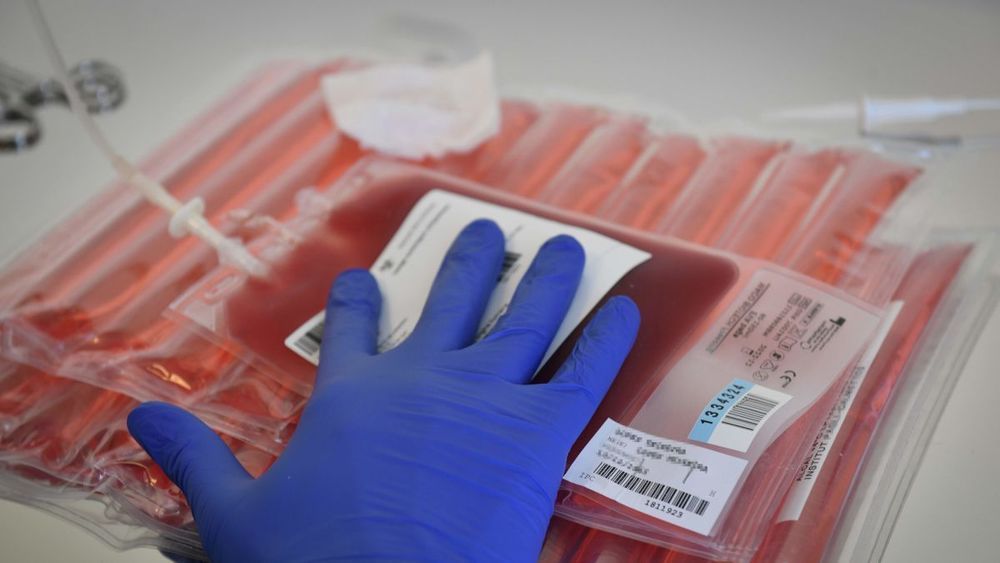
U.S. Trial Finds CRISPR-Edited Cells Are Safe in Cancer Patients
For years, scientists have hoped to use the gene-editing technology CRISPR to help treat all sorts of diseases, including cancer. Now for the first time in the U.S., researchers say they’ve shown that CRISPR-edited immune cells can be safely given to cancer patients and survive for up to nine months—a finding that may signal CRISPR’s future as part of an emerging cancer treatment known as immunotherapy.
The idea that we can boost the human immune system to help it fight off cancer isn’t new. But it’s only recently that researchers have been able to make substantial advances in the field. There are different techniques, but one that’s received lots of attention involves reprogramming our immune system’s shock troops, known as T cells, to attack cancer. T cells are drawn out from a patient’s blood, grown and modified in the lab so that they target tumor cells, and then reintroduced back into the body.

Cancer’s genetic secrets revealed through massive international study
Cancer is a hugely complicated disease, and understanding how it starts and how it can be treated requires an equally enormous effort from scientists. That effort is well underway with the Pan-Cancer Project, an international collaboration dedicated to analyzing thousands of whole cancer genomes. And now, the comprehensive results are being published in 23 separate papers, revealing new details about cancer’s causes and development, and how it can be classified, diagnosed and treated.
Otherwise known as the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) Project, the collaboration involves over 1,300 scientists from 37 countries. These researchers analyzed over 2,600 whole cancer genomes of 38 different types of tumors, probing deeper than ever into how the disease alters DNA.
One of the most optimistic outlooks from the project is that while the cancer genome is incredibly complex, it’s also finite. That means that it should be technically possible to document every genetic change that cancer can possibly induce. That information can then be used to diagnose which type of tumor a patient has and personalize a treatment plan based on the unique genome of their cancer.
Scientists Release Genetically Engineered Moths for First Time
The diamondback moth is a huge pest. It eats a variety of crops, but is largely resistant to insecticides, resulting in upwards of $5 billion in losses every year.
That could soon change, though, as an international team of researchers has created a strain of genetically engineered diamondback moths that could suppress the pest population in a sustainable way — and they just released them into the wild for the first time.
For the study, published Wednesday in the journal Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, the researchers engineered the moths so that when the males of the strain mated with wild females, the female offspring would die during the caterpillar life stage.
