This compact solar concentrator could be the perfect daylight harvesting device for Singapore’s underground spaces.
Category: futurism – Page 744



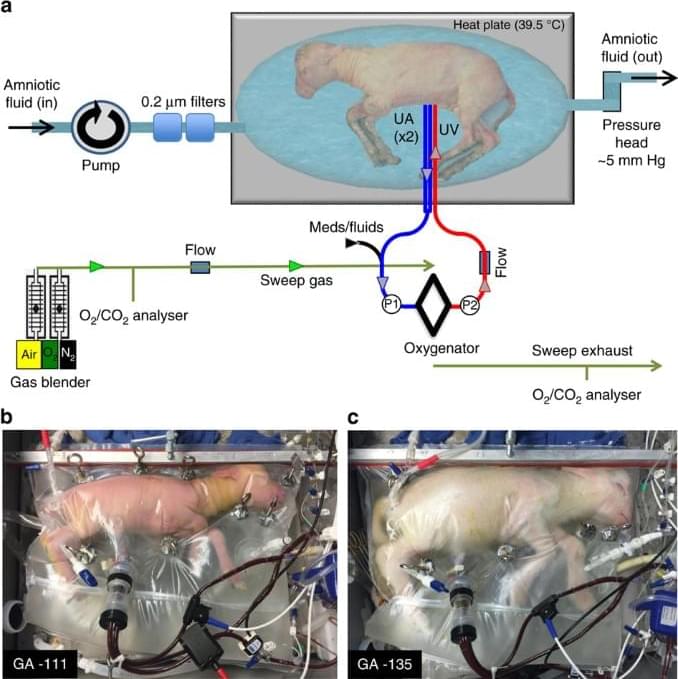
An extra-uterine system to physiologically support the extreme premature lamb
Circa 2017
The ability to support the development of a premature fetus in the form of an extracorporeal system has had limited success. Here, the authors show that an extra-uterine device that mimics the intra-uterine environment can provide physiologic support for the extreme premature lamb fetus for four weeks.


Wheels, Wings, and Legs: Choosing the Right Mining Inspection Platform
Mine operators often require regular inspections in hazardous areas for data capture, ensure worker safety, and more. Choosing the right inspection platform is … See more.
Choosing the Right Mining Inspection Platform – Let’s dive into the factors that could guide your next decision in picking the right platform for the mining environment. This is a guest post from our partners at Boston Dynamics.
What Russia’s war means for the International Space Station
Can the US and Russia still collaborate in space?
Subscribe and turn on notifications 🔔 so you don’t miss any videos: http://goo.gl/0bsAjO
The International Space Station has been orbiting above us for the last 20 years. It’s been home to astronauts from more than a dozen different countries — but mostly Americans and Russians. The two former “Space Race” countries control the main parts of the station. The science done there has required close collaboration and so it’s been largely insulated from politics on Earth.
But Russia’s invasion of Ukraine may change that. The two countries have agreed to cooperate through 2024… but after that, the future of the space station is uncertain.
Make sure you never miss behind the scenes content in the Vox Video newsletter, sign up here: http://vox.com/video-newsletter.
Vox.com is a news website that helps you cut through the noise and understand what’s really driving the events in the headlines. Check out http://www.vox.com.
Hydrolysis of ATP
This Video Explains Hydrolysis of ATP
Thank You For Watching.
Please Like And Subscribe to Our Channel: https://www.youtube.com/EasyPeasyLearning.
Like Our Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/learningeasypeasy/
Join Our Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/460057834950033
Support Our Channel: https://www.patreon.com/supereasypeasy.
Link of Adenosine Triphosphate ATP Video : https://youtu.be/SHSv789fyno