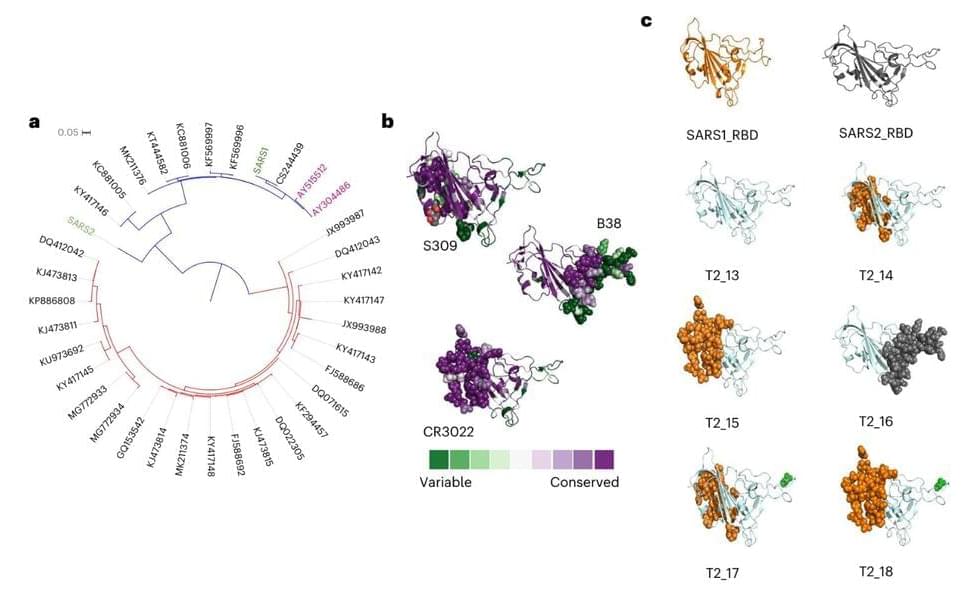
Studies of a “future-proof” vaccine candidate have shown that just one antigen can be modified to provide a broadly protective immune response in animals. The studies suggest that a single vaccine with combinations of these antigens—a substance that causes the immune system to produce antibodies against it—could protect against an even greater range of current and future coronaviruses.
The vaccine antigen technology, developed by the University of Cambridge and spin-out DIOSynVax in early 2020, provided protection against all known variants of SARS-CoV-2—the virus that causes COVID-19—as well as other major coronaviruses, including those that caused the first SARS epidemic in 2002.
The studies in mice, rabbits and guinea pigs—an important step before beginning human clinical trials, currently underway in Southampton and Cambridge—found that the vaccine candidate provided a strong immune response against a range of coronaviruses by targeting the parts of the virus that are required for replication. The vaccine candidate is based on a single digitally designed and immune optimized antigen.