US space agency NASA has forecast a recently-spotted asteroid, 2020 SW, for a fly-by on Thursday. It will fly by at an agonising distance of around 17,000 miles – closer than a weather satellite.



RS: The third world war is at our gate, and it will be about water, if we don’t do something about this crisis. These walks are to raise awareness—this year we covered 17 countries, and in nine of them there were displaced people. So many people in the Middle East and African countries are moving to places like Europe, in part because of water scarcity—after forced migration comes, tension, conflict, and terrorism. Where terrorism is active, there is usually a scarcity of water. Look at Syria—a long time ago, it had very good agriculture, but then Turkey built a dam that changed things. It’s a similar story with Libya. If we want a safe future, we need to start conserving water.
What role can regulation play in conservation? Do you think privatizing water is a good way to promote its efficient use?
RS: If we really think about legal changes, we have to first think about river rights, or the rights of nature, and only then about water rights for humans. This type of thinking doesn’t exist today but we need this kind of legal framework that assures that the land of the river is only for the river, that the flow of the river is kept clean, and that the river has greenery on both banks to prevent erosion and silting. Only with all these factors can we ensure that rivers are healthy and only then that we are healthy.
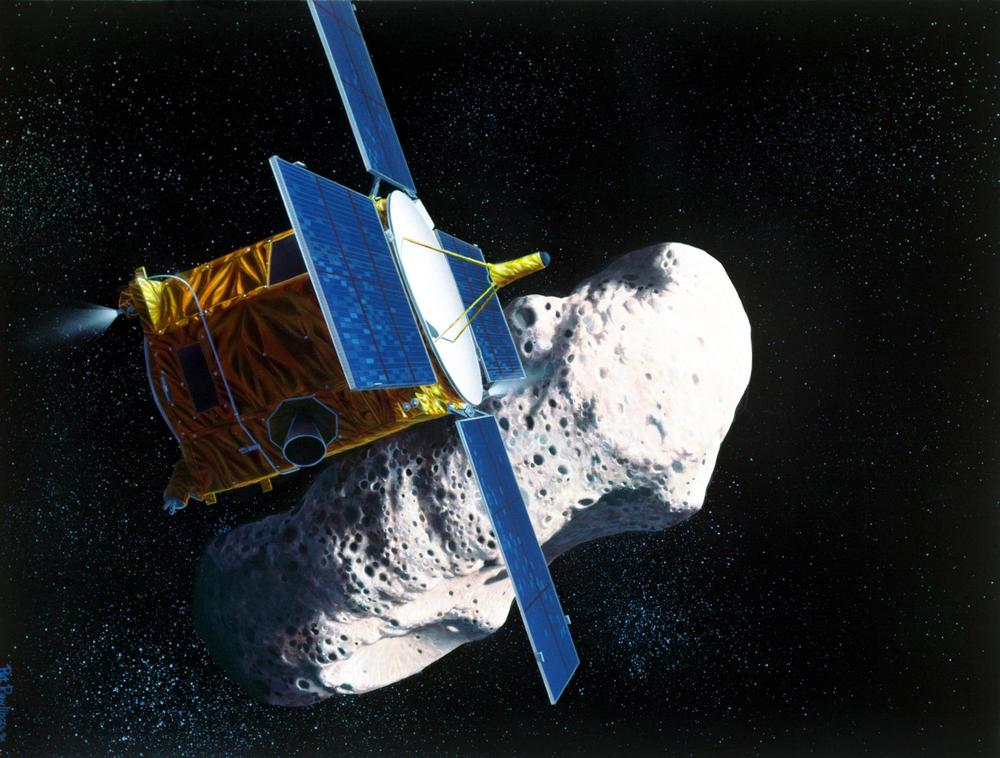

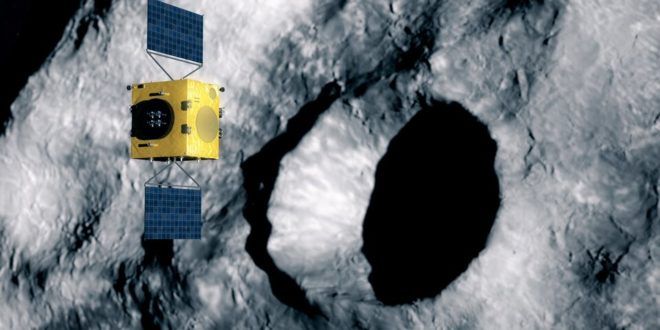
Darmstadt, 15 September 2020. – The European Space Agency (ESA) awarded a €129.4 million contract covering the design, manufacturing and testing of Hera, the space agency’s first mission for planetary defence, ESA announced today.
The contract was signed by Franco Ongaro, ESA Director of Technology, Engineering and Quality, and Marco Fuchs, CEO of Germany space company OHB, prime contractor of the Hera consortium, ESA said today. The signing took place at ESA’s European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany, which will serve as mission control for the 2024-launched Hera.
The mission will be Europe’s contribution to an international asteroid deflection effort, set to perform sustained exploration of a double asteroid system, ESA said.
Hera will be, along with NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirect Test (DART) spacecraft, humankind’s first probe to rendezvous with a binary asteroid system, a little understood class making up around 15% of all known asteroids, the agency said.
Hera is the European contribution to an international planetary defence collaboration among European and US scientists called the Asteroid Impact & Deflection Assessment (AIDA).

A HUGE meteor streaked in the skies above California, leaving onlookers stunned with one claiming it was “a close call”.
On GPT-3, achieving AGI, machine understanding and lots more… Will GPT-3 or an equivalent be used to deepfake human understanding?
Joscha Bach on GPT-3, achieving AGI, machine understanding and lots more
02:40 What’s missing in AI atm? Unified coherent model of reality
04:14 AI systems like GPT-3 behave as if they understand — what’s missing?
08:35 Symbol grounding — does GPT-3 have it?
09:35 GPT-3 for music generation, GPT-3 for image generation, GPT-3 for video generation
11:13 GPT-3 temperature parameter. Strange output?
13:09 GPT-3 a powerful tool for idea generation
14:05 GPT-3 as a tool for writing code. Will GPT-3 spawn a singularity?
16:32 Increasing GPT-3 input context may have a high impact
16:59 Identifying grammatical structure & language
19:46 What is the GPT-3 transformer network doing?
21:26 GPT-3 uses brute force, not zero-shot learning, humans do ZSL
22:15 Extending the GPT-3 token context space. Current Context = Working Memory. Humans with smaller current contexts integrate concepts over long time-spans
24:07 GPT-3 can’t write a good novel
25:09 GPT-3 needs to become sensitive to multi-modal sense data — video, audio, text etc
26:00 GPT-3 a universal chat-bot — conversations with God & Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
30:14 What does understanding mean? Does it have gradients (i.e. from primitive to high level)?
32:19 (correlation vs causation) What is causation? Does GPT-3 understand causation? Does GPT-3 do causation?
38:06 Deep-faking understanding
40:06 The metaphor of the Golem applied to civ
42:33 GPT-3 fine with a person in the loop. Big danger in a system which fakes understanding. Deep-faking intelligible explanations.
44:32 GPT-3 babbling at the level of non-experts
45:14 Our civilization lacks sentience — it can’t plan ahead
46:20 Would GTP-3 (a hopfield network) improve dramatically if it could consume 1 to 5 trillion parameters?
47:24 GPT3: scaling up a simple idea. Clever hacks to formulate the inputs
47:41 Google GShard with 600 billion input parameters — Amazon may be doing something similar — future experiments
49:12 Ideal grounding in machines
51:13 We live inside a story we generate about the world — no reason why GPT-3 can’t be extended to do this
52:56 Tracking the real world
54:51 MicroPsi
57:25 What is computationalism? What is it’s relationship to mathematics?
59:30 Stateless systems vs step by step Computation — Godel, Turing, the halting problem & the notion of truth
1:00:30 Truth independent from the process used to determine truth. Constraining truth that which can be computed on finite state machines
1:03:54 Infinities can’t describe a consistent reality without contradictions
1:06:04 Stevan Harnad’s understanding of computation
1:08:32 Causation / answering ‘why’ questions
1:11:12 Causation through brute forcing correlation
1:13:22 Deep learning vs shallow learning
1:14:56 Brute forcing current deep learning algorithms on a Matrioshka brain — would it wake up?
1:15:38 What is sentience? Could a plant be sentient? Are eco-systems sentient?
1:19:56 Software/OS as spirit — spiritualism vs superstition. Empirically informed spiritualism
1:23:53 Can we build AI that shares our purposes?
1:26:31 Is the cell the ultimate computronium? The purpose of control is to harness complexity
1:31:29 Intelligent design
1:33:09 Category learning & categorical perception: Models — parameters constrain each other
1:35:06 Surprise minimization & hidden states; abstraction & continuous features — predicting dynamics of parts that can be both controlled & not controlled, by changing the parts that can be controlled. Categories are a way of talking about hidden states.
1:37:29 ‘Category’ is a useful concept — gradients are often hard to compute — so compressing away gradients to focus on signals (categories) when needed
1:38:19 Scientific / decision tree thinking vs grounded common sense reasoning
1:40:00 Wisdom/common sense vs understanding. Common sense, tribal biases & group insanity. Self preservation, dunbar numbers
1:44:10 Is g factor & understanding two sides of the same coin? What is intelligence?
1:47:07 General intelligence as the result of control problems so general they require agents to become sentient
1:47:47 Solving the Turing test: asking the AI to explain intelligence. If response is an intelligible & testable implementation plan then it passes?
1:49:18 The term ‘general intelligence’ inherits it’s essence from behavioral psychology; a behaviorist black box approach to measuring capability
1:52:15 How we perceive color — natural synesthesia & induced synesthesia
1:56:37 The g factor vs understanding
1:59:24 Understanding as a mechanism to achieve goals
2:01:42 The end of science?
2:03:54 Exciting currently untestable theories/ideas (that may be testable by science once we develop the precise enough instruments). Can fundamental physics be solved by computational physics?
2:07:14 Quantum computing. Deeper substrates of the universe that runs more efficiently than the particle level of the universe?
2:10:05 The Fermi paradox
2:12:19 Existence, death and identity construction.

It is reported that the dimensions of the celestial body are from 22 to 49 meters. According to the space agency, at the minimum distance to the planet – about 120 thousand kilometers – the asteroid will come up at 19.12 Moscow time. The asteroid is moving at 8.16 kilometers per second.
Note that the celestial body was discovered on March 2, 2011. It belongs to the group of “Apollo”, that is, asteroids, whose flight paths cross the Earth’s orbit.

Amid a pandemic, civil unrest and a divisive US election season, we now have an asteroid zooming toward us.
On the day before the presidential vote, no less.
Yep. The celestial object known as 2018VP1 is projected to come close to Earth on November 2, according to the Center for Near Earth Objects Studies at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
As if 2020 hadn’t already thrown enough at us, NASA says an asteroid will come close to Earth on November 2.
