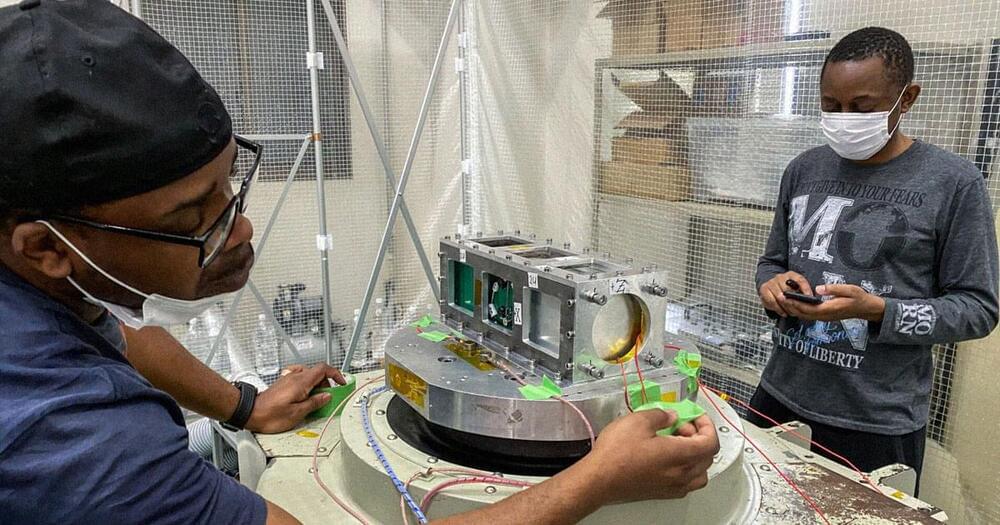
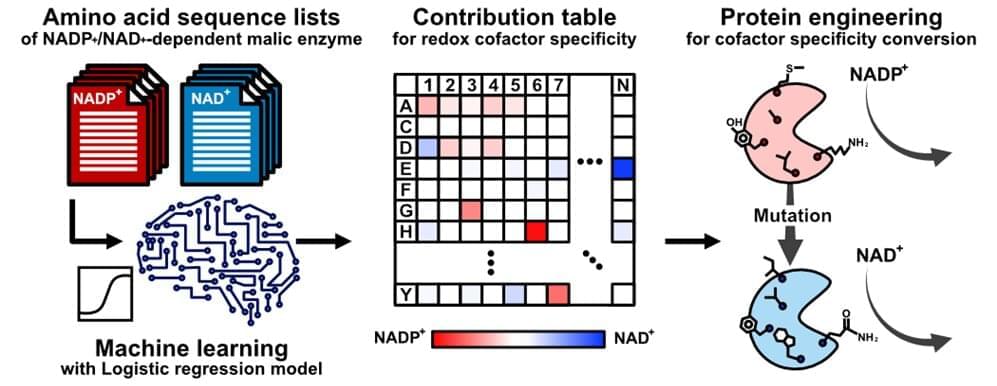
With the help of NASA and Japan, Uganda has officially become a spacefaring nation — and its newly-launched PearlAfricaSat-1 craft has some pretty nifty tech onboard.
As the Uganda-based Nile Post reports, the satellite launched out of NASA’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport facility in Virginia on the morning of November 7 will not only provide important agricultural and security monitoring features for the developing nation, but will also conduct experiments involving the 3D printing of human tissue.
Per the Ugandan news site, the tissues printed on PearlAfricaSat-1 will be used in research into the effects microgravity has on ovary function — and as Quartz notes in its write-up of the NASA and Japan-supported mission, the microgravity aspect of the experiments is key because “bioprinting” human organs is difficult to achieve with Earth’s gravity.