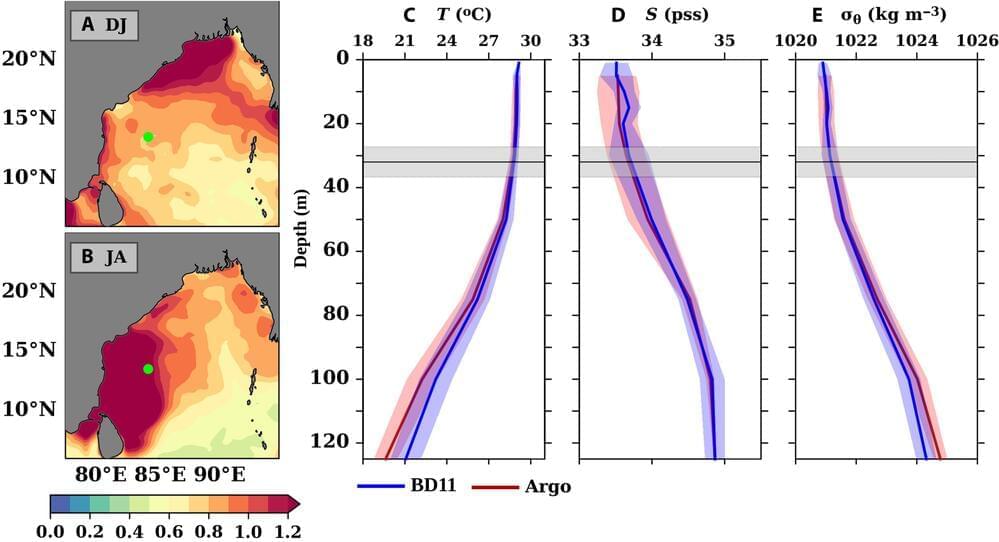
A team of planetary scientists and oceanographers from NOAA, the Indian National Center for Ocean Information Services, and the University of Zagreb, has found an example of an exception to Ekman’s theory of wind-driven ocean currents—wind and surface flow in the Bay of Bengal.
In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group analyzed several years of data sent by a buoy in the Indian Ocean, off the eastern coast of India.
In 1905, a Swedish oceanographer named Vagn Walfrid Ekman found evidence showing that ocean currents that flow near the surface, which were known to be impacted by wind, were found to deflect to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. Work since that time has backed up the theory, which has come to be known as Ekman’s theory of wind-driven ocean currents.