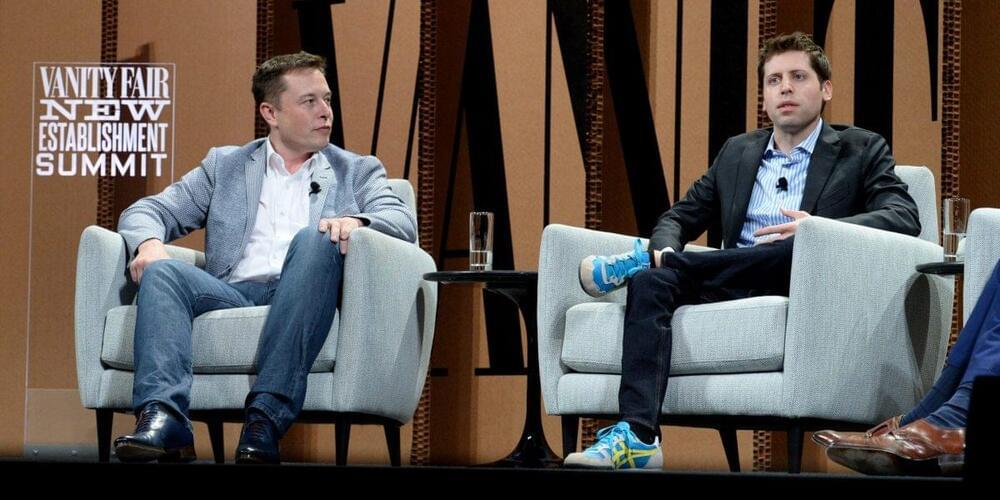
Musk cofounded OpenAI—the parent company of the viral chatbot ChatGPT—in 2015 alongside Altman and others. But when Musk proposed that he take control of the startup to catch up with tech giants like Google, Altman and the other cofounders rejected the proposal. Musk walked away in February 2018 and changed his mind about a “massive planned donation.”
Now Musk’s new company, xAI, is on a mission to create an AGI, or artificial general intelligence, that can “understand the universe,” the billionaire said in a nearly two-hour-long Twitter Spaces talk on Friday. An AGI is a theoretical type of A.I. with human-like cognitive abilities and is expected to take at least another decade to develop.
Musk’s new company debuted only days after OpenAI announced in a July 5 blog post that it was forming a team to create its own superintelligent A.I. Musk said xAI is “definitely in competition” with OpenAI.