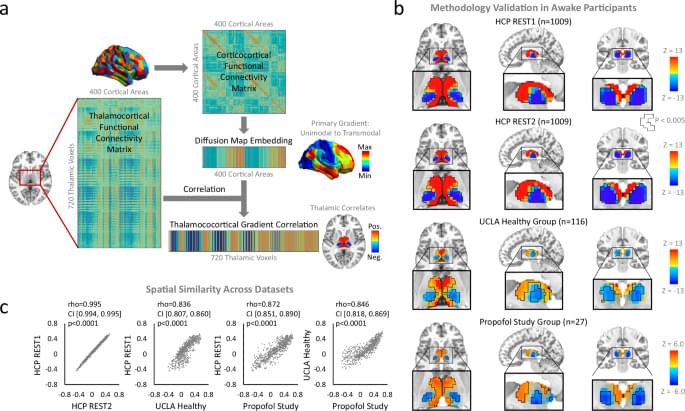
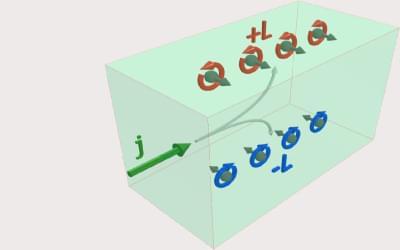
Orbital currents are the lesser-known cousins of spin currents. Both involve an alignment of angular momentum. But spin currents are carried by spin-polarized electrons, while orbital currents are carried by electrons in orbitals having the same angular momentum. Like their spin counterparts, orbital currents could be useful for transmitting information in so-called orbitronic devices, but researchers had expected that these currents would not travel well across material interfaces. Now Igor Lyalin and Roland Kawakami from Ohio State University have measured the flow of orbital currents across selected materials placed in multilayer structures. They find, surprisingly, that the transport of orbital currents is as good or better than the transport of spin currents for most of the sampled materials.
Orbital currents can be generated via the so-called orbital Hall effect—a surface magnetization effect that was predicted 20 years ago but directly detected only in 2023 (see Synopsis: Detection of the Orbital Hall Effect). Interest in orbital currents is growing, as they could be more effective than spin currents at switching the orientation of magnetic layers in data-storage devices.
To study orbital current transport, Lyalin and Kawakami fabricated structures consisting of chromium and nickel layers, separated by a thin spacer. For the spacer material, they tested nonmagnetic metals, ferromagnetic metals, and antiferromagnetic insulators. The researchers generated an orbital current by applying a voltage to the chromium layer, and they measured how much of this current flowed through the structures by observing a magnetization change in the nickel. They found that 12 of the 15 spacer materials transported orbital currents more efficiently than spin currents—a result that could be good news for developing future orbitronic devices, Kawakami says.