Venus is suddenly a new hotspot for astrobiology, but its real value may be in what it teaches us about the evolution of life on our own planet.



Summary: Glial cells not only control the speed of nerve conduction, but they also influence the precision of signal transduction.
Source: University of Münster
For the brain to work efficiently, it is important that a nerve impulse arrives at its destination as quickly and as precisely as possible. It has been long been known that the nerve fibres — also known as axons — pass on these impulses. In the course of evolution, an insulating sheath — myelin — developed around the axons which increases the speed of conduction. This insulating sheath is formed by the second type of cell in the nervous system — the glial cells, which are one of the main components of the brain. If, as a result of disease, myelin is depleted, this leads to neurological disorders such as Multiple Sclerosis or Morbus Charcot-Marie-Tooth.
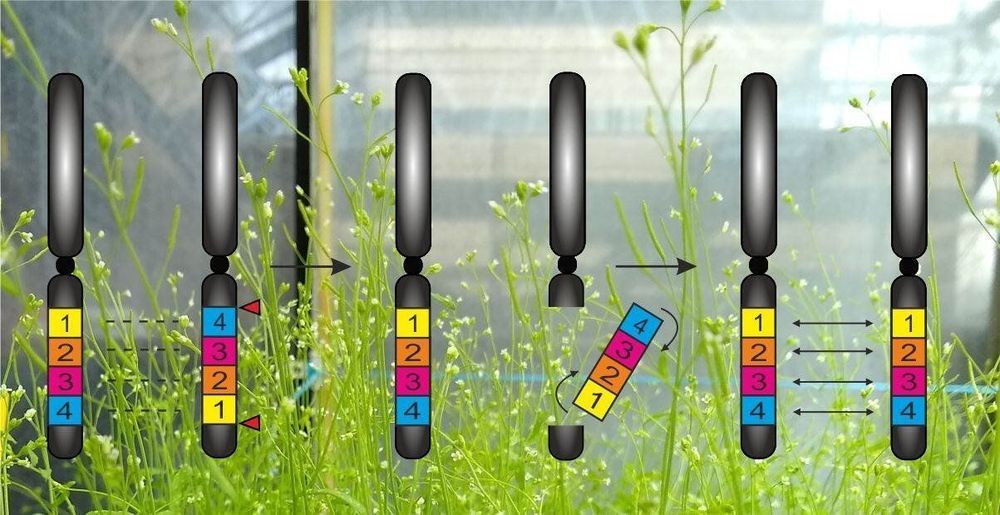
A new application of the CRISPR/Cas molecular scissors promises major progress in crop cultivation. At Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), researchers from the team of molecular biologist Holger Puchta have succeeded in modifying the sequence of genes on a chromosome using CRISPR/Cas. For the first time worldwide, they took a known chromosome modification in the thale cress model plant and demonstrated how inversions of the gene sequence can be undone and inheritance can thus be controlled specifically. The results are published in Nature Communications.
About 5,000 years ago, genetic information of thale cress was modified. To date, it has spread widely and is of major interest to science. On the chromosome 4 of the plant, a so-called inversion occurred: The chromosome broke at two points and was reassembled again. The broken out section was reinserted, but rotated by 180°. As a result, the sequence of genes on this chromosome section was inverted. This chromosome mutation known as “Knob hk4S” in research is an example of the fact that evolution cannot only modify the genetic material of organisms, but determine it for a long term. “In inverted sections, genes cannot be exchanged between homologous chromosomes during inheritance,” molecular biologist Holger Puchta, KIT, explains.

Electrons may have some type of extremely rudimentary mind.
While there are many versions of panpsychism, the version I find appealing is known as constitutive panpsychism. It states, to put it simply, that all matter has some associated mind or consciousness, and vice versa. Where there is mind there is matter and where there is matter there is mind. They go together. As modern panpsychists like Alfred North Whitehead, David Ray Griffin, Galen Strawson, and others have argued, all matter has some capacity for feeling, albeit highly rudimentary feeling in most configurations of matter.
Panpsychists look at the many rungs on the complexity ladder of nature and see no obvious line between mind and no-mind. Philosopher Thomas Nagel famously asked in 1974 what is it like to be a bat, to echolocate and fly? We can’t know with any certainty, but we can reasonably infer, based on observation of their complex behaviors and the close genetic kinship between all mammals and humans—and the fact that evolution proceeds incrementally—that bats have a rich inner life. By the same logic, we can look steadily at less-complex forms of behavior that allow us to reasonably infer some kind of mind associated with all types of matter. Yes, including even the lowly electron.


Min-Liang Tan, chief executive of gaming company Razer, said that the Covid-19 pandemic is driving the internet to the next stage of its evolution – something called the ‘Metaverse’ where cyberspace becomes more of an interactive 3D space with commerce and networking alongside content, much like the worlds in popular games such as Fortnite and Roblox.
The metaverse concept was brought to life by the 2018 sci-fi movie Ready Player One, directed by Steven Spielberg.

In a landmark study, scientists using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have mapped the immense envelope of gas, called a halo, surrounding the Andromeda galaxy, our nearest large galactic neighbor. Scientists were surprised to find that this tenuous, nearly invisible halo of diffuse plasma extends 1.3 million light-years from the galaxy—about halfway to our Milky Way—and as far as 2 million light-years in some directions. This means that Andromeda’s halo is already bumping into the halo of our own galaxy.
They also found that the halo has a layered structure, with two main nested and distinct shells of gas. This is the most comprehensive study of a halo surrounding a galaxy.
“Understanding the huge halos of gas surrounding galaxies is immensely important,” explained co-investigator Samantha Berek of Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut. “This reservoir of gas contains fuel for future star formation within the galaxy, as well as outflows from events such as supernovae. It’s full of clues regarding the past and future evolution of the galaxy, and we’re finally able to study it in great detail in our closest galactic neighbor.”

New opinions are always suspected, and usually opposed, without any other reason but because they are not already common.” –John Locke.
This introductory article summarizes the tenets of the Cybernetic Theory of Mind (CTM) with the five foundational axioms. All of these starting assumptions for the new ontological framework are discussed in my recent book The Syntellect Hypothesis: Five Paradigms of the Mind’s Evolution. Here I try to keep this summary short and simple for the reader, maximally leaning towards a more literary, “bookish” style rather than the overly scholarly one. Also, The Cybernetic Theory of Mind is a working title for my upcoming book to be published sometime next year for the general audience. It may be followed by academic papers to clarify some thorny issues that I intend to publish on my own or in collaboration.
The CTM model, a proposed version of the theory of everything, I’m currently working on, is an integral multi-disciplinary ontological model that allows to draw a wide variety of predictions and deductions from the intersections of two or more foundational axioms therein. The CTM model also allows integration of further epistemic elements under its broad ontological umbrella as they come to be known. In this summary, the formulation of each foundational axiom is followed by five exemplary deductions per axiom.
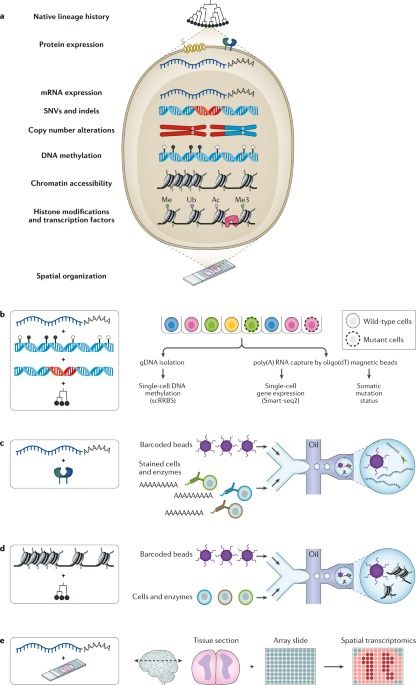
Both genetic and non-genetic factors underlie the intratumoural heterogeneity that fuels cancer evolution. This Review discusses the application of single-cell multi-omics technologies to the study of cancer evolution, which capture and integrate the different layers of heritable information and reveal their complex interplay.
We now know that all extant living creatures derive from a single common ancestor, called the ‘Last Universal Common Ancestor’ (LUCA). It’s hard to think of a more unifying view of life. All living things are linked to a single-celled creature, the deepest root to the complex-branching tree of life. If we could play the movie of life backward, we would find this microscopic primogenitor at the starting point of biological evolution, the sole actor in what would become a very dramatic story, lasting some 3.5 billion years leading to us.