Autofocus cameras and enhanced field of view promise next-level immersion.



A trove of arboreal fossils pushes back the origin of modern forests and sophisticated tree roots.
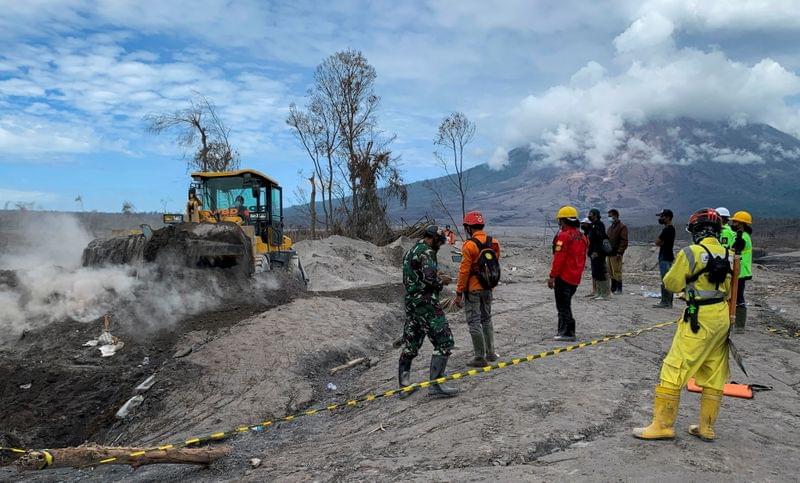

At the foot of Indonesia’s Mount Semeru, what is left of the houses along the main village road are covered in a thick layer of hardened volcanic ash. Curah Kobokan was among the worst-hit areas when the 3,676-metre (12,060 ft) Mount Semeru erupted on Saturday, sending a cloud of ash into the sky and dangerous pyroclastic flows into villages below. Since day one of the disaster, volunteer Dodik Suryadiawan, 36, has driven on the bumpy roads in his personal four-wheel drive, helping to retrieve the remains of those who perished.

OpenGPT is a promising toolkit for building custom chatbots like GPTs, but it is completely open-source and offers even more configuration options. Which means it is also more complicated.
With GPTs, OpenAI introduced the evolution of its plugin concept at Dev Days in November 2023. The AI company is giving end users different tools to create a chatbot tailored to their needs, without having to know how to code a chatbot. OpenAI even plans to give successful GPT creators a share of the revenue from ChatGPT Plus in the future.
When setting up GPTs, users can upload their files, link APIs, assign system prompts, and enable modules for web browsing, DALL-E, and code interpreters.

For the Gallery of Fluid Motion, researchers take the director’s chair and create videos on 3D printer patterns, frost formation, and paint swirls.
The APS Division of Fluid Dynamics has announced the 2023 winners of its annual Gallery of Fluid Motion video and poster contest. The videos below received the Milton van Dyke Award, which recognizes both videos and posters. A new traveling exhibit of past winners is currently on display at the National Academy of Sciences.

Update from 02. December 2023:
LAION releases the 70 billion version of LeoLM trained with 65 billion tokens. It is based on Llama-2-70b, but according to LAION it can beat Meta’s base model — in both German and English.
“With this release, we hope to bring a new wave of opportunities to German open-source and commercial LLM research and accelerate adoption,” the team writes.


AI with image recognition opens up new possibilities for designers and developers to quickly turn an idea into a prototype. There are several approaches based on OpenAI technology.
The introduction of multimodal capabilities in GPT-4 has laid an important foundation for future software development. Thanks to GPT-4V, the AI model accepts both text and images as input. This allows it to generate working code from screenshots or rudimentary drawings.
Recently, several products have been developed around this idea. The collaborative whiteboard tool tldraw has set up a playground on the website makereal.tldraw.com, where mockups of website elements can be created in the browser. GPT-4V converts these into code using the OpenAI API. A separate API key is required.