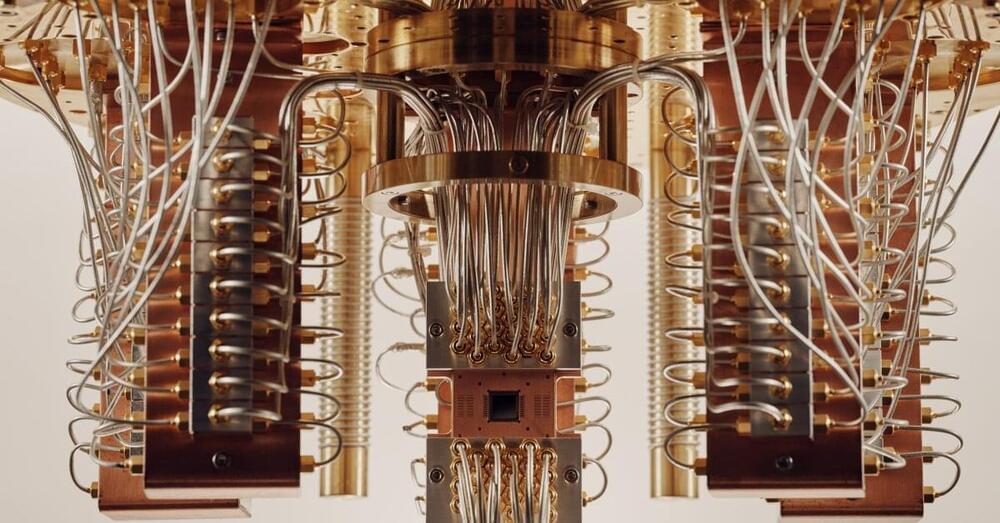
Tech giants from Google to Amazon and Alibaba —not to mention nation-states vying for technological supremacy—are racing to dominate this space. The global quantum-computing industry is projected to grow from $412 million in 2020 to $8.6 billion in 2027, according to an International Data Corp. analysis.
Whereas traditional computers rely on binary “bits”—switches either on or off, denoted as 1s and 0s—to process information, the “qubits” that underpin quantum computing are tiny subatomic particles that can exist in some percentage of both states simultaneously, rather like a coin spinning in midair. This leap from dual to multivariate processing exponentially boosts computing power. Complex problems that currently take the most powerful supercomputer several years could potentially be solved in seconds. Future quantum computers could open hitherto unfathomable frontiers in mathematics and science, helping to solve existential challenges like climate change and food security. A flurry of recent breakthroughs and government investment means we now sit on the cusp of a quantum revolution. “I believe we will do more in the next five years in quantum innovation than we did in the last 30,” says Gambetta.
But any disrupter comes with risks, and quantum has become a national-security migraine. Its problem-solving capacity will soon render all existing cryptography obsolete, jeopardizing communications, financial transactions, and even military defenses. “People describe quantum as a new space race,” says Dan O’Shea, operations manager for Inside Quantum Technology, an industry publication. In October, U.S. President Joe Biden toured IBM’s quantum data center in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., calling quantum “vital to our economy and equally important to our national security.” In this new era of great-power competition, China and the U.S. are particularly hell-bent on conquering the technology lest they lose vital ground. “This technology is going to be the next industrial revolution,” says Tony Uttley, president and COO for Quantinuum, a Colorado-based firm that offers commercial quantum applications. “It’s like the beginning of the internet, or the beginning of classical computing.”