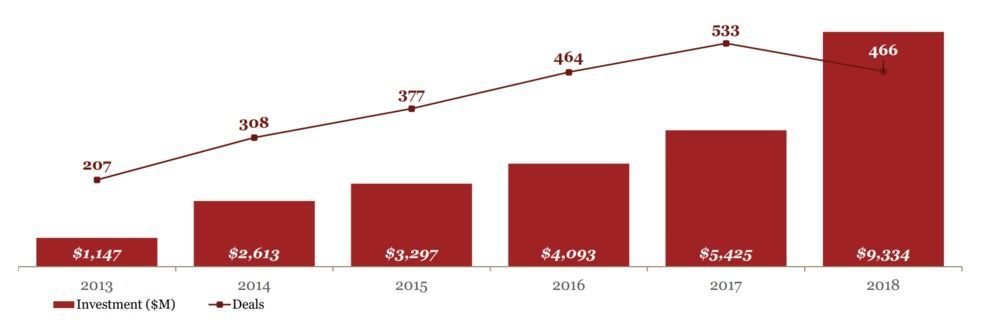
“If I can bring forward the defeat of aging even one day, I would have saved the lives of 110,000 people.” – Dr. Aubrey de Grey at EmTech Asia 2019.
The age-old quest for immortality was largely confined to the myths and legends of past civilizations until about just two decades back when telomerase, the active component for the gene that confers immortality to cells was successfully isolated in a science laboratory. That turned the tide on the entire conversation from whether aging could be treated, to how it could be treated.
Since then it has spawned a whole new medical field – ‘healthspan’ – where scientific research is conducted with the aim of extending healthy human lives for as long as hundreds and thousands of years, if not outright immortality. It is not surprising that the intensive research into anti-aging technologies has attracted financial backing from those who are interested in technological progress – the tech community, the likes of Google and even cryptocurrency tycoons such as Ethereum Founder, Vitalik Buterin, who donated $2.4 million worth of ether to the nonprofit foundation SENS Research Foundation, of which Dr Aubrey de Grey is the Chief Science Officer.