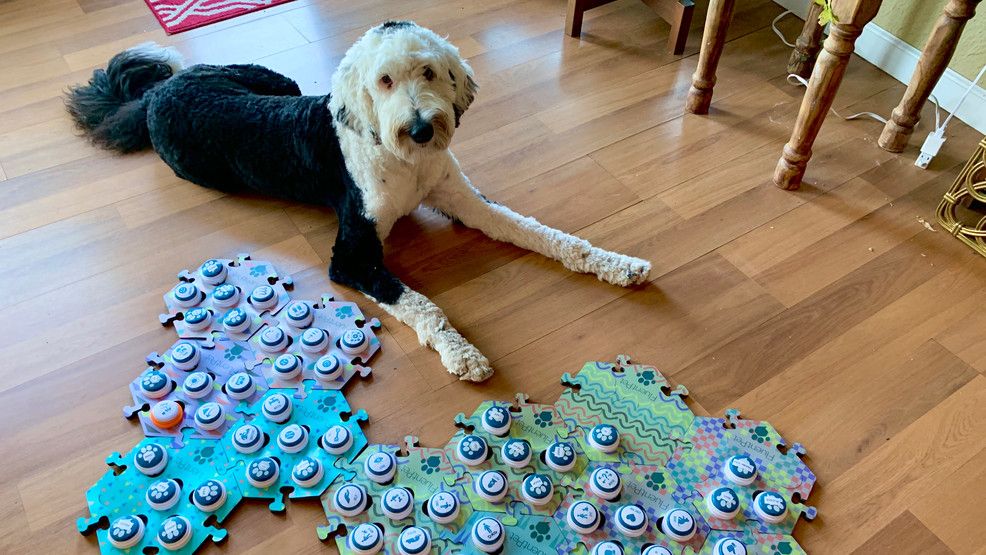
Alexis Devine of Tacoma no longer has to wonder what her Sheepadoodle, Bunny, is thinking. Bunny just tells her herself. From the day she brought Bunny home in September of 2019, Devine was determined to cement their bond and immediately began working on basic obedience and connection. She started following dog trainers on Instagram, joined Facebook groups, binge-watched YouTube videos, and read books on dog behavior to learn and put the motions into practice.